The development of fine motor skills of hands in preschool children
The development of fine motor skills of the hands affects the intelligence of the baby, his memory, attention and thinking. Therefore, every mother strives to start exercising with the baby as early as possible. Many parents think that only specialists in development centers can conduct such classes. Of course, you can take the baby to classes in groups, but it’s easy to study at home, having developed a system and lesson plan that will be of interest to the child at an early and preschool age and are aimed at developing physical activity.
What is fine motor skills
Fine motor skills are coordinated actions of the hands and fingers that are performed in conjunction with the nervous, bone, visual and muscular systems. In other words, this is the ability to manipulate small objects, in which only the small muscles of the body are involved.
Do not confuse the concepts of fine and gross motor skills, sensory. They are interconnected, develop in the child's body in parallel, but differ from each other:
- gross motor skills- these are the movements of the large muscles of the body, the basis of the physical development of the child: walking, jumping, turning the body, running and other active actions;
- sensorics- this is the perception of the surrounding world through sensations (tactile, visual, gustatory, auditory), thanks to which the child develops skills and preferences, he has an idea about various objects, phenomena and actions.
Scientists have proven that the development of the hand is closely related to the development of speech and thinking of the child, therefore, fine motor skills must be practiced from the very birth of the baby.
The mind of a child is at his fingertips.
V. A. Sukhomlinsky, teacher
This is not just a phrase, but a scientifically proven fact. It is at the fingertips that a huge number of nerve endings are located, through which impulses are fed to the brain, where information is processed, supplemented by data from various receptors: visual, auditory, olfactory. And only then the child perceives the whole picture, object or action. Teachers, together with famous scientists, have proved that by developing fine motor skills, the baby learns to speak, write, and think logically faster. Therefore, it is recommended to deal with it from an early age.
Fine motor skills for the development of speech and other skills
- The ability to control hands is the basis for mastering the skills that a child needs in everyday life.
- Fine motor skills are needed for the development of the most important mental processes: memory, perception of the world around us, thinking, logic, attention and speech.
- The level of development of fine motor skills is one of the main indicators of a child's readiness for schooling.
Fine motor skills begin to develop from birth: first, the baby examines his hands, then learns to squeeze and unclench his fingers, control them in order to grab a toy or a nearby object. As he grows older, he understands how to hold a brush or pencil correctly, learns to draw, and closer to 6-7 years old he tries to write. Of course, the child will be able to study some points on his own, because all children are inquisitive and show interest in unfamiliar objects. However, scientists and educators insist that parents engage with them through special toys and tasks, perform exercises that help improve fine motor skills of the hands.
The development of intellectual and thought processes begins with the development of the movement of the arms, fingers and hands - this is a fact proven by scientists. Therefore, in order for the child's brain to develop, it is necessary to train his hands. In addition, the rest of life will require coordinated movements necessary for drawing, writing and performing many other activities.
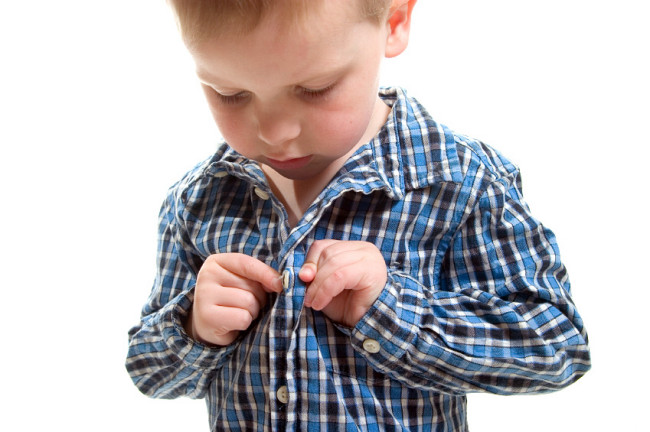

Improving fine motor skills develops the child's brain and prepares it for everyday activities.
The lack of development of fine motor skills can lead to such consequences for the baby:
- lack of interest in drawing, modeling and other activities;
- difficulties with adapting to the educational process at school: the child perceives new material worse, does not read well, so the pace of learning seems to him too fast and difficult;
- insufficient development of creative abilities, thinking and attention;
- inability to draw a straight line evenly, to remember and write numbers or letters correctly;
- if you ask him to draw a picture, in most cases he cannot correctly place objects on the sheet space, he lacks imagination, there is no variety of colors and a clear plot;
- such children begin to speak later, many have speech defects that are difficult to correct even during classes with specialists.
What affects fine motor skills - video
Ways to develop fine motor skills relevant for children of different ages
In order for the child to develop harmoniously, it is imperative to deal with him from birth, I improve fine motor skills of the hands. Today, there are many authoring techniques that develop toys and activities that are carried out in a playful way and help to learn new information through tactile sensations. Depending on the age and preferences of the baby, you can offer him:
- massage of the hands and fingers;
- games with cereals, beads, buttons, pebbles;
- finger gymnastics;
- graphic exercises, hatching;
- modeling from plasticine;
- collection of constructors and mosaics;
- drawing and coloring;
- cutting with scissors;
- paper work, origami folding, appliqué;
- rope games, lacing.
The importance of developing fine motor skills from an early age
The development of fine motor skills in children up to a year
Mom and dad can help their baby develop from birth. For children of the first year of life, such activities are suitable:
- massage of arms and legs;
- Finger paint.
Hand massage and massagers
Children up to a year are very useful massage of hands, fingers and legs. Parents can do it at any time of the day with no time limits. The main rule: the baby should like the exercises. If the baby feels discomfort, begins to act up and remove the arms or legs, it is better to postpone classes for a while.
- Gently sip the baby's fingers: the exercise should be slow and gentle, no sudden movements. Then each finger needs to be stroked. These actions can be carried out with children from two months and older.
- Make circular movements of the fingers in one direction, then in the other. The exercise is done with each finger separately.
- From 5 months, you can easily massage each finger of the child, then the palm and smoothly move to the hand. In addition to the development of fine motor skills, there is a general strengthening of the muscles of the upper limbs of the baby.
- At 8 months, it's time to connect more active exercises: tap your finger on the baby's palm, lightly press, bend and unbend your fingers. These actions can be done simultaneously with the pronunciation of the rhymes "Forty-white-sided", "There was a horned goat." The same is repeated with the legs of the crumbs.
It is very useful to use special simulators or massagers. They come in the form of a soft ball with an uneven surface, a roller or a ring that is worn on the finger. And you can use improvised materials: roll a walnut in your hands, sew bags from natural fabrics and pour different cereals into them. Give them periodically to the child in the hands - this is an excellent massage and stimulation of nerve endings.
You can perform exercises with a massager in different ways by rolling it:
- on the table;
- between palms;
- from fingertips to elbow;
- on the back of the hand.
The main thing to remember is that you need to deal with both upper limbs in turn. Some parents mistakenly believe that if they only pay attention to the right, their child will not be left-handed. This is an incorrect statement. For the harmonious development of the crumbs, two hands should be developed equally.
Exercise machines and massagers for the development of fine motor skills of hands - photo gallery
A walnut can be used to massage the hands. A ball-shaped hand massager. This finger trainer can be used when the child has learned to sit. Massagers can be of different types and shapes
Children love to draw. You should not think that it is impossible to accustom them to creativity before 1–1.5 years, when they can take a brush or pencil from their hands. Today, finger paints made from natural ingredients and safe even if swallowed are very popular. Hand drawing is an ideal option for developing fine motor skills in infants. The child not only feels all movements with his fingers, but also perceives the colors of paints, learns to recognize them. In this case, sensory thinking also develops.
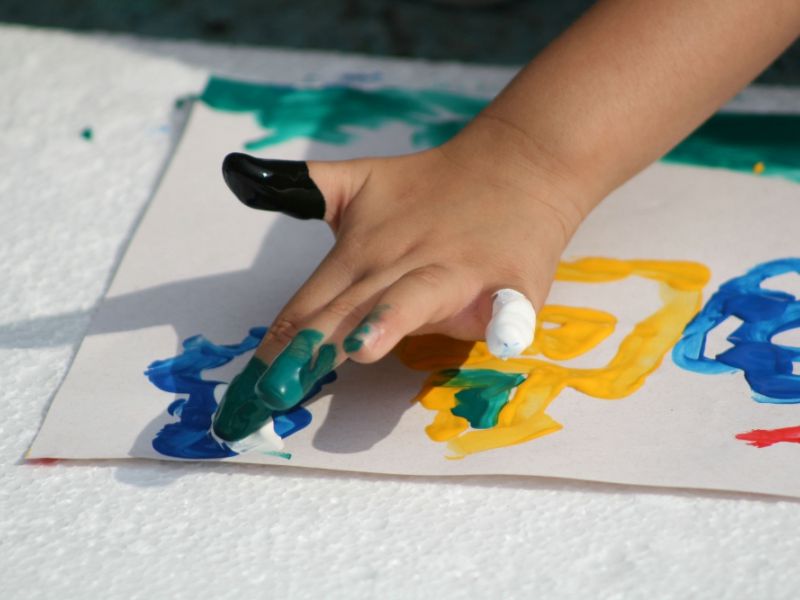

Finger painting promotes fine motor skills
We draw with finger paints - video
Topical methods for the development of motor skills in children from 1 to 2 years
At one year old, the child sits confidently, and perhaps already walks. Now he is more interested in educational toys, books and other objects around him. At this age, sensory perception is important for him, so you can connect the following activities:
- finger games, hand and hand massage;
- finger paints, gouache painting with a brush (children begin to paint with watercolors from the age of three);
- modeling: it is still difficult for small children to sculpt from plasticine, so the best option is dough;
- sorters and pyramids, soft puzzles - all this remarkably develops fine motor skills;
- bodyboards, games with lids - here the interest of the child and the scope of the imagination of the parents are important.
Toys and activities for young children - photo gallery
Modeling dough is softer than plasticine, so it is more suitable for children aged 1-2 years. With the help of a pyramid, you can work out coordination of movements. The sorter develops fine motor skills perfectly. With plastic covers, you can come up with a wide variety of games.
Educational games for children 1–2 years old - video
Tasks for kids 2-3 years old
At 2–3 years old, a child learns and masters skills very quickly. Children can already explain what they want to do, what they are interested in at the moment. At this age, the development of fine motor skills contributes primarily to the development of speech. The kid pronounces more and more new words every day, learns to perceive and copy sounds, begins to speak in whole sentences, so it is extremely important to deal with him during this period. Classes do not radically differ from those that the baby was fond of in 1-2 years. But they can be complicated and new ones added:
- stringing: invite the child to collect beautiful beads for mom, or distribute shapes of the same color on a string;
- lacing games are very popular with children of this age;
- building a tower: the baby learns to coordinate movements, distributes the cubes evenly so that they do not fall;
- modeling plasticine crafts: this modeling material is more complex than dough, and the child needs to make more effort to work with it;
- classes with cereals: invite the baby to choose one cereal from the container and leave another in it;
- games with water: a child from a container with a spoon or net catches various objects.
Games with cereals, water, plasticine, cubes and other activities for children 2–3 years old - photo gallery
Building with cubes develops coordination of movements The kid is interested in correctly lacing up a model of a boot or fastening buttons on a doll’s coat Stringing develops logic and patience Modeling from plasticine is a more difficult task than modeling from dough Water games captivate children of different ages
Games for the development of fine motor skills for children 2-3 years old - video
Development of fine motor skills with children of kindergarten age (4-5 years)
At 4-5 years old, the child prefers to perform many tasks only on his own. He is interested in how the development board works, why the wheels are spinning and much more. Curiosity and craving for new knowledge only contribute to the harmonious development of the individual. The kid already has a good command of the brush and pencil, so the main tasks are aimed at preparing the hand for writing. Many parents think it's early for this age. Do not be confused, at 4 years old no one forces the baby to write whole words or letters if he does not show interest. To the exercises and activities described above, it is worth connecting new ones:
- sand games, or sand therapy, as psychologists often call these exercises: let the child run his fingers along the sand, drawing pictures or objects;
- working with scissors: first, the child learns to cut out even stripes, then geometric shapes;
- application: the kid will learn how to create compositions on a paper plane, work with glue and a napkin;
- drawing, coloring small details, shading - these skills prepare the baby's hand for writing.
Drawing, applique, hatching and other activities for a child 4–5 years old - photo gallery
At the age of 4-5 years, get special children's scissors with round edges. Applications will teach the child to be neat. Sand games are soothing to the child and are very useful for developing motor skills.
Exercises for the development of fine motor skills in children 4-5 years old
Fine motor skills for preschoolers 6-7 years old
At 6–7 years old, the child goes to school, so he must be mentally and intellectually prepared for a new stage in his life. Lessons provide discipline, quick capture and understanding of new material, the ability to memorize and repeat tasks well. At this age, all exercises are aimed at developing speech and writing, reading skills. That is why parents should pay special attention to improving fine motor skills. Insufficient development in this area leads in most cases to learning problems: the child cannot write or does it very slowly, his creative skills, imagination and thinking are poorly developed.
The following activities will help prepare your child for school:
- physical exercises: finger gymnastics, hand massagers, finger games, finger theater;
- mosaic: small details that need to be correctly assembled according to the instructions are a great way to develop little fingers;
- constructor: at this age, the large cubes familiar to the baby are replaced with smaller parts, with the help of which not only fine motor skills develop, but also imagination;
- copybook: you can circle not only letters or numbers, but also various shapes that may interest the child.
Motor skills classes for preschoolers - photo gallery
Collecting a mosaic according to the model will help improve the fine motor skills of the preschooler's hands Constructors from small parts are very captivating for preschoolers Finger theater helps strengthen the muscles of the hand and fingers
On the importance of developing fine motor skills in preschool children - video
How to develop fine motor skills in left-handed children and toddlers and visual impairment
Studies conducted by scientists have shown that many left-handed children have problems with the development of speech, writing and reading, so it is very important to do exercises with them to develop fine motor skills. Parents of a child who actively uses his left hand, and not his right, during classes, you need to take into account some of the nuances.
- The light source during the exercise should be on the right side.
- Left-handed children do not visually perceive the space that is to their left, so all objects must be placed to the right.
- Classes should be held with breaks. For a left-handed child, this is important, he needs more rest, so try to plan your exercises so that you have a break every 20 minutes.
- While writing, the child often pushes the left shoulder forward - this is the norm for children who hold the pen in their left hand, you should not specifically change his position.
- The main thing is not to focus on the fact that the baby is somehow different from other children. He should feel the support of parents and teachers.

Children with a dominant left hand often have difficulty mastering speech, reading and writing, so the development of fine motor skills is especially necessary for them.
Today, preschoolers are often diagnosed with visual problems. There can be many reasons why a child does not see well, but such children should develop on a par with their peers. Very often they cannot perform actions with their hands, they do not understand what to do. That is why they need to develop fine motor skills from an early age. However, it is better to start exercises from the age of two: the baby will already understand what you want from him, and will not be afraid.
- Mandatory massage and finger gymnastics: tapping, stroking, playing with massagers - all this should be in the training program.
- All classes are aimed at learning information through tactile sensations, so the child is offered objects from different materials, different shapes, which he touches, remembers and tries to describe his feelings.
- Visually impaired children learn to read in relief-dot cipher, so parents prepare the baby for the perception and understanding of this form: you can use foil on which lines, waves, dots and other shapes are drawn. He circles the raised drawings with his fingers, trying to understand and remember them.
- At an older age, a child can draw figures or drawings himself, and then read them by touch, as it were.
Do not think that if a child has poor eyesight or there is a delay in speech development, then classes with him do not make sense. In most cases, regular fine motor development exercises help the baby catch up with their peers and adapt to new information for him.
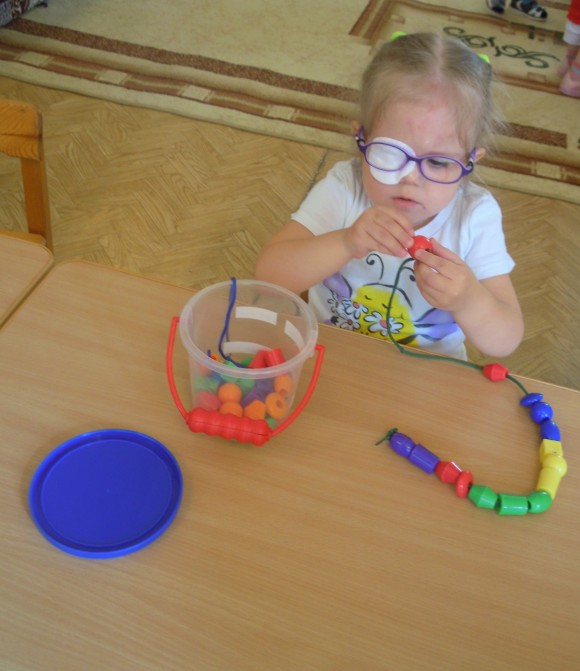

The development of fine motor skills and tactility is vital for visually impaired children
Diagnosis of the level of development of fine motor skills in children at different ages
Every day the child grows and develops. At a certain age, he should be able to perform various tasks. In order to assess the success of the baby, diagnostics are carried out. First of all, they look at how fine motor skills are developed in him. There are special tasks, as they are completed, the teacher or psychologist determines the level of hand motor skills. For each age, the complexity of such exercises is different. As a rule, children are diagnosed from the age of three.
- Exercises for 3-4 years.
- Collect the coins in the box. The kid is offered a small box and around it twenty coins are laid out in a chaotic manner. On a signal, he must collect all of them in a box as quickly as possible. The task must be completed first with one hand, then with the other. Normally, a child adds up all the pennies with an active hand in 15 seconds, with the other in 20 seconds.
- We draw in the air. The child must draw circles in the air of approximately the same size with his fingers for ten seconds, while the hands move one clockwise, the other counterclockwise. If the baby rotates his fingers in one direction, or the circles are very different in size, the task is considered failed.
- Draw a circle, horizontal and vertical lines on paper.
- Lacing and buttoning exercises: the child must lace up the mock boot, unbutton and fasten the buttons.
- Exercises for 4-5 years.
- Ringlet. You need to connect the index and thumb in the form of a circle, and raise the rest up. The child is asked to hold the fingers in this position for 10 seconds.
- They check how the child can draw straight, curved lines, waves.
- Cutting with scissors: the child should be able to cut simple geometric shapes along the contour.
- Fold the sheet in half: the baby should fold a sheet of A4 paper as evenly as possible.
- Exercises for 5-7 years.
- Draw straight, broken, wavy lines. Draw a person.
- On each hand, alternately extend the index finger and little finger at the same time, hold them in this position for five seconds.
- Cut out a circle from the square.
- Ask the child how to salt the soup, so that the baby slowly rubs the pieces of salt between his fingers.
If, as a result of the diagnosis, a lag in the development of motor activity of the hands is found, you should not leave this information unattended: you need to select tasks and work hard with the child for the development of fingers.
Card file of exercises and games for the development of fine motor skills of hands
The development of fine motor skills is best done in a playful way. So the child will be interested in the process, and the time spent in class will increase significantly. Many parents ask a completely logical question: how to choose the necessary and most effective ones from so many existing exercises and tasks. The answer is simple: it all depends on the interests of the child. Some children prefer building blocks, others drawing, so parents can make a list of activities and exercises depending on the child's preferences.
Finger gymnastics, self-massage and pencil exercises
For children from a very early age and preschoolers, finger gymnastics and self-massage are important. There are about one thousand biological points on the palms that regulate the work of human organs. Gymnastics for fingers is carried out simultaneously with rhymes that are so interesting to children.
Finger gymnastics on the table:
- free patting with brushes on the table alternately and simultaneously;
- free tapping with fingers on the table with both hands and alternately;
- alternately raising and lowering the fingers (the hands lie on the table) of the right and left hands, then both at the same time;
- imitation of playing the piano.
Exercises for finger gymnastics, self-massage and exercises with a pencil and ball - photo gallery
Exercises for finger gymnastics No. 1 Exercises for finger gymnastics No. 2 Exercises for finger gymnastics No. 3 Exercises with pencils Light finger massage Self-massage with balls Finger massage with a special massager Playing with a ball to warm up fingers Developing fine motor skills with a ball Games with a ball with rhymes
Self-massage of fingers and hands - video
finger games
Between classes, preschoolers play finger games. They are accompanied by verses and proverbs that the child easily remembers and can play with his fingers on his own at any time. Such breaks provide an opportunity to relax and stretch your arms, and then proceed to perform new tasks.
Finger games help:
- develop speech skills and improve them during the game;
- learn to listen to the teacher or parents and repeat after them;
- stimulate the development of creative abilities, because the child represents his hands in the form of animals, plants or certain natural phenomena;
- to train dexterity and flexibility of hands;
- concentrate attention;
- train memory (the child remembers rhymes and finger actions during their pronunciation);
- establish contact between children and adults.
There are many videos on the Internet with examples of finger games. But, in addition, you can buy books with a description of actions, cards with rhymes and explanations in stores for children.
Rhymes and finger games - photo gallery
Finger game "Swan" Finger game "Snail" Set of cards "Playing, learn!" The book "Finger games"
Playing with fingers - video
Development of motor skills with the help of sensory pouches, business board, sorters, lacing, Lego bricks, finger theater and others
Lessons with developing toys are very useful for fine motor skills. For children from one to three years old, bodyboards are interesting, which are soft and hard, in the form of a board. With their help, the child develops thinking, logic, mindfulness, intelligence, remembers colors, learns letters and numbers, objects and different animals.
Young children perceive information not only visually, but also through tactile sensations. Parents can offer them sensory pouches filled with various materials.. It can be cereals, small or large items, toys, balls, designer parts.
Today, many children prefer games with a designer, lacing or sorters. They are interesting not only for kids, because here you can use your imagination and have fun. At an early age, offer your child a sorter: let him try to pick up shapes that fit the holes. Then interest him in the designer, the details of which, as they grow older, will become less and less, and the tasks will become more difficult.
Many toys can be made with your own hands, for example, a business board, a soft book, sensory bags, lacing, a sorter, and filling with details can be done depending on the preferences and interests of the baby. But it’s better to buy a ready-made designer in a store, you won’t be able to make it at home.
Toys for the development of fine motor skills - photo gallery
A soft business board in the form of a book is designed for the smallest children A large development board is interesting for children of all ages Transparent bags for the development of fine motor skills Developing bags for the development of fine motor skills are easy to make with your own hands Unusual sensory bags in the form of birds Learn to string objects on a rope Develop fine motor skills with lacing