Master class “Teaching children to compose riddles. Composing riddles with children of the compensating group
Riddle is a type of oral art. The riddles that we inherited as the cultural heritage of the past are mostly folk. They reflect in a figurative allegorical form the work and life of people, the world around them, natural phenomena, animals, birds, plants. The language of modern riddles - literary ones with their own authors - is closer to us and understandable. Nevertheless, many folk riddles will delight and surprise us endlessly. They serve as classic models for composing new riddles.
Riddles are a question or task that contains a figurative description of an object, its characteristic features and which requires a solution. Most often, the riddle is in the form of a poem, which makes it more attractive.
Composing riddles is not an easy task for children. To do this, they need to learn how to briefly describe objects, phenomena. Find and highlight in them the most essential qualities, signs, properties, discarding the secondary and insignificant. To learn how to come up with riddles, you need to know what methods you can use. Let's consider some of them.
1 the question riddle
Who wears his house on? (Snail.)
Who is afraid of everyone, is saved under the bush? (Hare.)
2.The riddle in the form logical task, or riddle-savvy
Seven brothers have one sister, how many sisters? (One.)
Seven brothers have one sister. How many children are there? (8 children, 7 brothers with one sister.)
3 humorous riddles, or joke riddles
The essence of such riddles is a trap or a play on words. They are witty, amaze with the unexpectedness of the answer. Such a riddle does not suggest the answer, and sometimes, on the contrary, makes the thought work in the wrong direction.
What stones are there in no sea? (Dry.)
How to write a "mousetrap" in five letters? (Cat.)
Who was the first Russian woman who mastered the aircraft? (Baba Yaga.)
4.Indication of only parts of the object and their number
Six legs, two heads, one tail - what is it? (Rider and horse.)
Two rings, two ends, studs in the middle. (Scissors.)
5. Enumeration of the actions of an object without naming it
Flows, flows - does not flow out, runs, runs - does not run out. (River.)
You stroke - caress, tease - bite. (Dog.)
6. Direct description of the characteristic features of an item without naming it
Gray in summer, white in winter. (Hare.)
7.Metaphorical representation of an object, when the description of the characteristic features of one object is given through another object
A small ball fumbles under the bench. (Mouse.)
In the middle of the yard there is a shock, a pitchfork in front, a broom in the back. (Cow.)
8 the denial riddle
Liquid, but not water, white, but not snow. (Milk.)
With a beard, not an old man, with horns, not a bull. (Goat.)
9 the contradiction puzzle
I am sour and sweet, I am hard and soft, I am pale and ruddy.
Come on, get to know me! (Apple.)
When composing riddles, they rarely use one way, most often they are combined.
Although we have four legs
We are not mice or cats.
Although we all have backs
We are not sheep or pigs.
We are not horses, even on us
You have sat down many times. (Chairs.)
It is advisable to teach children all these methods of making riddles, starting with preschool age... The work on inventing riddles with children provides excellent material for expanding and activating the vocabulary of children with words denoting the qualities, signs, states of objects and their actions. What makes these games more valuable is the alignment of developmental goals logical thinking and figurative speech. Special attention is paid to the development of associative thinking in children, which is one of the components of any kind of creativity.
We offer some ways to teach children how to compose riddles. We start with the simplest, for example, by listing the parts of an object and their quantity. Show the children a picture of a rider on a horse. There is no need to ask children a riddle. You will "invent" it with them. You can do this in a math class. Ask the children to count how many legs the horse and rider will have together, how many heads and tails. Both eyes and ears can be counted. It remains to formulate a riddle, learn it by heart and make a guess to someone, for example, employees kindergarten, parents. In the next activity, take two pictures: one with a chair and one with a cat or dog. Count the details with the children: 8 legs, 2 backs, 1 head, 1 tail. Solution: the cat is sleeping on a chair. Children can independently come up with riddles based on pictures depicting the Serpent Gorynych, a fox with a duck in its teeth, a bird on a cow, a rhinoceros, a fly on a watermelon (6 legs, 1 head, 2 belly). An interesting riddle you can come up with a picture depicting a person sitting at a table on a chair and eating a chicken, etc. In such riddles, you can teach children to form complex adjectives: "eight-legged hunting six-legged." (The spider follows the flies.)
A fairly easy and affordable way of making riddles for children is based on the principle of denial. This method, like the previous one, can be taught from the age of five. The teacher himself can first come up with his own riddle about any subject and offer it to the children for compilation, for example:
Round but not orange
Rolls, but not a car
Jumps, but not a bunny? What is it? (Ball.)
Consider another way of composing riddles through contradictions. In the development of creativity in children, the development of antonyms is of great importance. J. Rodari draws attention to the fact that thought arises from paired concepts: “The concept soft does not appear before or after the concept hard, and at the same time, in the process of their collision, which is creation. " The contradiction method is of practical importance for the child. A preschooler will definitely become a schoolboy. This method will help him in studying the laws of the world around him.
In order to form a riddle with children, using the contradictory qualities of the subject, it must first be invented by the teacher himself. To do this, you need to learn how to find contradictions in objects and phenomena. Dialectics teaches us that contradiction lies at the heart of any development. In every subject, in every process, there are opposites. Internal contradictions are the cause of "self-movement", "self-development". It is the internal contradictions in the subject that are always hidden, and it is not easy to discover them. They are a mystery, a mystery. Humanity has been struggling to resolve contradictions from the very moment of its inception. They will accompany him in the future. The method of contradictions in the study of properties and qualities allows the child to penetrate into the essence and depth of objects and phenomena. Children should be specially taught this logical technique. First, it is necessary to teach children to select opposite signs, states, actions, to enrich their vocabulary with antonymic words. Work on antonyms can be carried out in different games and in the classroom. In mathematics classes, children compare objects and phenomena in quantitative, temporal, spatial relationships (a lot - a little, early - late, far - close). In speech development classes, objects are compared by qualities, properties, states (positive - negative, cunning - simple-minded). You can come up with the following riddle with children:
I am different:
Clean and dirty
Full and empty
Deep and shallow
And I'm called a plate.
Of course, one should not expect children to create masterpieces in the full sense of the word. The child's creativity is in the making. But only in an atmosphere of creativity, active cooperation of children with a teacher and with each other, can a free personality be raised. Not to control, but to direct development without suppression, improving the children's ability to play - these are the principles that make up the essence of personality-oriented pedagogy.
Olga Kostrubova
goal master class: demonstrate the technique making up riddles, techniques for working with pictures and mnemonic tables. Using the example of a specific lesson, introduce the stages making up riddles.
Tasks:
Teach make up figurative characteristics of objects by making riddles;
Develop creative speech activity, the ability to think independently, analyze, compare; logical, visual-figurative thinking; Attention;
Develop the sensory sphere;
To educate resourcefulness, ingenuity, speed of reaction; the ability to listen to each other.
Development environment: toys (cat, bunny, plates, object pictures, mnemonic tables, chest, scarf.
Preliminary work: drawing up descriptive stories, d \\ and "Which one?", "Selection of epithets", "Selection of actions".
The course of the lesson.
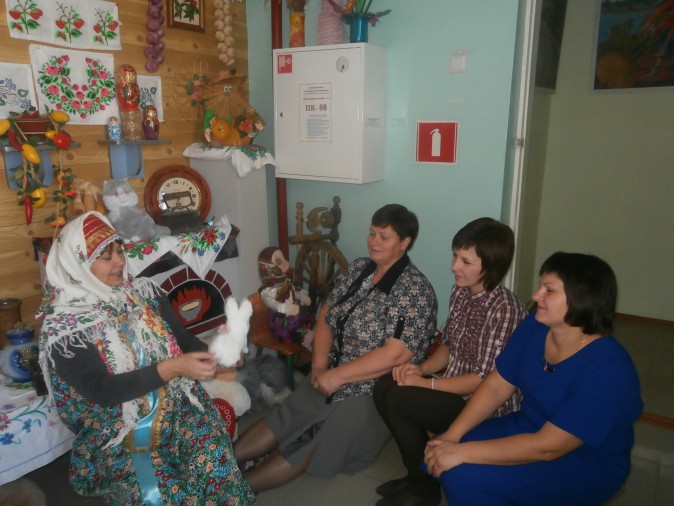
The teacher informs that the grandmother invited everyone to visit her - Riddle... The adult offers to close your eyes and be transported to mysterious countrywhere the same grandmother lives.
The guests are met by a sad grandmother - Riddle and informsthat she had a granddaughter Masha, who forgot to close the chest where they kept puzzles... All riddles disappeared. Riddle turns to children for help.
1. Direct description of the characteristic features of an object without its name.
A grandmother with her children examines a toy cat.
What about the cat? What is she like? (gray, soft, fluffy)
What does a cat like to eat the most? (milk)
What song is he singing?
Children with grandmother make up a mystery: “Gray, fluffy milk lapping, sings a song - meow, meow! Who is it?"
Grandma offers to repeat riddle near the chest and closes it. For a new the riddle remained in the chest.
Consider a bunny and make up a mystery: “Little white lump, long ears, loves carrots. Who is it?"
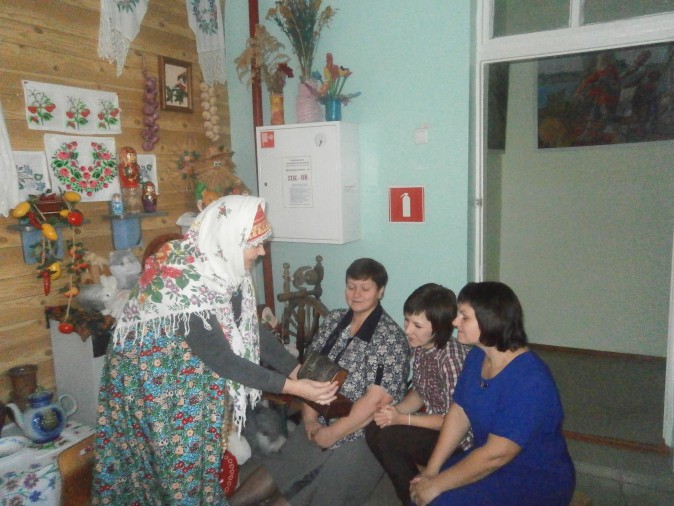
2. Riddle, drawn up by the method of contradictions.
After examining a deep and shallow plate, a new riddle: “I am different:
Clean and dirty
Full and empty
Deep and shallow. And my name is ... "
3. Riddle, negated.
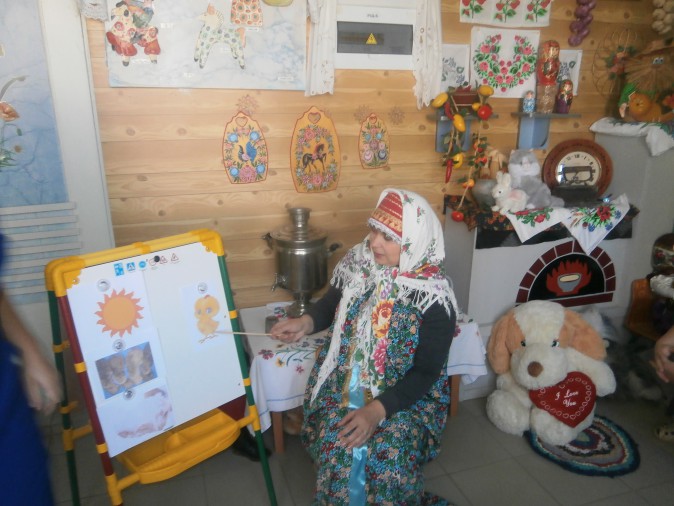
Pictures of chicken, sun, fur, fluff and phrases are composed: yellow like the sun; fluffy like fur; as light as thistledown. Dividing each pair with the expression "but not" get comparison phrases with an element puzzles: "Yellow, but not the sun"
"Fluffy, but not fur"
"Lightweight but not fluff"
New riddle“Yellow, but not the sun.
Fluffy, but not fur.
Lightweight but no fluff.
Who is it?" they also hide in a chest. By this method, children together with an adult make up the puzzle about the ball.
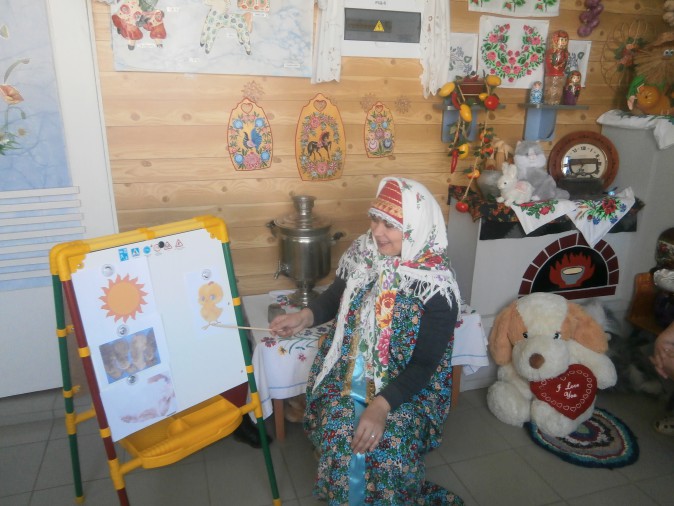
The turnip puzzle make up using a mnemonic table shown by an adult.
“Round, not a ball. Yellow, not the sun. With a tail, not a mouse ".
The grandmother thanks for the help and says goodbye to the guys.





Related publications:
Correction of the development of general motor skills One of the divisions of our holding was created to help children with visual impairments. Daily.
Master class "Teaching senior preschool children to work with the children's developmental constructor" Velkroshka " Master class "Teaching senior preschool children to work with the children's developmental constructor" Velkroshka "(This master class.
Musical card Amusing: -Hello, good people! Hello, well done Russians! Hello girls are red! Deign people.
Purpose: Teaching the participants of the master class to use noise musical instruments in working with preschool children. Tasks:.
Master class for teachers of speech therapy groups "Teaching children with GPs to read and write" Municipal budgetary preschool educational institution Child Development Center kindergarten № 88 "Smile" Administration Administration.





■ I meet the children in the hall.
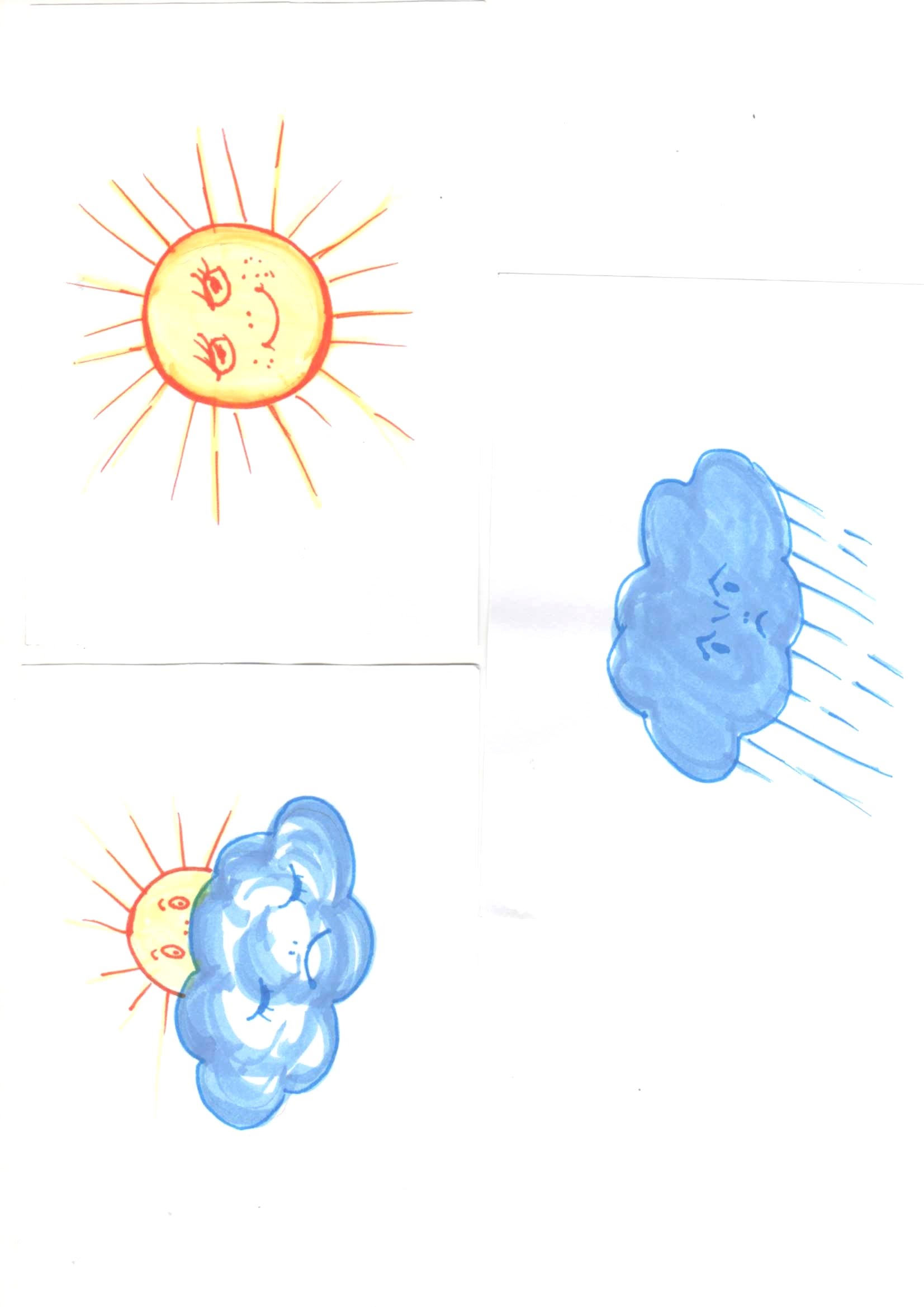
Welcome guests. I ask the children about their mood by showing pictures:
Who's in the mood like this? (Sun)
Who has a mood similar to this picture? (the sun is half covered with a cloud)?
Who's in the mood like this (cloud, it's raining)?
If someone is in a bad mood, I use the verses of the Laughing Tron "Fables":
Zebras buzzed in the bushes
In the July heat
Bloomed, swaying on their tails
Live kangaroos.
Grandpa flew through the window
And the sparrow carried grain
Rode a cactus on the window
Leading the old woman on a belt
And the dog at this time
I washed Vanya on the window.
■ Game "Yes and No"
What we are going to talk about today will become known if you guess what I have guessed.
Ask questions.
■ "Magic screen"
You guessed right. I guess the word AUTUMN. Imagine meeting us
alien and says: "I don't understand what the fall system means." How are we going to explain?
Let's turn on the "Magic Screen"
-What is Autumn? -(season)
-Autumn, what is it? (golden, deciduous, rustling, early, late, sad, wet,
rainy, festive, colorful, dirty, slushy, cloudy, dank, gray,
light, warm, cold, windy, foggy, rainy, dry, etc.)
- What are the signs of autumn? (Leaf fall, birds flying away, cleaning
harvest, preparing animals for winter, mushrooms, rains,)
-What will autumn be remembered for?
People - beauty, inspiration, new clothes are shown, kids are invited to study in schools,
gives the harvest ...
For birds travel to distant lands
Beasts -warm coats, supplies for the winter, vacation, rest
And now everything that we know about autumn, let's bring it into the system, put it on the shelves:
(funny, dreary, mischievous, angry, brooding, romantic)
What color could it be?
yellow, bright red ...)
Does autumn have a smell? (smells like foliage, smoke, mushrooms, rain).
Can you hear autumn? (rustle of leaves, noise of rain, cry of birds flying away, noise of wind ...)
What has changed in the life of plants in the fall? (trees shed their leaves, vegetables and fruits are ripe,
What has changed in the life of animals? (the bear and the hedgehog are preparing for hibernation;
music and songs ...)
(cold snap,
wind, rains, fog, drizzle, mud, slush, bad weather, leaf fall ...)
Good-bad game
Once the wind flew over the park. Sees a lot of people walking in the park. The wind decided to joke.
He took and made all the trees golden and the leaves on the ground were also golden.
Do you think this is good? So what's so good about it? (you can become rich, make gold jewelry,
give others gold)
And what is wrong with the trees turning golden? (do not clean the air, there is no coolness, do not bloom,
birds and animals feel bad ...)
IQR -. Let gold be only in stores.
■ Game-diagnostics:
"Who would you like to be in the fall?"
And now you have the opportunity to become wizards. You can find yourself in the kingdom of Autumn.
And become any object of this kingdom. You will be able to tell on behalf of this object:
Who you are? (or what are you?) -What are you? -What do you like to do? -What are you dreaming about?
(children's stories)
The tale of the cloud:
You had very interesting stories. I also want to tell you mine.
Hello! I am a small and fluffy cloud. I live high in the sky. I have
wonderful breeze friend. Together with him we often play and fly above the ground,
because I am very curious, I want to see everything.
I really have one peculiarity. If I see something sad, I cry, and then above the ground
a dull and long rain is falling. And when I have a lot of fun, I cry again, with joy. And then above the ground
raindrops sparkle and sparkle, and in them, as in a mirror, everything that I can see is reflected.
And I dream that you children would paint autumn in a drop of rain so that everyone could see
what is she. I know you can do it!
Fizminutka
Are you tired? Well then, everyone stood up together, stamped their feet, patted their hands,
They bent down, straightened up, And whirled in place. We close our eyes tightly
We count up to five together.
We open, blink And continue to work!
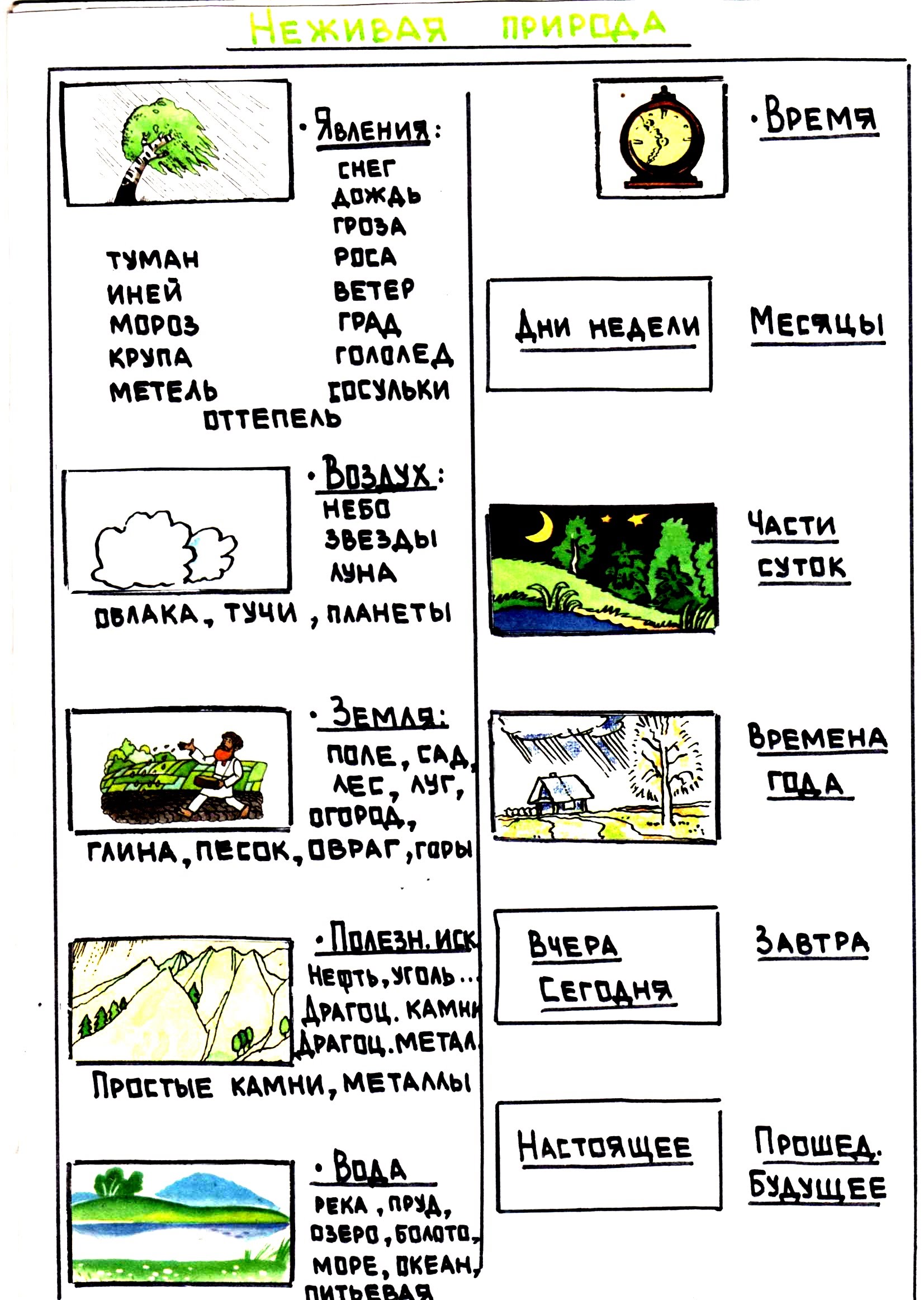
TRIZ and RTV methods
|
Methods |
Child's age |
||||
|
3-4 years |
4-5 years old |
5-6 years old |
6-7 years old |
||
|
Simulation tools |
|||||
|
Focal Object Method |
|||||
|
Directory method |
|||||
|
Morphological analysis |
|||||
|
Synectic method: ■ Empathy ■ Direct analogy ■ Symbolic analogy ■ Fantastic analogy |
|||||
|
Typical methods of fantasizing |
|||||
|
System Operator |
|||||
|
Brainstorm |
|||||
|
Little people technique |
|||||


"WHAT IS AUTUMN?"
Goal:Consolidate knowledge of the season.
Replenish the children's dictionary with adjectives, nouns.
Strengthen children's knowledge of basic emotions (joy, sadness).
Learn to think analytically.
Methodological techniques:
The game "one - two - three - freeze the mood!"
The game "Yes and no"
Finger gymnastics "Rain"
The game "Good - bad"
Game "Who would you like to be in the fall?"
The tale of the cloud.
Children's drawings - what an autumn in a drop of rain or in a maple leaf.
Material:
Picture - illustration (What is autumn?)
Picture - illustration - of emotions (cloud)
Course of the lesson:
I meet children.
I ask the children about their mood by showing pictures:
Who's in the mood like this? (Sun)
Who has a mood similar to this picture? (the sun is half covered with a cloud)?
Who's in the mood like this (cloud, it's raining)?
If someone is in a bad mood, I use the poems of the Laughing Tron "Fables":
Zebras buzzed in the bushes
In the July heat
Bloomed, swaying on their tails
Live kangaroos.
Grandpa flew through the window
And the sparrow carried grain
Rode a cactus on the window
Leading the old woman on a belt
And the dog at this time
I washed Vanya on the window.
■ Game "Yes and No"
What we are going to talk about today will become known if you guess what I have guessed.
Ask questions.
■ "Magic screen"
You guessed right. I guess the word AUTUMN. Imagine meeting us
alien and says: "I don't understand what the fall system means." How are we going to explain?
Let's turn on the "Magic Screen"
-What is Autumn? -(season)
-Autumn, what is it? (golden, deciduous, rustling, early, late, sad, wet,
rainy, festive, colorful, dirty, slushy, cloudy, dank, gray,
light, warm, cold, windy, foggy, rainy, dry, etc.)
- What are the signs of autumn? (Leaf fall, birds flying away, cleaning
harvest, preparing animals for winter, mushrooms, rains,)
-What will autumn be remembered for?
People - beauty, inspiration, new clothes are demonstrated, kids are invited to study in schools,
gives the harvest ...
For birds travel to distant lands
Beasts - warm fur coats, supplies for the winter, vacation, rest
And now, let's bring everything we know about autumn into the system, put it on the shelves:
What kind of character can autumn have? (funny, dreary, mischievous, angry, brooding, romantic)
What color could it be? (multicolored, gold, green, light brown,
yellow, bright red ...)
Does autumn have a smell? (smells like foliage, smoke, mushrooms, rain).
Can you hear autumn? (rustle of leaves, noise of rain, cry of birds flying away, noise of wind ...)
What has changed in the life of plants in the fall? (trees shed their leaves, vegetables and fruits are ripe,
the grass dries up, flowers wither, rowan trees turn red)
What has changed in the life of animals? (the bear and the hedgehog are preparing for hibernation;
the squirrel and the hare changed the color of their fur coats, the hare got rabbits, ...)
What has changed in people's lives? (harvest, change clothes, feel sad and compose
music and songs ...)
How does inanimate nature manifest itself? (cold snap,
wind, rains, fog, drizzle, mud, slush, bad weather, leaf fall ...)
Finger gymnastics:
Children in a circle stand on outstretched arms to each other with their backs
The rain runs across the roof
Boom Boom Boom. (fingers)
On cheerful, ringing roofs
Boom, boom, boom (by the edge of the hand)
At home, sit at home
Boom, boom, boom (by fists)
Do not go anywhere
Boom, boom, boom (palm)
Good-bad game
Once the wind flew over the park. Sees a lot of people walking in the park. The wind decided to joke.
He took and made all the trees golden and the leaves on the ground were also golden.
Do you think this is good? So what's so good about it? (you can become rich, make gold jewelry,
give others gold)
And what is wrong with the trees turning golden? (do not clean the air, there is no coolness, do not bloom,
birds and animals feel bad ...)
IQR -. Let gold be only in stores.
Game diagnostics:
"Who would you like to be in the fall?"
And now you have the opportunity to become wizards. You can find yourself in the kingdom of Autumn.
And become any object of this kingdom. You will be able to tell on behalf of this object:
Who you are? (or what are you?) -What are you? -What do you like to do? -What are you dreaming about?
(children's stories)
The tale of the cloud:
You had very interesting stories. I also want to tell you mine.
Hello! I am a small and fluffy cloud. I live high in the sky. I have
wonderful breeze friend. Together with him we often play and fly above the ground,
because I am very curious, I want to see everything.
I really have one peculiarity. If I see something sad, I cry, and then above the ground
a dull and long rain is falling. And when I have a lot of fun, I cry again, with joy. And then above the ground
raindrops sparkle and sparkle, and in them, as in a mirror, everything that I can see is reflected.
And I dream that you children would paint autumn in a drop of rain so that everyone could see
what is she. I know you can do it!
Fizminutka
Are you tired? Well then, everyone stood up together, stamped their feet, patted their hands,
They bent down, straightened up, And whirled in place. We close our eyes tightly
We count up to five together.
We open, blink And continue to work!1. The value of riddles in the development of children's speech.
2. Requirements for the selection of riddles for children of different age groups.
3. Algorithm for guessing riddles.
4. Methodology for teaching children to compose riddles based on the description and comparison of objects.
1. Riddle is one of the most ancient forms of folklore. Previously, people used riddles as allegorical speech to hide any important information, protect your home, family. Ancient hunters, cattle breeders, farmers called tools of labor, animals, hunting places with allegorical phrases, riddles. Often a riddle was also a way to test a person's ingenuity, resourcefulness, and wisdom. This was reflected in many rituals (initiation of a young man into warriors, ransom of the bride by the groom) and in folklore. For example, in the fairy tale "The Frog Princess" Ivan has to guess the riddle "Who is the most precious in the world?" Many peoples held evenings of riddles, usually in the fall, at the end of agricultural work. The elders made riddles to the younger ones, grouping them according to themes: about a person, about animals, about vegetables and fruits.
V.P. Anikin calls a riddle "an intricate question, presented in the form of an intricate, brief, usually rhythmically organized description of an object or phenomenon." Many riddles contain a fairy tale plot, fairy metaphors and comparisons, this brings them closer to fairy tales. For example, "Ivashka stands in a red shirt, whoever passes, bows to him." The main signs of the riddle can be distinguished:
In form, the riddle is often in the form of a question or a short laconic poem;
Rhythm is inherent in the riddle, rhyme is often used.
Considering these signs, Yu.G. Illarionova gives the following definition of the riddle. The riddle is short description object or phenomenon, often in a poetic form, containing an intricate task in the form of a direct or hidden question. Many researchers of folklore note that riddles have an impact on the mental, aesthetic and moral education of children.
Many teachers noted the wide pedagogical potential of the puzzle. K. D. Ushinsky called them a useful exercise for the mind. Riddles contribute to the development of memory, imagination, figurative thinking, speed of mental reactions. Riddles are used as a means of forming love for folk art, the native language.
2. You can use riddles in working with children from early preschool age. It is important to choose the right texts in accordance with the age capabilities of the children, so that the children learn to consciously guess the riddle, and not memorize the answer or select by listing all the appropriate options.
Children of younger preschool age are available riddles-descriptions, in which the real signs of objects or phenomena are called. Riddles for toddlers should be short, the child will not remember a large number of signs and will not be able to compare. Among all the signs of the object referred to in the riddle, the most important, essential, and distinctive ones should be named: appearance, onomatopoeia of animals.
Long, sweet
Orange smooth
Bunnies eat
And they tell us.
3. In the process of learning to guess riddles, it is important to teach children to analyze the surrounding reality, to see general and specific signs in objects and phenomena, to notice bright, individual characteristics processes and phenomena. Children should learn to solve the riddle, and not choose the correct answer by listing possible or random options. It is important to give children different riddles, even about the same objects, so that children do not remember the correct answer, but learn to guess consciously.
The algorithm (a sequence of actions necessary to achieve a certain result) for guessing riddles was developed by Y. G. Illarionova, taking into account the basic mental actions that need to be performed by the child.
1) analysis of the condition of the riddle: it is necessary to highlight all the signs that are listed in the riddle - what to look for, where, what object it is, etc.
2) synthesis, combination of features, their reduction to one or more objects (phenomena);
3) generalization of all signs and the naming of appropriate answer options (hypotheses);
4) checking the expected answers by substituting them to the condition of the riddle, choosing the correct answer.
Let's analyze the guessing algorithm using the example of the riddle "Under the pines, under the trees, a bag of needles is running."
1) we analyze the signs of the object: it is under the pines and trees, runs, looks like a bag, there are needles;
2) we connect the signs: under the pines and Christmas trees, it means in the forest, it looks like a bag, that is, of a rounded shape, has needles;
3) children can give expected answers, focusing on any one sign: squirrel (under pines, under trees), hedgehog;
4) we substitute the word "squirrel" in the riddle, we see that it does not fit by all the signs, we conclude that this is a hedgehog.
Riddles can be used on literary quizzes, holidays and entertainment such as: "Evenings of Riddles", "Riddles of the Wise Owl", etc. You can start any activity with a figurative riddle (acquaintance with nature, visual activity, music lesson etc.) to draw the attention of children to the topic of the lesson, to the objects or phenomena under consideration.
4. Teaching children to compose riddles begins when children have already mastered the genre features of its content and form. In addition, children should have a sufficient stock of knowledge about objects and phenomena of the world around them in order to display them in riddles. In the process of teaching children how to compose riddles, the dictionary of preschoolers is being improved (figurative words: comparisons, personifications, metaphors), the structure of sentences (common, complex), the skills of coherent speech (story-description, reasoning) are developing. Therefore, it is advisable to teach how to compose riddles at an older preschool age.
As a set of activities, you can offer children a trip to the "Land of Riddles". In this country, mysterious inhabitants, they hide and appear only when they are solved. There are many different cities in the land of mysteries. For each lesson, you can take topics from a separate city. The first city of the simplest riddles. Purpose: to teach children to make simple riddles, focusing on the main signs: color, shape, size, material. The streets of the city will tell children how to make a riddle. For example, Form Street, in one house all round objects live (children name all possible objects), in another - cylindrical ones, etc. But there are items that can be different shapes (cookies, a leaf of a tree). Gradually, the inhabitants of the streets are considered with the children: Color (rainbow colors, shades for comparison), Size (here you need to compare objects in opposite parameters thick - thin, high - low, wide - narrow, etc.), Material (we fix the concepts of solid, liquid, gaseous). After exploring all the streets of the city, children are invited to go to the central square, where all the streets intersect and make riddles about objects, based on the main signs. At the same time, it is important to show children the accuracy in determining all the signs for the riddle, otherwise there may be several options for the correct answers. For example, in the riddle "winter and summer - one color" the answer can be a tree, a pencil, a notebook, a crocodile and any other object.
The next city in the land of mysteries is the city of the Five Senses. On the street, Sight teaches children to name all the signs of an object that can be seen. You can offer to make up the longest riddle about the subject, listing the maximum number of signs seen. On the street Rumor teach children to guess objects and phenomena by sound and to guess sounding riddles. Osyazanie Street is inhabited by objects that need to be guessed by touch and riddles should be created based on their signs (smooth, soft, warm, sharp, etc.). Similarly, we invite children to get to know the inhabitants of the streets Olfactory, Vkus. At the end of the lesson, we suggest making riddles about objects and phenomena of the city of Five Senses.
Then the children are offered to travel around the city of Mysterious Parts, in which objects are hidden so that only some part of the house looks out or leaves traces, it is necessary to find the inhabitants of the city in parts. For example, Unfinished Pictures Street. Children are offered a fragment of the drawing, which must be completed in order to get an object. This is how a riddle in pictures turns out. The verbal riddle teaches children to compose Strange objects on the street. To do this, first, parts of the object are distinguished, then each part is compared with something (what it looks like), then a riddle is made based on the comparison of the parts. For example, a chair consists of a seat, a backrest, and four legs. These parts are like boards and sticks. A riddle is composed: two boards, four sticks.
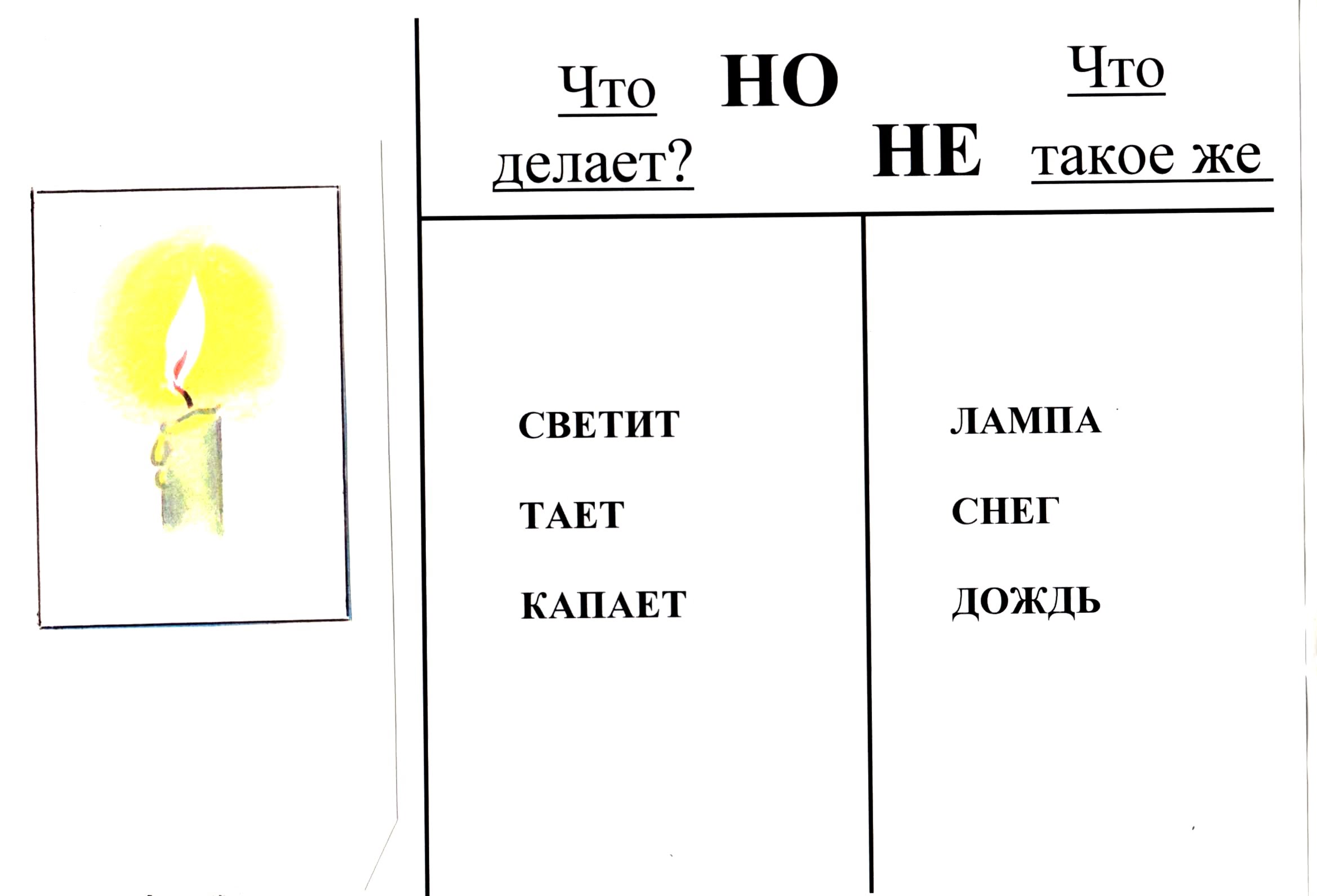
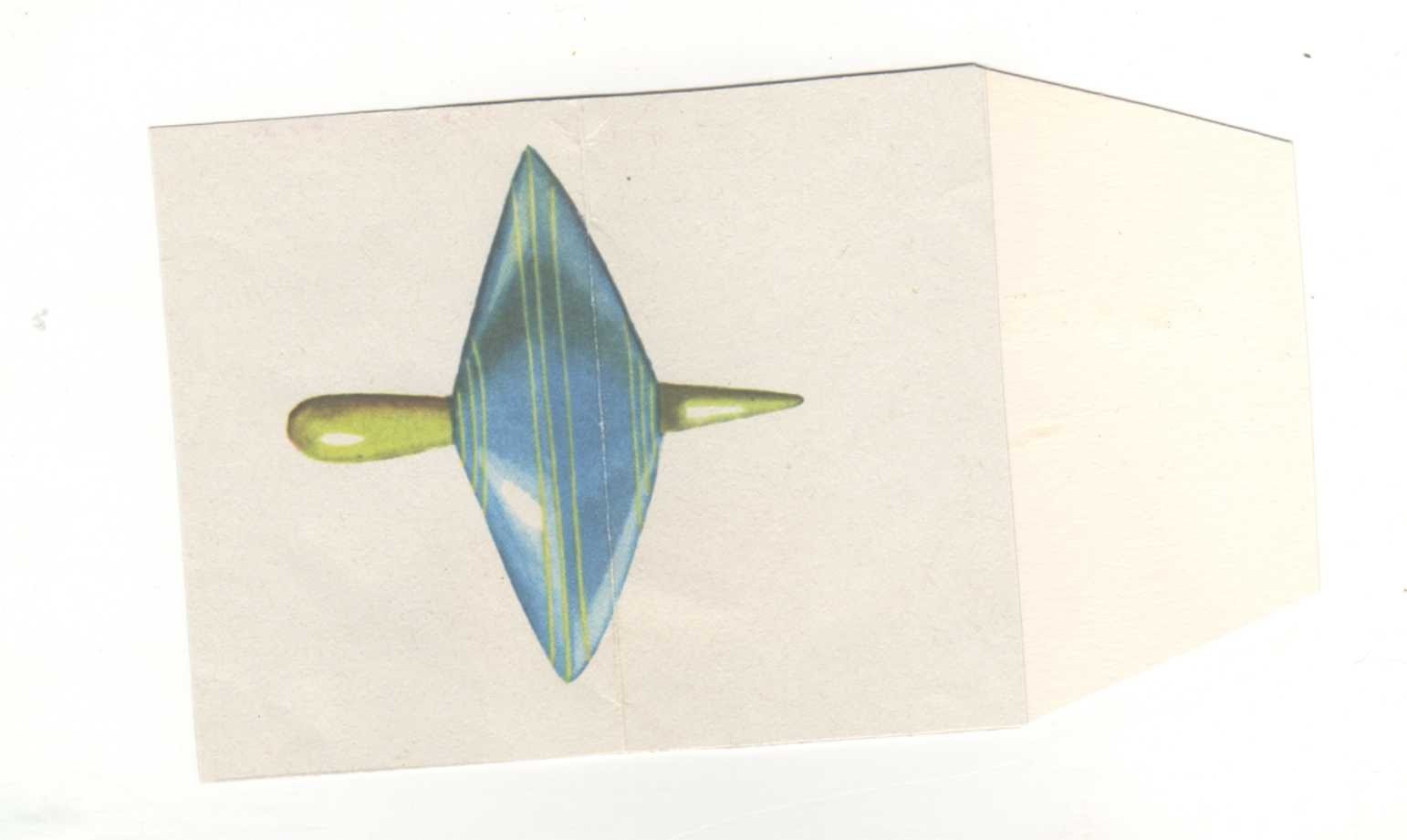
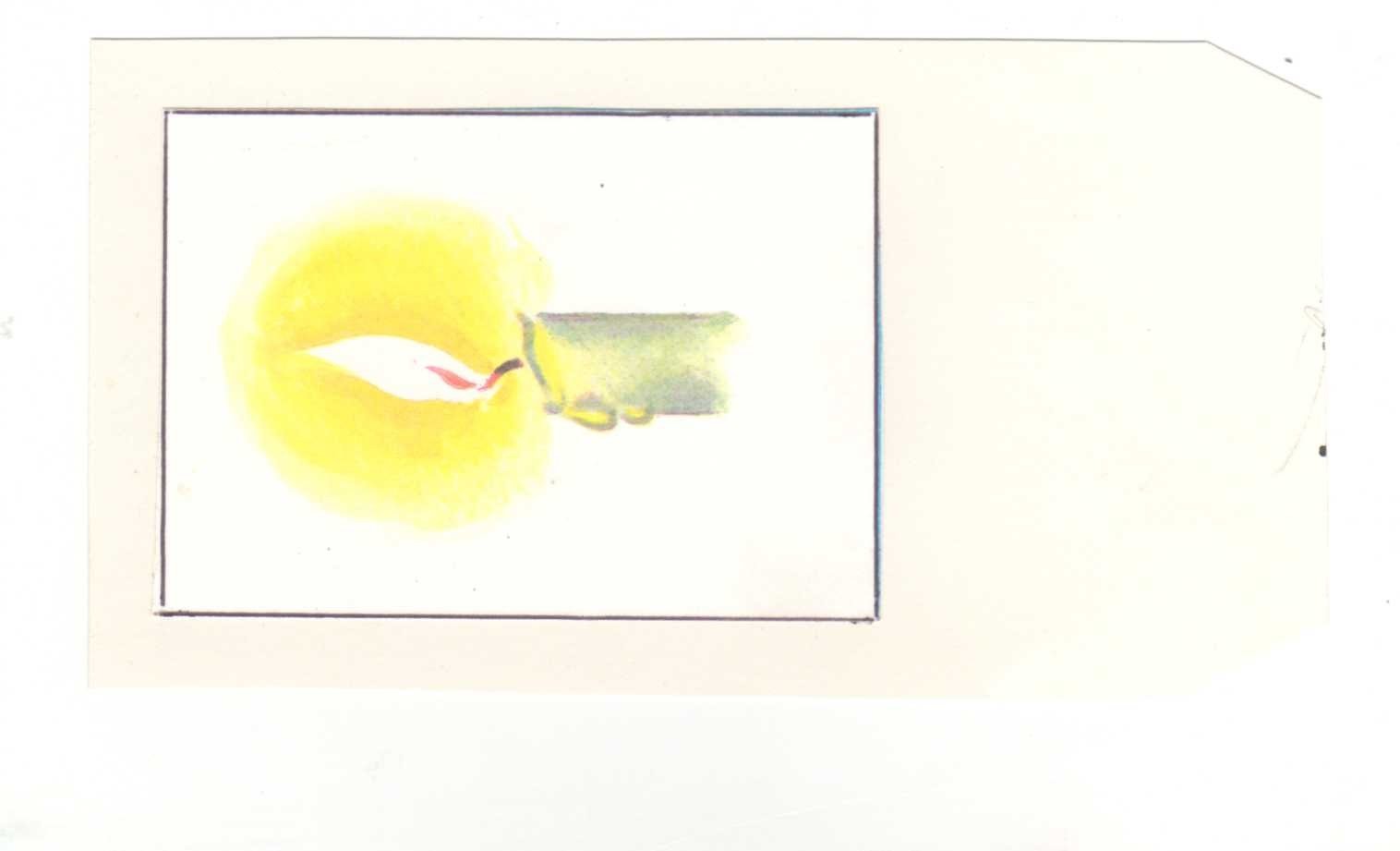
In the city of Similarities and Differences, you can teach children to make comparison puzzles based on the development of associative thinking. To do this, the children are given support questions (it can be in the form of a diagram): what does it look like? What is the difference? For example, let's make a riddle about the whirligig. What does it look like - like a ballerina, like an umbrella, like a mushroom; what is the difference - not alive. Very small, not edible. It turns out a riddle: like a ballerina, but not alive, like an umbrella, but much less like a mushroom, but not edible. Another version of the pivotal questions: what does it do? What is similar to him / her? For example, a riddle about a candle: the lamp is shining but not, it is melting, but not snow, it is dripping, but not rain.
Thus, the cycle of classes "Land of Riddles" is aimed at teaching children to compose riddles of different types using a variety of thinking techniques (comparison, generalization, juxtaposition, analysis) and in various verbal forms (sentence, question-answer form, story).
Various methods are used to organize teaching children how to compose riddles. At the first stages, the teacher together with the children makes up the riddle for one child (the guesser) who first goes out the door. A riddle is made about an object in the group room, then the object is hidden and the guesser is called. In another version, the child-guesser does not leave the room, but simply turns away. The teacher shows the children an object about which a riddle needs to be made, and each child makes up his own riddle about the same object.
A peculiar way of teaching children how to compose riddles is the "Yes-no" game, which is offered according to the TRIZ method. The teacher explains to the children that he thought about the object, and to guess it, children can ask questions, but they can only answer "yes" or "no." First, preschoolers, as a rule, ask questions in the form of assumptions, guesses: “Is this a notebook? Is that a cup? " or questions that cannot be answered yes-no: “What form? What colour?". Gradually, children learn to ask the right questions, such as: “Is it round? Is it hard? " etc.
A diagram or model can be a visual aid for teaching children to compose riddles. She gives the children an outline of the riddle, supporting signs that need to be reflected in the riddle.
Literature
1. Illarionova, Yu.G. Teach children to guess riddles / Yu.G. Illarionov. - M .: Education, 1982 .-- 180 p.
2. Kislova, T.R. On the way to the alphabet / T.R. Kislov. - M .: Balass, 1999 .-- 144 p.
3. Literature and fantasy: a book for kindergarten teachers and parents / comp. L.E. Streltsov. - M .: Education, 1992 .-- 256 p.
Composing riddles is an interesting creative process that solves many correctional problems and is suitable for preschoolers and junior schoolchildren... The algorithm for composing riddles is not complicated. The result is the enrichment of vocabulary, the development of figurative characteristics of speech, the ability to compare, analyze, and compose complex sentences.
Learning to compose riddles - the development of imagery of speech
Teaching children a detailed and expressive speech is one of the tasks remedial education and education. The expressiveness of speech is understood not only the emotional coloring of the sound, achieved by strength, the timbre of the voice, but also the figurativeness of the word, the accuracy of its use. In order to motivate a child to use figurative characteristics in speech, it is necessary to interest him.
Play and creative work are the best helpers, since the child will enjoy this activity, and the teacher will get the result. One of the forms of children's artistic creativity of children is the compilation of riddles. In this process, all the child's mental operations develop, and he gets joy from speech creativity.
Traditionally, working with riddles is based on guessing them. Observations of children show that guessing occurs in the smartest children or by enumerating options. Moreover, most of the children in the group are passive observers. The adult acts as an expert. The correct answer to a specific riddle is very quickly remembered by other children. If the teacher asks the same riddle after a while, then most of the children simply remember the answer.
Riddle Learning Technology Begins with making comparisons... Exercises are carried out not only in speech development classes, but also in their free time.
For example: an object is called, its characteristic is designated, the value of this characteristic is determined, this value is compared with the value of a characteristic in another object.
The chick (object) is yellow (characteristic by color). The same yellow as the sun (comparison with the value of the attribute in another object).
For convenience, you can fill in the plates in the form of sketches, letter designations, diagrams.
Another example:
"The ball is round in shape, as round as an apple."
Further, children are offered several objects with a given value of the attribute (round sun, wheel, plate, etc.). Repetitions of such long combinations allow children to understand that a feature is a more general concept than the meaning of a given feature alone.
We select signs according to the interests of children and their relevance for age (shape, color, composition, taste, sound, temperature, etc.).
For example:
Samovar - (object) round (feature by shape), shiny (feature by color), hissing or bubbling - (feature by action).
Compare with other objects. Children are given figurative characteristics according to given characteristics.
What happens the same?
Shiny - like an iron coin, a jewel, snow in the sun, etc.
Hissing, seething - like a volcano, a snake, a storm at sea, a waterfall, etc.
Round - like a watermelon, sun, wheel, etc.
Characteristics of signs in co-creation are clarified using leading questions.
An iron coin shines more when polished. A volcano hiss or rages when it "wakes up", a waterfall when it is in the mountains and an echo carries its sound, etc.
We connect the compared signs by inserting the conjunctions “How” or “But, not”, “A, not” for the link between the two parts.
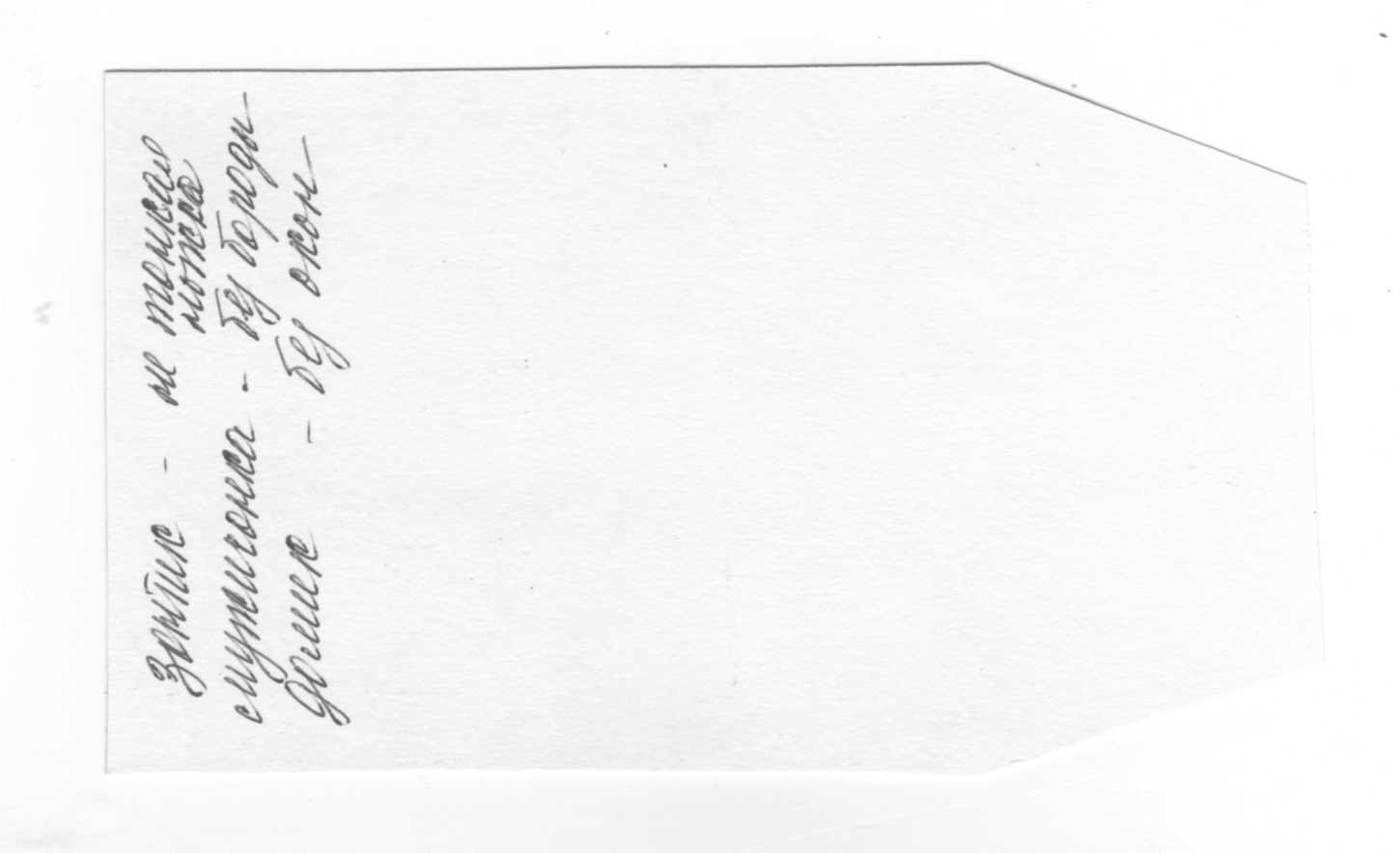
The final riddle about the samovar may sound like this:
“Shiny as a polished coin; hissing like an awakened volcano, round, but not a watermelon. "
Another form of making riddles.
The peculiarity of mastering this technology is that the child compares two objects, finds common and different between them. What does it look like? What is the difference?
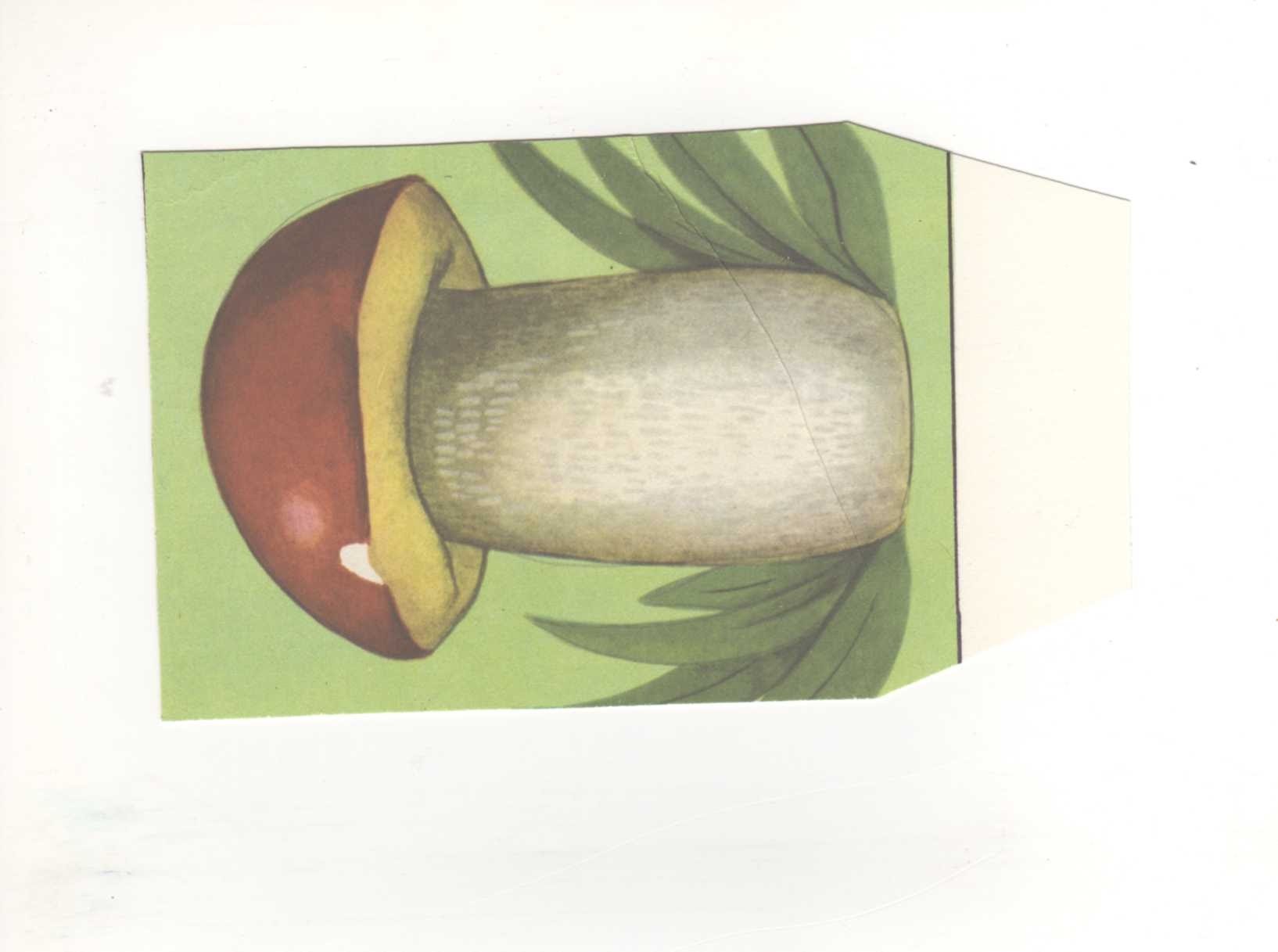
We compose a riddle about a mushroom:
What does a mushroom look like? - The gnome.
And how is it different from a gnome? - The mushroom has no beard.
What else does it look like? - To the house.
How is it different from a house? The mushroom has no windows.
What else does it look like? - On an umbrella.
How is it different from an umbrella? The umbrella has a thin handle.
The approximate text of the resulting puzzle:
“Looks like a gnome, but without a beard;
looks like a house, but without windows;
like an umbrella, but on a thick leg. "

The process of making up riddles is very exciting for children, the entire children's team participates in the creative process, and members of the child's family are often involved. The result is the enrichment of vocabulary, the development of figurative characteristics of the word, the ability to compare, analyze, highlight the main and secondary features, and make complex sentences.
I wish you good luck and creative success!
Ilyicheva S.V.,
teacher speech therapist






