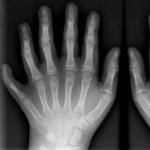
Rudiment 6 fingers in a child. Polydactilia in newborn children
Polydactilation is a congenital pathology, which is characterized by the presence of the sixth finger on the hands or feet. In the overwhelming majority of situations double the little finger or thumb. Currently, the factors of such pathology remain unknown, but clinicians believe that one of the reasons may be the heredity and negative impact of various sources on the body of a pregnant woman.
For multipleness, it is characterized by the presence of an extra finger, which can be both fully and present as a skin process that has no ability to function normally.
To put the correct diagnosis of the doctor can already at the stage of primary examination of the patient, however, to clarify the variety of illness and determining the tactics of therapy, the patient's instrumental examinations will be required. Treatment is based on a surgical operation.
The International Classification of Diseases of the Tenth Assembly allocates a separate value for such pathology. Code of the ICD-10 - Q 69.
Etiology
The polydactilation is considered fairly widespread illness, since it is diagnosed by one kid for 1-5 thousand newborns. As for the prevalence among boys and girls, such pathology is equally found among the representatives of both sexes.
Despite the fact that the pathogenesis and the predisposing factors of the appearance of such a disease are unknown, clinicians believe that the most likely cause of multiplying in hand or legs is a genetic predisposition.
The transfer of such a disease is carried out according to an autosomal dominant type with partial tolerance. This means that the carrier of the Mutation gene is one of the parents, but it will be completely healthy. The probability of the hereditary factor reaches 50%.
Some experts believe that the causes of the polydactilia are hidden in leaking completely different diseases. In such cases, congenital anomaly will be a clinical sign of one of the following ailments:
- - this is a severe chromosomal violation;
- nEUCH MECKEL;
- ellis-Van Kreveld syndrome;
- lorenes-Muna Barda-Bidla's disease.
In general, genetics knows more than a hundred syndromes, which may accompany multipliness.
In addition, the likelihood of the disease is not excluded against the background of the irrational pregnancy. These include:
- flowing during the period of tooling the child of severe illness of infectious nature;
- addiction to the future mother to harmful habits;
- unfavorable working conditions or living;
- drug abuse;
- effect of irradiation on the body.
It is assumed that such reasons affect the occurrence of this anomaly about the eighth week of the intrauterine development of the fetus, when bone tissue is set. At the same time, most likely, a significant increase in the number of mesodermal cells occurs.
Classification
Polydactile foot or brush, at the location of the defect localization, happens:
- preacial - characterized by doubling the thumb of the upper or lower limb;
- central - It is considered a rare form, since deformation is exposed from two to four fingers;
- tarsia - It is distinguished by the duplication of the fifth finger. Tarsial polydactilation, along with a preacial, is the most frequent form of illness.
The classification of polydactila in the form implies the division of the disease into several types:
- first - The sixth finger is considered a rudiment, because it represents only the skin process;
- second - pathology, as a result, split the main finger;
- the third - The extra segment is fully functional, has its own bone and tendon.
Multipality of the brush is most often diagnosed, but it does not exceed the split fingers in the footsteps. In some cases, the combination of multipleness of the upper and lower extremities is diagnosed.
According to the statements of clinicians, one-sided pathology, in the frequency of diagnosis, prevails over the two-sided polydactyl, the approximate ratio is 65 and 35%. The deformation of the right side is observed more often than two times.
Symptomatics
The fundamental clinical manifestation of the alend is the presence of additional segments in the hands of the child or legs. At the same time, additional segments are completely normal in size and functions or act as a non-functional appendage.
Often, extra fingers are characterized by:
- in small sizes, in comparison with the healthy fingers of the upper or lower limb;
- reduced phalange;
- the absence of a bone or tendon base is quite rarely superfront will be full. Often it is non-functioning soft-tissue formation on the leg of the skin;
- a doubling of the nail phalanx - is observed extremely rarely.
In addition to the excessive amount of fingers, with such pathology there is a deformation of the bone-articular apparatus. Such a violation will progress, the older will be a person that will contribute to the emergence of deformations and various violations of a secondary nature.
Multipleness is often accompanied by:
- shortening the striking limb;
- lowness;
- excess body weight;
- deformation of the sternum or skull;
- pigment retinit;
- underdevelopment of genital organs;
- syndactilia;
- fingering contractures of fingers;
- turbidity of the cornea;
- violation of the functioning of internal organs, in particular the cardiovascular system and the gastrointestinal bodies;
- microftralmia;
- distortion of ear-sinks;
- or ;
- mental retardation.
Diagnostics
Despite the fact that such an abnormal development is diagnosed immediately after the birth of the baby, instrumental examinations are needed to establish a variety of multipleness.
Initially, the clinician must independently implement the primary examination that can be implemented:
- children's orthopant traumatologist;
- pediatrician;
- children's surgeon.
Thus, the first stage of diagnostic measures includes:
- studying the history of the disease and life anamnesis not only a small patient, but also his parents;
- careful physical inspection;
- consulting a specialist in genetics is necessary to exclude or confirm the influence of an anomalies of a gene or chromosomal nature.
Laboratory tests of blood, urins and cartoons in the presence of such a disease do not have diagnostic value.
Instrumental examinations suggest implementation:
- radiography and MRI of the upper or lower extremities;
- electromyography - for evaluating regional blood flow;
- renowmography - to find out the muscles;
- stabilography;
- press - it is necessary to determine the load on the amazed leg or hand.

Since the likelihood of hereditary predisposition is great, then genetic diagnostics may include:
- genealogical analysis;
- finding out the nature of inheritance.
If such an abnormality is associated with chromosomal or genitous violations, prenatal diagnostic measures implied to the fore.
- obstetric ultrasound;
- amniocentesa;
- chorion biopsy - for karyotyping of the fetus.
When the isolated anomaly is detected during the bottom of the child, pregnancy is not interrupted, but with severe chromosomal disorders, the question of interruption of pregnancy is solved individually.
Treatment
The elimination of such congenital multipleness is carried out only with the help of medical intervention.
If the extra finger is attached to the basic only with soft tissues, then the operation aimed at eliminating can be carried out in the first few months of the life of the infant. In other cases, the optimal age for the treatment of polydactilia is Overlook, one year and older.
Operated pathology correction can be carried out in several ways, namely:
- removing the extra finger without engaging in the operation of the main;
- excision of an additional segment with subsequent corrective osteotomy of the main finger;
- exciration of the extra finger with the implementation of skin, tendon or bone plastic.
- passage of the course of therapeutic massage;
- physiotherapy, in particular, magnetic therapy and impact on the operated area of \u200b\u200binfrared radiation.
Prevention
To specific prophylactic measures that reduce the likelihood of the formation of such pathology, it is worth attributed:
- rational pregnancy, especially on the first trimester;
- regular visit to the obstetrician-gynecologist;
- consultations from a specialist in genetics - shown to those pairs, in the family of which were cases of diagnosing polydactilia;
- pregnancy planning.
Forecast
Isolated pathology has a favorable forecast and is fully cured with surgical intervention. However, with the combined polydactilia, the outcome will be dictated by the main ailment.
Children who have transferred the operation to eliminate the polydactilia must be on the reaches of the fifteen years to be on the dispensary accounting from the orrkest children's doctor. This is due to the fact that at that age the intensive growth of the body ends, and the probability of deformation is reduced to zero.
Polydactilation is a congenital pathology of the development of fingers, which is expressed in increasing their quantity. It is more often observed in the hands, but may affect the fingers of the legs, or at the same time the upper and lower limbs.
As a rule, this anatomical defect is inherited as a dominant sign at the polydactila from one of the parents. It is not dangerous for life, but it may cause psychological injury, to break the functions of the limbs, as well as slow down physical development and limit the choice of profession in the future.
According to statistics, the polydactics occurs with the same frequency of boys and girls. According to various sources, it is noted at one of the 660-3300 infants and can be combined with other hereditary disorders of the musculoskeletal system, such as climbing, brachidactics and dysplasia of the joints.
Causes of polydactilia
The etiology of the development of polydactilia was not sufficiently studied, but genetic predisposition is considered the main cause. The probability of transmitting anomaly by inheritance is 50%, since the dominant sign of polydactila is characterized by a low degree of penetration. Thus, a healthy child can be born from the carrier of the gene.
According to some versions, pathology can occur at the embryo on the 5-8 week of development due to an uneven increase in the number of mesodermal cells. In addition, sometimes it is only one of the symptoms of serious gene or chromosomal disorders. The medicine is known about 120 syndromes, which may be accompanied by polydactile, among which can be called:
- Rubinstein-Taibi syndrome;
- Carpenter syndrome;
- Smith-Lemli-Optic syndrome;
- Laurens Moon-Biedl syndrome;
- ChondroEctodermal dysplasia;
- Trisomy 13;
- Thoracic dystrophy with asphycia.
Often, to establish the exact cause of the occurrence of additional fingers is not possible.
Polydactilia classification
Polydactile is classified on localization and doubling type. Depending on which fingers are duplicated, there are three types of anomalies:
- Presenter (radial) - thumb;
- Central - index, medium and unnamed;
- Calling (ulnar) - Mysiline.
Additional fingers, both on hand and legs, can be formed in different ways, depending on their qualitative characteristics and functionality. It depends on what type of doubling took place, they may be the following entities:
- Rudiment. Consists of soft tissues, without bones. It holds on the skin leg. Non-functional;
- Split main finger. It is formed as a result of the doubling of the corresponding mills or tall bone. Almost always underdeveloped and has a smaller number of phalange;
- Full finger. It has normal sizes and shape.
In the polydactilia, the deformation of bones and joints is often observed at the place of lesion, which is able to progress over time and lead to secondary changes in the bone-articular apparatus.
Diagnosis of pathology
The diagnosis of polydactilia is carried out with the help of clinical, genetic, radiological, biomechanical and other research methods. The clinical examination of the child is carried out by a pediatrician, orthopedic and genetic to identify functional and anatomical disorders of development, as well as to establish the type of inheritance of polydactilia. Radiography of the affected brush or foot is made to assess the state of the articular and bone apparatus. If it is necessary to inspect the cartilage structures and soft tissues, magnetically resonant tomography is carried out. Additional methods, such as stability and electromyography, allow you to supplement the results obtained.
Genetic analysis is aimed at drafting the forecast of the probability of birth in a given pair of a child with anatomical anomaly. Since the most characteristic autosomal dominant type of inheritance of polydactilia is enough to develop a disease, so that a mutant allele passes from one of the parents.
If the minimity is a symptom of chromosomal or genetic deviation, it requires careful prenatal diagnosis, which includes the amniocentesis and the biopsy of the chorion, as well as an ultrasound study. With an isolated polydactile, pregnancy is recommended to preserve, and during chromosomal disorders - interrupt.
Treatment of polydactilia
 Treatment of polydactilia is carried out exclusively surgically. If additional fingers consist of soft tissues, they are removed in the first months after birth. In other cases, no more than a year is resorted to surgery. It is necessary in order to study the condition of the main fingers, which is impossible to do in the newborn.
Treatment of polydactilia is carried out exclusively surgically. If additional fingers consist of soft tissues, they are removed in the first months after birth. In other cases, no more than a year is resorted to surgery. It is necessary in order to study the condition of the main fingers, which is impossible to do in the newborn.
Clinical data indicate that after the usual removal of additional phalanx in 70% of cases, repeated deformation is developing. Therefore, during operation, the elimination of additional phalange can be combined with the correction of the deformation of the main fingers or with their restoration using remote tissues. The duration of the recovery period depends on this. Sometimes for normalizing the functions of brushes or stops may be required for several years.
Isolated polydactide treatment is best of all at an early age. If this pathology is a consequence of chromosomal or gene syndrome, the forecast depends on the severity of the underlying disease.
The prevention of polydactilia is to carry out genetic consultations during pregnancy planning, and subsequently - in the implementation of prenatal diagnosis.
Video from YouTube on the subject of Articles:
●
Label or God's gift?
A sixpalic child was born in Blagoveshchensk. As the doctors of the city maternity hospital assure, such cases in their practice have already been, there is no danger to the health of the child.
In the Blagoveshchensky maternity hospital, a boy appeared on the right handle formed by the sixth - added - finger. "The child is usual, only fingers for one more. Moreover, on the left handle and on the left stop, he also has extra fingers, only they are not bone, but on the skin leg, like a small phalanx, "Svetlana Chipizubova says the head of the branch of the newborn city maternity hospital. - It is usually difficult to say with such vices, but in this case it is heredity. The mother of the child told us that the Pope also had an additional - sixth - finger. " Such cases, according to doctors, in Blagoveshchensk occur infrequently, 10-12 in the history of the hospital.
Sixpanity, or polydakia, is an anomaly of the limbs, in which, instead of five fingers, six or more are observed on the brush. The origin of it is exactly unknown, some consider it a hereditary disease, the second - the unfavorable consequence of radioactive irradiation, the third - the "label of the devil" (this is from the area of \u200b\u200bsuperstitions). However, many consider the sixth finger to God for God's gift and a sign of a special chosenness. As the story demonstrates, the sixpasses were: Pope Sikst II, the Queen of England Anna Boleyn, well-known residents of Buryatia, the minister of the Ivolginsky Dacana Sanja Lama and Shaman Valentin Khaev. In Russia before the revolution, there were whole villages of six-legged people. "Sixpal" is one of the nicknames of Stalin, he had six fingers on his leg. It is rumored that six fingers on the leg and the actress Marilyn Monroe. The singer, the star of the Russian stage Maxim also appeared on the light of a sixpall - with two thumbs on his left hand. This anomaly of the surgeon was corrected in childhood, saying that the girl would never be able to play piano. Having learned this, Youth Maxim called everyone asked her mother to record it in a music school. Let her a great pianist, she did not, but his life still tied up with music.
According to statistics, one baby out of every 5,000 newborns is born. In mystics, the six occupies a special position. The geometric analogue of the six - hexagram (six-pointed star, or the correct equilateral polygon) - is considered to be in magic symbol of protection, good luck and love. In the magical maps of Tarot, for example, the Six Staff card symbolizes good luck, triumph, and the sixth is called the "Lovers" card and means felt and love for a person around. In China, the six is \u200b\u200balso considered happy and associated with this people with success in a variety of endeavors. Another hexagram can be found on Orthodox icons and crosses. By the way, six fingers can be not only in humans, but also in animals - dogs, cats, rodents.
Plug of the development of a brush or foot, in which the presence of one or more of the extra fingers is called polydactyl. The size of this finger can be different - from a small tubercle on the skin, to the full and functioning finger of the brush or foot. In most cases, however, the addition fingers are smaller than others and are not so well formed.
Baby brush with an extra finger located outside of the maidena (ulnar polydactilation).
Sometimes the extra finger looks underdeveloped and is associated with a brush or stop only by means of a thin skin bridge. If the finger is better formed, then it may have in its composition all the fabrics inherent in the normally formed finger - such as bones, muscles, blood vessels and nerves and has a more complete connection.
Three types of polydactilia distinguish between the arrangement of the addition finger.
The arrangement of the addition finger in the central part of the brush or foot is called central polydactile.
When the extra finger is located outside the thumb, then it is a preacial or radial (radial) form of polydactilia. If the additional finger is located outside the thumb of the foot, then this is called tibial (tibial) polydactile.
When it is located outside the maiden on the brush, it is a complete or unarround (elbow) form of polydactilia. If it is an extra finger located outside the little finger on the foot, this is called a fibular (muloberts) form of polydactilia.
The synonyms of the polydactilia are "additional finger" or "doubling of the finger" (for example: "doubling the first finger of the brush", "the addition of the fifth finger of the foot", etc.).
Polydactilia in children
 Child brush with an extra finger located outside of the thumb (prehasal polydactilation).
Child brush with an extra finger located outside of the thumb (prehasal polydactilation).
Polydactilia is a frequently common malformation among children. It occurs in about one case per 1000 newborn children. In some families, he is inherited, but most often he meets only one person in the family due to genetic features.
Usually an extra finger appears only on one hand or one leg. In some cases, children are born with an extra finger on both brushes or both footsteps - and, in rare cases, on both hands and both legs.
Many children with polydactile have no other diseases. But also polydactilation can be combined with Sindactile (then the disease is called polysindactile) or with other genetic syndromes.
Examination at polydactilia
If your child was born with an extra finger, the doctor carefully examines the child. During the inspection, he will look for other features of development to decide whether your child has more complex diseases.
The child may need to produce radiography to see if there are dice in an extra finger, how they are formed and how to go to other brush / foot kites. If a doctor believes that your child may have other genetic syndromes, he can direct you to consult a genetics.
In most cases, doctors remove an extra finger in early childhood. The purpose of treatment is the achievement of maximum functional and aesthetic results. Sometimes it is necessary to solve and practical problems, such as removing the addition of the foot, interfering with the wear of the shoes.
Methods of treatment of polydactilia
The method of removing the extra finger depends on whether it is located on the brush or on the foot, and how it is attached to it - a thin skin bridge or is fully developed.
Vascular clip, thread.
If the finger is bad formed and does not contain bones, sometimes the next treatment method is used - a thread child, or vascular clip, tighten the skin "bridge". It stops the influx of blood to the finger, and soon it will disappear as the umbilical cord after birth.
Surgical method of treatment of polydactilia
If the additional finger of the child is formed more fully, the operation is required. The latter is produced at an early age. Its complexity depends on the degree of development of the addition finger. Sometimes it is necessary to make partial bone removal, transfer the place of attachment to the tendon, produce the joint capsoplastic, remove the vessel or nerve. It is also often necessary to produce various types of skin plastics to achieve a maximum aesthetic result.
After surgery, it will take some time to wear a gypsum glue to the moment of healing the postoperative wound and the formation of the brush. At this time, it will takes observation of the doctor as well as various types of physiotherapy to reduce the scarring and full development of the function of the brush.
Treatment of polydactilia in DGKB No. 13. N.F. Filatova
The first thing that Mom does when she put a newborn on his chest, quickly considers the baby's fingers on their legs and arms. And does it not in vain. Some cases of babies appearance end with the birth of children with an abnormal number of fingers on hand or leg.
An important basis for the appearance of polydactilia is negative heredity. This happens not often, but there is a place to be. The disease is transmitted from one of the parents. They may be carriers of the pathological gene, but they themselves do not hurt in this disease.
Various chromosomal disorders also carry with them the development of polydactilia. In the presence of Patau syndromes, mekkel and others, irreversible processes occur in genes.
The reasons for an isolated anomaly are definitely not identified. Experts suggest that such pathology begins development on the fifth week of intrauterine life and is due to the quantitative growth of mesodermal particles.
Symptoms
The disease is manifested by the occurrence of an innate anomaly structure of the hand or foot brush. The child is detected with an extension segment on foot or hand. Famous cases when multipliness is detected in the newborn.
Distortions can be different. Often, extra processes are devoid of bones, and look underdeveloped appendages. Sometimes, however, they can be ordinary sizes and traditional structure. Everything is very individual.
In addition to the formation of additional fingers, the deformation of the most motor apparatus is detected for the disease, which, after years, progresses and contributes to the risk of repeated changes and static-dynamic pathologies.
At the ailment of Louurenz-Barda Muna-Bidla, a lag is found in the development, skull deformation, obesity and other pathological processes. In case of Pataau's disease, children suffer from multiple developmental anomalies: the formation of the cleft of the upper lip and the neba, the problem of the cornea of \u200b\u200bthe eye, the ugliness of ear forms. In case of Ellis-Van Kreveld's disease, the pathological anomaly is marked together with the development of closures, low-consumption, heart defects.
Diagnosis of polydactilia in newborns
The diagnosis of pathology is carried out on the basis of physical, electrophysiological, biomechanical, radiological, genetic surveys.
The surgeon inspects a small patient, determines the anatomical pathology, features of deformations. In addition to the surgeon, the baby should inspect the pediatrician and genetics.
X-ray allows you to estimate the bone-bone apparatus and those violations that can be detected there. In addition to X-ray, MRI is shown to determine the status of structures of brushes or stop.
Also as additional studies are used electromyography, renowmography. These methods allow you to see the condition of muscular fabrics, the feature of the blood flow during pathology.
Biomechanical examination (stabilography, for example) is shown to identify the static load on the legs during the deformation of the foot.
Molecular genetic diagnostics is a genealogical analysis, the installation of the type of inheritance, the forecast of the possible risk of the appearance of a baby with pathology in a certain family. For the disease, the flow of which is associated with chromosomal and gene syndromes, prenatal diagnosis plays a crucial role. When a separate deformation anomaly is detected from the embryo continue; In case of detection of a serious chromosomal violation, an abortion decision is made.
Complications
As a rule, when carrying out operation, the disease is completely eliminated if there was a diagnosis of isolated pathology. Surgical intervention is better carried out at the earliest age. After operating the child, it is necessary to observe up to 15 years from orthopedic. In case of ailment associated with gene and chromosomal mutations, consequences can be the most different. Depends on the severity of the main syndrome.
Treatment
What can you do
All that is required from parents during the treatment of the child, this is a special massage after surgery, control over the study of therapeutic physical education and the fulfillment of the remaining recommendations of the specialist.
When complying with all necessary manipulations, complete recovery without any complications are quite real.
What does the doctor do
Treatment by experts is carried out only by the operation. The operating date is prescribed individually. The expert is watching the character of deformation and decides. So, if the extra finger is connected to the basic only skin jumper, it is removed in the first six months after the birth of the baby. In other cases, surgery is postponed to a one-year-old age.
There are several options for the operational correction of this congenital pathology. Of great importance is the type of deformation and the peculiarity of the flow of anomaly.
- Elimination of the extra finger without the use of the scalpel on the main finger.
- Operating the process with the use of plastic surgery: skin, tendon or bone.
- Liquidation of a segment with a corrective osteotomy of a healthy finger.
Prevention
Preventive measures are to ensure that the pairs in which in the family are such a parable, when planning conceptions, appealed to the reproductist genetics.
The specialist will make a number of research and correction activities to increase the chance of birth of a healthy child.
With regard to the prevention of postoperative negative consequences, it consists in determining the adequate technique of operating correction and the implementation of good rehabilitation.