Break or puncture? When and why the fetal bladder is opened. Piercing the amniotic fluid before delivery When contractions begin after piercing
The culture of birth shapes practices and incorporates established rituals. The movement from hospital birth to natural birth with a midwife is now popular; this is happening as women and birth care professionals re-evaluate some of the practices and interventions that are typical of hospital births. Amniotomy is a long-standing practice that is considered permissible in order to reduce the length of labor. There are practically no publications on the effect of amniotomy on a child. This article explores the pros and cons of amniotomy, its role as a ritual for help in childbirth, and its possible psychological effects on the baby.
Puncture of membranes of the membranes or amniotomy is a common, not to say routine, practice in North American childbirth culture. Amniotomy is perceived as a useful technique to improve labor if it weakens (1). During pregnancy, amniotic fluid is the baby's natural habitat. In the aquatic environment, the child masters the first movements, learns to breathe and swallow; all this prepares him for extrauterine life. During labor, amniotic fluid serves as a "safety cushion" for the baby during contractions and while passing through the birth canal (2). The decision to pierce the bladder or, conversely, wait for the natural rupture of the membranes is an important part of the birth plan. But since amniotomy has long become a common practice and is perceived as such even in the circles of supporters of natural childbirth, this issue is often overlooked altogether.
When a doctor or midwife decides to have an amniotomy, the puncture is done with a special instrument, like a hook; the instrument is inserted into the birth canal, the fetal membranes are picked up and pierced. As a result, it is assumed that the baby's head will press on the opening cervix, which will speed up the opening and the birth itself. Some studies (3-6) have found that amniotomy does not speed up labor too much, up to an hour or two. Another study (7) argues that amniotomy makes contractions more painful and interferes with the formation of maternal attachment immediately after birth, as many women feel that the natural course of the birth process has been grossly disrupted (8). However, in some women, especially multiparous women, amniotomy reduces pain during the second stage of labor (9). There is practically no contraindication to amniotomy in case of fetal distress (10). Amniotomy is routinely used to access the fetal head when distress is suspected to confirm or disprove this assumption (11). Puncture of the fetal bladder helps doctors examine the waters for meconium or blood. Amniotomy also allows monitor probes to be attached directly to the baby's head when signs of distress are present. However, there is insufficient scientific evidence on the advisability of a bladder puncture in the early stages of labor in order to study the amniotic fluid in case of suspected fetal distress. Early amniotomy can exacerbate distress, as it reduces the amount of fluid, which can lead to partial compression of the umbilical cord, reducing the flow of oxygen to the baby, and as a result, it is often even necessary for an emergency caesarean section.
Spontaneous rupture of the membranes
Spontaneous rupture of the fetal bladder before the onset of labor occurs in about 12% of cases (12). Premature discharge of water can create a critical situation, as there is a risk of umbilical cord prolapse. If the umbilical cord is pressed against the bones of the maternal pelvis, then there is a risk of fetal hypoxia. If childbirth proceeds without intervention, then two-thirds of women with healthy full-term pregnancies achieve good dilatation in the presence of an entire fetal bladder (13). In an online obstetric discussion, one midwife argues that out of 300 unstimulated labor without intervention, about 15% of women had a bladder intact until almost the end of the second stage of labor (14). One of the advantages of trusting nature and expecting spontaneous rupture of the membranes is that in this case, the child's entire body experiences only hydrostatic pressure and thus receives protection during contractions, and the head does not change its configuration so much when passing through the pelvic bones (15 ). In addition, intact membranes reduce the chance of intrauterine infection.
The presence of meconium in waters does not necessarily mean an increased risk to the baby. A full-term healthy baby can expel meconium in utero and even swallow it (16). Routine bladder piercing “just in case” is unwise and unethical (17, 18). On the other hand, some studies show that sometimes the presence of meconium in the waters lowers their pH and then the child's APGAR score. Dr. Marsden Wagner says: “ Early bladder puncture as a routine procedure is not scientifically substantiated" (nineteen). Amniotomy is a procedure that takes away from a woman some of the experience of childbirth and reinforces the subconscious belief that childbirth is an unnatural process (20).
Hormonal, chemical and physiological adaptation During childbirth, there is a biochemical and hormonal adaptation of the mother and child to each other. The baby's pH is influenced by the mother's pH and changes over the course of labor (21). PH measures the acidity of the environment (acidic, neutral or alkaline) and determines the body's ability to get rid of decay products. A neutral pH of 7 is optimal and the body works to maintain the pH at this level. Blood levels of catecholamines (adrenaline and norepinephrine) increase as the stress associated with normal labor increases and facilitates its progress (22). Optimal changes in hydrostatic pressure and pH (downward) have a beneficial effect on the child's cardiac activity and his cardiovascular system, prepare for adaptation to extrauterine life. However, excess stress and excitement raise hormone concentrations above the functional limit, which causes a drop in pH and slows down labor. The second stage of labor is marked by changes in pressure, position and position of the baby, when he leaves the aquatic environment, unbends and experiences the effect of gravity.
The level of anxiety and stress a woman experiences during childbirth depends on the culture of birth in a given society. Women need accurate, unbiased and complete information to be active participants in their childbirth. Women who do not have such information are often passive and afraid (23). The medical model of childbirth trusts machines more than a woman's body, and this model is more likely to have interventions and unnecessary procedures. Ultimately, women do not participate at all in decision-making during childbirth, and all that remains for them is to worry about what happens to them and their children.
Functions of the amniotic fluid
There is a huge amount of research that studies the chemical composition of the amniotic fluid and its role in fetal maturation, as well as during childbirth. Although the hormonal, chemical and physiological mechanisms of adaptation of mothers and babies are largely understood, the composition of the amniotic fluid, its changes during the first and second stages of labor and how the baby uses amniotic fluid during such an important period for its development as childbirth are all this is not yet fully understood (24). There is recent research on the carbohydrates, proteins, fats, electrolytes, enzymes, and hormones found in amniotic fluid, and how these all relate to baby's birth weight, onset of labor, and pregnancy progress (25).
Research suggests that early spontaneous rupture of the bladder may be related to the composition of the amniotic fluid. Another study points to an increase in the concentration of prostaglandins in the amniotic fluid, suggesting that this growth triggers labor; this postulate contradicts the generally accepted opinion that the concentration of prostaglandins increases as a consequence of the onset of labor (26). Other studies (27, 28) investigate the relationship between the presence of one of the parathyroid peptides (PTHrP) in the amniotic fluid and its effect on labor and the functioning of the membranes in late pregnancy (29). Another study (30) investigates the role of interleukin-2 in the mother-fetus immune system during early pregnancy and possibly during childbirth. Amniotic fluid, a baby's natural habitat, is taken for granted and manipulated without fully understanding its function in childbirth. Research points to the need for additional study of the chemical changes in amniotic fluid composition during labor and the effect of these changes on the child's experience of labor. Although everyone knows that amniotic fluid creates a protective layer for the baby during labor, bladder piercing continues to be a routine procedure. It is possible that there are still important, but not yet known to us, functions of the amniotic fluid, which help the child to adapt to the new life conditions after birth.
Rituals surrounding birth The process of birth is reflected in the culture of any society, and any culture uses various rituals to overcome the fear of the unknown. Childbirth can be unpredictable, carry elements of a spiritual mystery. With the help of rituals, it is possible to avoid dangers and come to a good ending. Medical interventions, explains childbirth anthropology researcher Robbie Davis-Floyd, give physicians a psychological sense of power over the forces of nature and help relieve fear (31). The ritual includes symbolic objects (for example, a hook to pierce the bladder), ideas (for example, "amniotomy speeds up labor, which is good for a woman") and actions such as taking responsibility, explaining the meaning of the procedure. The imagery associated with amniotomy implies forces that “release water and bring life”, while still in the hands of the person giving birth. Such rituals convey an unconscious message that the woman feels rather than consciously perceives. The effect is incredibly powerful. The hospital birth culture is based on technical symbols and procedures that try to transcend nature and individuals, as if telling us that a woman's body is imperfect and that, using tools, doctors can manipulate nature.
The obstetrician, mobilizing the strength of the woman in labor, allows the natural process to develop independently, he understands that the woman's body itself knows what to do (including the moment when it is time to get rid of the amniotic fluid). Such an obstetrician accepts the fact that amniotic fluid helps the cervix open by pushing outward in the bladder, working like a wedge, using hydrostatic pressure to gently and evenly open the cervix (32). This is the progress that mother and child are making together, not the hasty mechanical intensification of labor that amniotomy produces and which takes away the birth experience that is rightfully theirs for mother and child.
Types of influences and behavior
Childbirth is a biological frontier. Recent studies on prenatal causes of adult illness indicate that more changes occur during the prenatal and early postpartum periods than at any other age. Studying the interaction of the organism with its environment during critical periods of development, the study concludes that the child makes compensatory efforts in utero, which increase his susceptibility to disease (33). The researchers also found that this type of reprogramming can be passed down from generation to generation. It is impossible not to ask the question: is not a sharp change in the conditions of a child's existence when a bladder is punctured the reason for an increase in the number of children with sensory integration difficulties, who then receive such neurological diagnoses as "attention deficit hyperactivity disorder" (this diagnosis is more often given to boys of preschool and early school age ). There is a hypothesis that the consequences of a puncture of the bladder in girls appear later, since the eggs in her body register this interference at the level of cellular memory, and when she grows up and becomes pregnant, this will change the properties of the membranes in her children. From the prenatal and perinatal point of view, it is known that how our heredity and our personality traits manifest itself depends, among other things, on the events that accompanied conception, intrauterine life and birth (34). The effect of amniotomy on early psychological development is unfortunately not taken into account, while the ritual of puncturing the bladder to enhance labor is widespread. Amniotomy is routinely used to speed up labor and to diagnose fetal distress, while amniotomy itself promotes irregular heartbeats in the fetus (which is a sign of distress!) By decreasing the amount of water in the uterus, thus compressing the umbilical cord and access of placental blood and oxygen to the child. When the membranes are left untouched, there are far fewer heart rhythm disturbances in the baby during labor. Part of the irregular heartbeat is caused by the delivery itself, and this is natural (35). It is likely that amniotomy is used to diagnose fetal distress much more often than is actually necessary. Amniotomy forces the child to urgently adapt to the fact that his body is subjected to strong mechanical compression, and the head passes through the bony ring of the maternal pelvis without any protection. A sharp drop in hydrostatic pressure and an unexpected squeezing of the head in the bone ring that a child experiences in connection with an amniotomy is perhaps too much stress on the child's body. When the bladder is punctured, it experiences symbolic, physiological and psychological loss (36). When the environment around the child - the protective and nourishing amniotic waters - suddenly pours out, the child instantly experiences a sense of irreparable loss. He passes through the birth canal on command, this is his first "loss of himself." " Stress matrix”Is a conceptual model that helps us better understand the shock and trauma that a baby experiences during childbirth (37). As the physiological shock increases, the changes may be overwhelming and excessive for the child. Shock is “a sudden disturbance of psychological balance” (38) and it certainly affects behavior. The body will recall the experience of childbirth at the motor, vestibular, emotional and social levels (39). Some of the physical signs that are noted in children who have experienced stress during birth are limb twitching, muscle hyper- or hypotonia, manifestations of rage, fear, or lack of response to the world around them (40). Their condition is often attributed to infantile colic, ignoring the trauma they suffered. While these signs must be noticed and accepted, working with them, if we do not want them to take hold and influence the development of the personality throughout life.
Young children are often diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), when their nervous systems aggressively resist stimuli from their environment. Either the child may be unresponsive, non-contact - this is a reaction of "escape" from environmental stimuli. Such children are at risk of getting depression in the future, as teachers and parents often misjudge their condition. As they grow up in the modern high-tech world, these children often isolate themselves from society and immerse themselves in computer games, which, of course, negatively affects their behavior. Technology affects the social life of a child from the very beginning, it has such a strong impact that stressed children prefer to connect with the world through technology. In the worst case, the latent desire for human contacts with oneself and with others (and the rage of their impotence to establish these contacts) is fueled in such children by electronic games in which violence and murder are glorified. Accordingly, these contacts are carried out in the form of aggression directed at oneself or others.
Early developmental psychology
Amniotomy is rarely, if ever, mentioned as an intervention that could potentially be psychologically traumatic for the mother or child. An abrupt change in intrauterine conditions is stressful for the baby, and the mother may perceive amniotomy as a rude intrusion into the process of childbirth. Without a doubt, a baby can be born in a state of shock, and no one will notice, this procedure has become so routine in our culture of childbirth. One of the principles of early developmental psychology, related to the development of human potential, refers us to the capabilities of the infant, which include intellectual, sensory and energetic adaptation. It seems clear that the decision to perform an amniotomy will have many consequences for the child. From the very beginning of its nascent life, the child is influenced by the thoughts and feelings of his mother, and during childbirth he is also influenced by the thoughts and feelings of those taking birth. The foundations for the growth and development of a baby are laid during pregnancy and childbirth. He reacts to the sensations and emotions of the mother and her environment, and this affects his development. The behavior and thoughts of others during childbirth can have a lasting impact on him. Amniotomy means that a stranger appears with an instrument that grossly violates the environment of the child and causes its abrupt changes, for which the child is completely unprepared. It is an invasive procedure that violates the child's innate need for belonging, safety, and care. The bladder piercing makes contractions more painful for both mother and baby, and can disrupt their telepathic connection. The drastic changes caused by the outpouring of water trigger the release of stress hormones that affect the sympathetic nervous system, and this process can be reproduced whenever a child finds himself in a stressful situation throughout his life.
Problem solving strategies
To overcome the widespread use of amniotomy, it is necessary to open your mind to unfamiliar statements and break through stereotypes. We are moving forward as textbooks already indicate that amniotomy is useless in shortening labor (41, 42). It is also recognized that amniotomy "just in case" to assess the condition of the fetus does not justify itself. It is necessary to educate and educate people working with children on how to recognize the symptoms of shock in infants, children and parents in order to facilitate healing from its effects. It will take passionate people to carry this information about every toddler and every parent and personally to parents, and those who work with these children and parents, it will take many people to organize conferences and publish credible research. We need an environment that gives us a sense of security. She will be able to heal the trauma we received in the early stages of development. As workers in obstetrics, we must slow down the pace, reduce our activity in order to enable the child's body to turn on self-regulation and adaptive mechanisms (43). Slowing down the pace helps us connect. " here and now»And form full-fledged relationships. Being calm increases our empathy for babies and allows us to recognize their unique bodily manifestations of trauma.
We have a long journey ahead of us - we have to create and maintain a softer birth culture. This requires communicating to the community, pregnant women, childbirth trainers and policymakers the need for a change in the delivery system to empower women. We must recognize the value of the art of midwifery and support it everywhere, as it makes our society better.
Verna Oberg received her master's degree from the Institute's Department of Prenatal and Perinatal Psychology in Santa Barbara in 2010. She works as an early development consultant, monitors the developmental stages of newborns and young children, promotes parent-child attachment, and advocates that newborns and young children are full-fledged people with consciousness and feelings. Verna expresses her deep gratitude to Dr. Jean Rhodes for her help with this article.
Literature: 1. Goer, H. 1999. The Thinking Woman's Guide to a Better Birth. New York: The Berkeley Publishing Group. 2. Simkin, P. 2001. The Birth Partner, 2nd ed. Boston: The Harvard Common Press. 3. Davis-Floyd, R., and C.F. Sargent, eds. 1997. Childbirth and Authoritative Knowledge: Cross-cultural Perspectives. 3rd ed. Berkeley and San Francisco: University of California Press. 4. Enkin, M., et al. 2000. A Guide to Effective Care in Pregnancy and Childbirth, 3rd ed. New York: Oxford Press. 5. May, K.A., and L.P. Mahlmeister, eds. 1994. Maternal & Neonatal Nursing, 3rd ed. Pennsylvania: JB Lippincott Company. 6. Wagner, M. 2006. Born in the USA. Berkley, CA: University of California Press. 7. Robson, K. M., and R. Kumar. 1980. Delayed Onset of Maternal Affection. Br J Psychiatry 136: 347-53. 8. Mayes, M. 1996. Mayes Midwifery, 12th ed. Oxford: Baillière Tindall. 9. Brenda. 2001. Artificial rupture of membranes: breaking the waters. Message posted to UK Midwifery Archives at http://www.radmid.demon.co.uk/arm.htm. Accessed 2 Jun 2010. 10. See Reference 6. 11. See Reference 4. 12. Childbirth Graphics. 1993. Directional Learning. Wasco, Texas: A Division of WRS Group, Inc. 13. See Reference 6. 14. Rehana. 2001. Artificial rupture of membranes: breaking the waters. Message posted to UK Midwifery Archives at www.radmid.demon.co.uk/arm.htm. Accessed 2 Jun 2010. 15. See Reference 2. 16. See Reference 5. 17. Ibid. 18. See Reference 6. 19. See Reference 3. 20. Davis-Floyd, R. 1987. Hospital birth routines as rituals: Society's messages to American women. J Prenat Perinat Psychol Health 1 (4): 276-96. 21. See Reference 5. 22. Ibid. 23. McKay, S. 1991. Shared power: The essence of humanized childbirth. J Prenat Perinat Psychol Health 5 (4): 283-95. 24. See Reference 5. 25. Gotsch, F., et al. 2008. Evidence of the involvement of caspase-1 under physiologic and pathologic cellular stress during human pregnancy: a link between the inflammasome and parturition. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 21 (9), 605-16. 26. Lee, S. E., et al. 2008. Amniotic fluid prostaglandin concentrations increase before the onset of spontaneous labor at term. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 21 (2): 89-94. 27. Ferguson II, J. E., et al. 1992. Abundant expression of parathyroid hormone-related protein in human amnion and its association with labor. Proc Nati Acad Sci USA. 89: 8384-88. 28. Wlodek, et al. 1992. Abundant expression of parathyroid hormone-related protein in human amnion and its association with labor. Reprod Fertil Dev 7 (6): 1560-13. 29. Ibid. 30. Zicaria, A., et al. 1995. Interleukin-2 in human amniotic fluid during pregnancy and parturition: implications for prostaglandin E2 release by fetal membranes. J Reprod Immunol 29 (3): 197-208. 31. Davis-Floyd, R. 1990. Obstetrical rituals and cultural anomaly: Part I. J Prenat Perinal Psychol Health 4 (3): 193-211. 32. See Reference 12. 33. Nijland, M.J., S.P. Ford and P.W. Nathanielsz. 2008. Prenatal origins of adult disease. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 20 (2): 132-38. 34. Odent, M. 2008. New Criteria to Evaluate the Practices of Midwifery and Obstetrics. J Prenat Perinat Psychol Health 22 (3): 181-89. 35. Barrett, J. F. R., et al. 1992. Randomized trial of amniotomy versus the intention to leave membranes intact until second stage Br J Obstet Gynecol 94: 512-17. 36. Emerson, W.R. 1997. Birth Trauma: The Psychological Effects of Obstetrical Interventions. Petaluma, CA: Emerson Seminars. 37. Castellino, R. 2005. The Stress Matrix: Implications For Prenatal and Birth Therapy. Santa Barbara, CA: Castellino Prenatal and Birth Therapy Training. 38. Ibid. 39. Perry, B. 2009. On the brain: How we remember. CYC-Online (122) http://www.cyc.net.org/cyc-online/cyconline-apr2009-perry.html. Accessed 14 Apr 2009. 40. See Reference 37. 41. See Reference 3.42. See Reference 6. 43. Glenn, M. 2002. The use of body-centered psychotherapy in working with prenatal and perinatal imprints within a group. Paper presented at Third United States Association of Body Psychotherapy Congress and Emergence in Body Psychotherapy. http://www.sbgi.edu/cont_edu/glenn/glennceuя.html. Accessed 30 Sep 2009.
Labor is always preceded by contractions. With their onset, the cervix begins to open. The fetus moves along the birth canal, the muscles of the uterus are intensely contracted, and the cervix is \u200b\u200bsmoothed.
The fetal bladder also promotes the opening of the cervix, while protecting the head and neck of the newborn from injury. It reliably protects newborns from various types of infections, and labor, if present, is almost painless and natural. If childbirth proceeds normally, the amniotic fluid begins to flow away on its own, and the bladder breaks painlessly (there are no nerve endings in it).
In some women in labor, the discharge of water occurs before the onset of labor. Amniotic fluid is poured out in a small amount (200 ml). If the fetal bladder ruptures before leaving the neck, then the water is released in drops.
So why pierce the fetal bladder during childbirth?
For this, there are the following medical indications:
- prolonged pregnancy;
- syndrome of disruption of the work of some body systems and organs of a pregnant woman (gestosis);
- irregular contractions;
- weak labor activity;
- very dense amniotic fluid. A baby can be born “in a shirt,” that is, in an unexploded bubble. This is dangerous because the newborn cannot take a full first breath;
- polyhydramnios;
- various pathological conditions of women in labor.
Often, during the period of any childbirth, the following can occur: childbirth takes a long time, the fetus moves slowly, abundant discharge with an admixture of blood appears from the genital tract, there is a threat of placental detachment, the occurrence of hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of the fetus. All this also applies to medical indications for opening the amniotic fluid.
Bladder opening procedure
The bladder is opened by a doctor during examination with a special sterile instrument. There is no need to be afraid of this manipulation, as it is absolutely painless. After the bladder is opened, the amniotic fluid begins to drain, mechanical irritation of the baby's head of the mother's birth canal, stimulation of the production of special biologically active substances (prostaglandins). They also begin to intensify generic activity.
Sometimes the bladder is also opened in order to carry out a diagnostic measure, when there is a suspicion of hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of the fetus. In any case, if the doctor decided to puncture the bladder, then it is necessary for the health of the woman in labor and the baby.
In utero, the baby is protected by a special shell - amnion, filled with amniotic fluid. They protect it from shock when moving, and the membrane prevents the ascending penetration of infection from the vagina.
During labor, the baby's head is pressed against the cervix and a fetal bladder is formed, which, like a hydraulic wedge, gradually stretches the cervix and forms the birth canal. Only then does it break on its own. But there are situations when a bladder puncture is performed before childbirth without contractions.
This procedure is not prescribed at the request of the woman or the whim of the doctor. The success of an amniotomy is possible under certain conditions:
- the head of the fetus is presented;
- full-term pregnancy at least 38 weeks with one fetus;
- the estimated weight of the fetus is more than 3000 g;
- signs of a mature cervix;
- normal indicators of the size of the pelvis;
- there are no contraindications for natural childbirth.
Amniotomy types
The moment of the puncture determines the type of procedure:
- Prenatal - is carried out before the onset of labor, its goal is labor arousal.
- Early - before the disclosure of the neck by 6-7 cm, it is able to speed up this process.
- Timely - performed with effective contractions, neck opening 8-10 cm.
- Late - in modern conditions it is rarely performed, it is performed at the time of the expulsion of the fetus. An amniotomy is needed to prevent bleeding in a woman in labor or hypoxia in a child.
How is labor going after a bladder puncture? The process of the birth of a child in this case does not differ from the natural one. In any case, the condition of the fetus is monitored using the CTG apparatus.
Indications for a puncture of the bladder during labor
A bladder puncture stimulates or is performed during planned labor.
Labor induction with amniotomy is indicated in the following cases:
- gestosis, when there are indications for urgent delivery;
- premature placental abruption;
- fetal death in utero;
- prolonged pregnancy;
- severe chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system, lungs, kidneys, in which delivery is indicated from 38 weeks;
- rh-conflict between mother and child;
- pathological preliminary period.
The latter condition is the onset of small contractions over several days that do not develop into normal labor. This causes fetal suffering from lack of oxygen and fatigue of the woman.
How long will labor start after the bladder is punctured? The onset of labor is expected no later than 12 hours later. However, doctors do not spend that much time waiting at this time. Prolonged stay of a child in a waterless environment increases the risk of infection. Therefore, 3 hours after the opening of the amnion, if contractions have not begun, stimulation with medication is used.
With already developed labor, the puncture is performed according to the following indications:
- The cervix opened 6-8 cm, and the water did not leave. Their further preservation is impractical, the bubble no longer fulfills its function.
- Weakness of labor. Bladder puncture in most cases leads to its activation. After the amniotomy, they wait 2 hours, if there is no improvement, then they resort to oxytocin stimulation.
- Polyhydramnios overstretches the uterus and interferes with the development of normal contractions
- With low water, a flat fetal bladder is observed. It covers the baby's head and does not function during labor.
- A low-attached placenta may begin to flake off after the onset of contractions. Opening the amnion will allow the head of the fetus to snuggle tightly against the lower segment of the uterus and contain detachment.
- In multiple pregnancies, the bladder of the second child is punctured 10-15 minutes after the appearance of the first.
- High blood pressure decreases after opening the waters.
Bladder puncture technique in a woman in labor

- 30 minutes before the stimulation of labor by puncturing the bladder, the woman is injected with the antispasmodic Drotaverin.
- Later, an examination is carried out on the obstetric chair, the doctor assesses the neck, the location of the head.
- With a sliding movement of the fingers, a special branch is inserted into the vagina - a hook.
- With its help, the shell clings during the contraction, and the gynecologist inserts a finger into the resulting hole. The tool is being removed.
- Holding the head of the fetus through the abdomen with the other hand, the membranes are gently divorced and the anterior amniotic fluid is released.
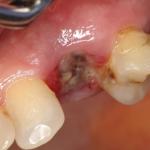
They are collected in a tray, and their condition is visually assessed. Green waters with flakes of meconium indicate intrauterine fetal hypoxia. This condition deserves additional attention. The pediatric service is warned in advance about the possible condition of the child.
If a large volume of water is drained at once, it can lead to the loss of umbilical cord loops or small parts of the fetus.
After the procedure, the CTG apparatus is connected to the mother in labor for 30 minutes to assess the condition of the child.

Is it painful or not to puncture the bladder before giving birth? The membranes are not penetrated with nerve endings, so the procedure is absolutely painless.
At the same time, complications sometimes develop:
- trauma to the umbilical cord vessel, if it was attached to the shell;
- loss of umbilical cord loops or parts of the fetus (arms, legs);
- deterioration of the fetus;
- rapid labor activity;
- secondary birth weakness;
- infection of the child.
How long does labor last after a bladder puncture? The duration depends on their parity or quantity:
- In primiparas, the normal duration of labor is 7-14 hours.
- Multiparous ones need less time - from 5 to 12.
Contraindications to a puncture of the bladder in a pregnant woman

Despite the simplicity of the procedure and the small number of complications of the manipulation, there are serious contraindications for its implementation. Most of them coincide with contraindications for natural childbirth:
- A herpetic rash on the perineum will lead to infection of the child.
- Pelvic, leg, transverse or oblique presentation of the fetus, umbilical cord loops in the head area.
- Complete placenta previa. In this case, childbirth is impossible - the placenta is attached over the internal pharynx and prevents the lower segment of the uterus from expanding.
- Inconsistency of the scar on the body of the uterus after cesarean section or other surgical procedures.
- Narrowing of the pelvis 2-4 degrees, bone deformities, tumor processes in the small pelvis.
- Fruit weight over 4500 g.
- Severe scars causing deformation of the cervix or vagina.
- Triplets, conjoined twins, breech presentation of the first child of twins.
- High myopia.
- Fetal growth retardation grade 3.
- Acute fetal hypoxia.
In the absence of the listed contraindications, amniotomy is a safe procedure and does not affect the condition of the fetus.
Yulia Shevchenko, obstetrician-gynecologist, specially for the site
Useful video
An obstetric operation aimed at stimulating labor is to open the fetal bladder. The procedure is painless and does not affect the health of the mother and fetus.
 The period of waiting for the baby is a wonderful time in the life of every woman, which is accompanied by various problems and not particularly pleasant moments.
The period of waiting for the baby is a wonderful time in the life of every woman, which is accompanied by various problems and not particularly pleasant moments.
One of those moments is the absence of contractions. If labor does not start for too long, doctors may decide to stimulate it. The most popular way to induce labor is to puncture the amniotic fluid. Manipulation is completely safe for the health of a woman, a baby, and does not cause any painful sensations.
Indications for an amniotomy
A puncture of the amniotic sac is a type of surgical intervention that is completely painless and is performed without anesthesia. It is carried out according to medical indications, under the supervision of a qualified doctor. Amniotomy can be recommended, both before the onset of labor, in order to simulate them, and during an inactive (sluggish) delivery process.
 Reasons for this manipulation:
Reasons for this manipulation:
- pregnancy lasts longer than expected. If all the deadlines for the start of contractions have already passed, but labor has not begun;
- gestosis in late pregnancy. This complication threatens with oxygen starvation of the fetus;
- chronic impairment of blood circulation between the placenta and the fetus, when oxygen deprivation increases and it cannot be eliminated with medication;
- a large amount of amniotic fluid. This pathology can cause hypoxia, fetal injury. For this reason, even with a small opening of the cervix, doctors pierce the bladder to avoid possible complications;
- ineffective contractions;
- the bubble is flat;
- low attached placenta. A puncture with a low location of the placenta helps to avoid uterine bleeding, the occurrence of its premature detachment;
- rhesus conflict;
- dense shells. If the cervix is \u200b\u200bcompletely open, and the bladder has not burst, then the doctors carry out this manipulation in order to preserve the baby's health.
How is the puncture of the fetal bladder carried out
 Amniotomy is an obstetric operation that takes several minutes and is completely harmless. The puncture procedure is carried out exclusively by a gynecologist, not an obstetrician.
Amniotomy is an obstetric operation that takes several minutes and is completely harmless. The puncture procedure is carried out exclusively by a gynecologist, not an obstetrician.
The manipulation is carried out directly during the vaginal examination in the gynecological chair. To do this, the external genital organs are initially treated with an antiseptic, then the doctor carefully punctures the amniotic fluid with a special medical sterile instrument. The tool for this procedure is made of plastic and visually looks like a crochet hook.
How long

A puncture is assigned to expectant mothers when they are at 41-42 weeks of gestation, if the uterus is already ready for labor and there is no activity.
Is it possible to pierce without contractions
 The bladder can be punctured before labor begins. The main reason for this procedure is the stimulation of contractions in the late stages or when the cervix is \u200b\u200bfully open.
The bladder can be punctured before labor begins. The main reason for this procedure is the stimulation of contractions in the late stages or when the cervix is \u200b\u200bfully open.
Puncture process
This type of surgical intervention is carried out exclusively by the doctor who will deliver the baby. The procedure is performed during a vaginal examination, the puncture is carried out with a special medical device. After the manipulation, doctors monitor the baby's heartbeat throughout the entire time.

The puncture process is not dangerous for the woman and her baby. But it stimulates the onset of labor, accelerates labor, helps the child to be born faster.
Does it hurt to pierce the bubble
Obstetric intervention to puncture the bladder does not cause pain, since it does not have any painful nerve endings.
How long after the puncture of the fetal bladder the contractions will begin
 If the bladder was punctured during the prenatal period, then normally contractions should be expected for the next two hours. At this time, doctors connect the woman to the CTG apparatus to monitor the baby's condition and readiness for labor.
If the bladder was punctured during the prenatal period, then normally contractions should be expected for the next two hours. At this time, doctors connect the woman to the CTG apparatus to monitor the baby's condition and readiness for labor.
In a situation where, after a set time, the contractions did not come, the doctors decide to stimulate them with the help of special drugs.
This is due to the fact that for a future child, being in an anhydrous state for more than 12 hours is a huge danger. If stimulant drugs did not help in delivery, then the expectant mother is urgently carried out by a cesarean section.
Is childbirth different after amniotomy
During a natural bladder puncture, oxytocin is released and the uterus begins to contract naturally. After the manipulation of the amniotomy, labor takes place, as well as after their stimulation, no difference is observed. But before piercing the amniotic sac, the doctor must: 
- examine the birth canal of a woman and assess how ready they are for the childbirth process;
- determine the degree of dilatation of the cervix. If a woman is already at 41 or 42 weeks pregnant, and no contractions are observed, the neck is soft, worn out and elastic, then this manipulation can be performed. But a puncture is not recommended if the expectant mother's birth canal is not yet prepared for labor; In contact with
- Only an obstetrician-gynecologist in a hospital setting should carry out the manipulation.
- The cervix must be fully prepared for the birth process.
- The baby should be in the correct position, and his head should be in the correct position in the mother's pelvis.
- A contraction-free amniotomy should only be performed if all of the above conditions are met and indicated.
- Gestosis, accompanied by severe edema, increased pressure, increased protein content in the urine.
- Postterm pregnancy, when labor does not begin before 41-42 weeks.
- Weak labor activity.
- Placental insufficiency.
- The bubble shell is too tight.
- Rhesus conflict between mother and child.
- Flat fetal bladder, i.e. lack of anterior water.
- Low position of the placenta.
- Polyhydramnios.
- High blood pressure in the mother.
- Before the operation, the doctor checks the condition of the fetus.
- Further, on the obstetric chair, the gynecologist assesses the condition, the degree of cervical dilatation.
- If the cervix is \u200b\u200bin the right condition, the doctor inserts a plastic hook into the uterus.
- In a contraction, when the wall of the bladder protrudes, the doctor punctures it carefully.
- Then, with a finger, he carefully widens the opening and releases the amniotic fluid.
- In the next 30 minutes, the woman in labor should be monitored, the condition of the fetus is monitored using CTG.
- malposition;
- presentation of the umbilical cord loops;
- full placenta previa.
- genital herpes;
- immunodeficiency virus;
- hepatitis.
- scars on the uterus;
- pathological conditions of the birth canal;
- large fetal weight;
- placental abruption;
- retinal tears;
- fundus changes;
- tears of the 3rd degree during the previous birth;
- acute fetal hypoxia according to CTG.
- prolapse of the umbilical cord: in this case, the formation of acute hypoxia in the baby is possible, therefore urgent surgical intervention is required in the process of childbirth;
- damage to a large vessel of the fetal bladder: for this reason, bleeding forms, which can threaten the life of the child;
- rapid labor: this is possible due to a sharp change in pressure in the uterus, which is fraught with ruptures of the cervix and perineum;
- if the puncture did not lead to an increase in labor, then after a certain time it is necessary to apply other methods of stimulation, since without protection in the form of a fetal bladder, there is a danger of infection of the uterus and fetus.
Amniotomy is an obstetric procedure that involves piercing the fetal bladder.
In maternity hospitals  safe indications for its implementation
safe indications for its implementation
Amniotomy pregnant hard
sleep food listening
It is produced only by qualified employees to stimulate the birth process.
What is this process?
Amniotomy is one way to induce labor. During the procedure, the doctor pierces the fetal bladder, which is why the amniotic fluid leaves, and the process of contractions starts or intensifies.
Usually, the waters are poured out during childbirth on their own, but about 7% of women still need such a procedure. After the puncture, part of the water that is in front of the baby's head leaves, irritation of the birth canal occurs, which helps to intensify the contractions.
Also, when the water is poured out, the hormone prostaglandin begins to be produced in the expectant mother, which enhances the contractions of smooth muscles, thereby stimulating contractions.
Some women are afraid of amniotomy during childbirth - this is completely in vain. It is safe for the mother and child, and is done only according to indications. Amniotomy, judging by the reviews, is completely painless; it does not require any pain relief.
Conditions for the procedure

Performed in about 7% of all births
Despite the fact that the procedure for opening the fetal bladder is quite simple, and also does not require the presence of a surgeon, certain conditions are still required for its implementation.
If all the conditions for the procedure are met, the amniotomy is performed according to the indications and the manipulation technique is followed, the likelihood of negative consequences will be very small.
Indications for manipulation
The procedure is done according to indications, and not at the request of a doctor or a woman in labor. There is a list of reasons for this procedure.
There are also indications for an early amniotomy.
Quite often, the procedure is done with twins, since in this case, a weakening of labor is often observed. The need for conducting should be assessed by the doctor during the labor process.
Types of procedure
In total, there are 4 types of amniotomy, the technique does not change, and the difference lies only in the timing of the manipulation.
| Procedure type | The essence of the procedure |
| Prenatal | Antepartum amniotomy is performed before the onset of labor, in order to start the labor process. This is done in case of a post-term pregnancy or in the presence of certain pathologies, when it is preferable for the child's health to induce labor prematurely. |
| Early | It is performed during the initial stage of labor, when the cervix is \u200b\u200bopen by no more than 7 cm. Early amniotomy is indicated in the case of weak and irregular contractions. |
| Timely | It passes when the cervix is \u200b\u200balmost completely open, 8-10 cm, but the bladder has not yet burst on its own. |
| Late | With late amniotomy, the baby's head is already in the small pelvis, the second, tighter period of labor is underway. As a rule, the bladder ruptures on its own, but sometimes the intervention of a gynecologist is required. |
Late amniotomy is performed if the fetal membrane is too dense, and the baby cannot tear it apart during childbirth. She is considered the most dangerous, since with her the probability of hitting the child's head is highest.
However, it must be carried out, otherwise the most severe consequences for the health of the newborn are possible - he may face hypoxia and suffocation. The most favorable time for a puncture is the period of contractions, since at this time the fetal bladder is clearly visible.
How is the manipulation carried out

This is a safe and painless procedure, since the bladder has no nerve endings.
Both planned and conventional amniotomy are performed in exactly the same way. The procedure does not give the woman any unpleasant sensations, therefore, one should not be afraid of it. However, it must be remembered that for its implementation, the doctor must obtain the consent of the woman in labor, and also inform her about all possible consequences.
Amniotomy is performed according to the following algorithm.
You can learn more about how an amniotomy is performed by watching a video recording of this procedure.
Contraindications for conducting

It is carried out only if there are significant indications for its implementation
Despite the simplicity of this operation, sometimes it can be contraindicated. An experienced doctor will never puncture the bladder if at least one of the following factors is present:
Opening of the fetal bladder is not done in the presence of viral infections in a woman in labor. These include:
When carrying out manipulations, the risk of infection of the child increases, therefore gynecologists prefer to protect the baby from a possible disease.
In addition, the fetal bladder is never pierced if the woman has contraindications for natural childbirth. To date, the indications for a cesarean section are:
Possible complications

Like any medical operation, it has its complications.
If the operation is performed correctly, complications after it are practically not encountered. This method is considered completely safe for the child and the mother, if there are no contraindications. However, in extremely rare cases, when a woman has an amniotomy, the following risks may arise:
Some women categorically refuse to puncture the fetal bladder, forgetting that only a qualified specialist is able to correctly assess the need for one or another obstetric intervention. Find out what it is.
Refusing this procedure because of prejudice or unfounded fears, you can seriously harm yourself and your child. Therefore, listen to the doctor's opinion - do not risk the life and health of your own child.
: Borovikova Olga
gynecologist, ultrasound doctor, geneticist