Definition of oil is light heavy and shale. Lightweight heavy oil
Oil is divided into light, "middle" and severe, based on its density. Light oil in one cubic centimeter contains less than 0.87 grams, heavy - more than 0.98. The cubic centimeter of middle oil can weigh, respectively, from 0.87 to 0.98 grams.
Each of the species has its characteristics reflected on the processing and number of products obtained. In fact, these varieties differ little from each other. In their composition, the same hydrocarbons, the exit is the same products.
Heavy oil
Heavy oil requires additional purification, as it contains unwanted impurities, in particular, wax. In addition, it gives at the exit a large number of "dark" petroleum products (for example, fuel oil, gas oil or oil VM-6). They are cheap, sometimes the price of them is even lower than on raw materials. Therefore, it is more profitable to produce as much bright products as possible and less - dark. So, oil refineries appreciate heavy oil much less.
Light oil
From light oil, therefore, it is possible to obtain more light products (gasoline, Lubricant NP). It contains more light fractions, is distinguished by a large high viscosity indicator and is valued above heavy. As a rule, in light oil below the sulfur content, which is also a plus.
Russia, like a number of other countries, delivers both oil varieties to the global market. Heavy is represented by the URALS brand, and the light is Siberian Light. Some brands are mixtures of oil of different density mined at different fields.
Oil and gas, their composition and physical properties
OIL
Oil is a fuel, oily liquid, most advantage of dark color, with a specific odor. In the chemical composition, oil is mainly a mixture of various hydrocarbons contained in it in a wide variety of combinations and determining its physical and chemical properties.
In oils there are the following hydrocarbon groups: 1) methane (paraffin) with a general formula with I H 2I + 2; 2) Naphthenovye with the general formula with "H 2P; 3) aromatic with general formula
SPN 2l -B- /
The most common hydrocarbons of the methane row. The hydrocarbons of this row - methane CH 4, ethane C 2 H, propane with 3 H 8 and butane with 4 nu - at atmospheric pressure and normal temperature are in a gaseous state. They are part of oil gases. With the increase in pressure and temperature, these light hydrocarbons can partially or completely move into a liquid state.
Pentanes with 8 H 12, \\ hexane with in H 14 and heptane from 7 H 1B under the same conditions are in an unstable state: easily passed from a gaseous state into liquid and back.
Hydrocarbons from 8 H 18 to C 17 H - liquid substances.
Hydrocarbons, in the molecules of which there are over 17 carbon atoms relate to solids. These are paraffins and ceresines contained in certain quantities in all oils.
The physical properties of oil and oil gases, as well as their qualitative characteristic depend on the predominance of individual hydrocarbons or their various groups. Oil with a predominance of complex hydrocarbons (severe oil) contain fewer gasoline and oil fractions. Contents in oil
In, M-Agrieve in
a large number of resinous and paraffin compounds makes it a viscous and low-liner, which requires special measures to extract it to the surface and subsequent transportation.
In addition, oil is divided according to the main qualitative indicators - the content of light gasoline, kerosene and oil fractions.
The fractional composition of the oil is determined by the laboratory distinguishing of them, which is based on the fact that each hydrocarbon comes into its composition has its own a specific boiling point.
Light hydrocarbons have low boiling points. For example, Pentan (C b H1a), the boiling point is 36 ° C, in hexane (C 6 H1 4) - 69 ° C. In heavy hydrocarbons, the boiling point is higher and reach up to 300 ° C and higher. Therefore, when heating oil, its lighter fractions will be evaporated and evaporate, with raising the temperature, heavier hydrocarbons begin to blame and evaporate.
If the pairs of oil heated to a certain temperature, collect and cool, then these pairs will again turn into a liquid that represents a group of hydrocarbons, sculpting from oil in this temperature range. Thus, depending on the heating temperature of the oil, the lighter - gasoline fractions first evaporate, then heavier - kerosene, then solar and so on.
The percentage in oil of individual fractions, scolding in certain temperature ranges, characterizes the fractional composition of oil.
Usually in the laboratory conditions, the disappeared of oil is produced in temperature ranges up to 100, 150, 200, 250, 300 and 350 ° C.
The simplest refining of oil is based on the same principle as the described laboratory distinguctor. This is a direct distillation of oil with separation from it under conditions of atmospheric pressure and heating to 300-350 ° C of gasoline, kerosene and solar fractions.
In the USSR there are oils of a variety of chemical composition and properties. Even the oil of the same deposit can vary greatly with each other. However, the oil of each region of the USSR has their own specific features. For example, the oil of the Ural Volzhsky district typically contain a significant number of resins, paraffin and sulfur compounds. The oil of the Embune district is distinguished by a relatively low content of sulfur.
Oil of Baku District and physical properties are the greatest variety of composition and physical properties. Here, along with colorless oils in the upper horizons of the Suurakan field, consisting practically from the gasoline and kerosene fractions, are found oil, not containing gasoline fractions. In this area there are oils that do not contain resinous substances, as well as highly resistant. In many oils of Azerbaijan, naphthenic acids are contained. In most oils there are no paraffins. According to sulfur content, all Baku oil belongs to a little sulfur.
One of the main indicators of product quality oil / is its density. Oil density at a standard temperature of 20 ° C and atmospheric pressure ranges from 700 (gas condensate) to 980 and even 1000 kg / m 3.
In commercial practice, the magnitude of the density of crude oil is approximately judged by its quality. Light oil with a density of up to 880 kg / m 3 are the most valuable; They, as a rule, contain more gasoline and oil fractions.
Density, oils are usually measured by special ranges. The hydrometer is a glass tube with an extended lower part in which a mercury thermometer is placed. Due to the considerable weight of mercury, the area at diving in oil takes a vertical position. In the upper narrow part, the aometer has a scale to measure the density, and at the bottom - the temperature scale.
To determine the density of oil, the areaometer is lowered into the vessel with this oil and at the upper edge of the generic meniscus count its density.
To obtain the measurement of oil density at a given temperature, lead to standard conditions, i.e., to a temperature of 20 ° C, it is necessary to introduce a temperature amendment that is taken into account by the following formula:
p2O \u003d P * + B (<-20), (1)
where p 20 is the desired density at 20 ° C; P / - Density at measurement temperature I; and- the coefficient of volume expansion of oil, the value of which is taken from special tables; she
Oil prices are as an integral part of the news release as the weather forecast. On the extraction and use of hydrocarbon fuel keeps the entire economy of the modern world. But why is oil from different countries stand differently, and what are the features of different brands of black gold?
All oil fields differ from each other primarily in the quality of oil. Depending on which chemical composition has oil, it is referred to in one or another brand, and on the basis of this, its price is also formed in the world market. Today in different places plants produce more than 20 oil brands.
The main stamps regarding which the monetary evaluation of all other varieties is underway, is British Brent Oil, American WTI and Middle Eastern Middle East Crude. Their quality is one of the best, and with them compare all other varieties of oil.
Crude oil, that is, in the form in which it is mined is practically not used in the economy, therefore it is processed to obtain a fuel or other product. Depth and cost of processing, and therefore, the price of the finished product is directly dependent on the chemical composition of oil. The main indicators affecting the quality of oil is its density and content of various impurities in it, mostly sulfur.
Of the varieties of low density (they are called light varieties) and the low content of impurities, gasoline, kerosene and diesel fuel are obtained as a result of minor processing. These are the most sought-after products on the liquid hydrocarbon market. But the thick and viscous oil having a high density is used mainly for the manufacture of fuel oil and fuel for production furnaces. Therefore, light varieties of oil with a minimum amount of sulfur (no more than 1%) require minimal material costs for processing and cost more than heavy varieties.

Among the whole world oil, the reference, along with the brand of Severvorsk Brent, was recognized by WTI-brand oil (mined in Texas) and Dubai CRUDE (United Arab Emirates).
Russia delivers several oil brands on the global market with a different chemical composition. The main brand of Russian oil is URALS, which is a mixture of oil produced in the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug and in the Republic of Tatarstan. Easy Siberian oil is mixed in one pipeline with European. But Tatarstan oil contains many sulfur and other impurities, which in the end and lower the cost of this brand. Another brand SIBERIAN LIGHT, the supply of which to the world market is insignificant, is in the pure form of Siberian oil produced in the Khanty-Mansiysk JSC. The content of sulfur in it is almost 3 times less than in URALS. And the oil that is mined on the Arctic shelf belongs to the Arctic Oil brand. It is rather heavy and contains a lot of sulfur. The remaining varieties of Russian oil (Sakhalin Sokol, East Espo ESPO and Sakhalin Vityaz) have a light composition and very low content of strangers. And the oil of the Sokol brand is closest to light Oman oil.
If we compare countries that are world leaders in oil production, then they tend to have high-quality fields of raw materials. For example, Indonesia oil, the largest supplier of hydrocarbons to the markets of the world, is sold under the MINAS brand. This is very light oil with a minimum content of sulfur - less than 0.1%. Oil produced in Nigeria and Angola also has low impurities and refers to light oil. The same can be said about oil countries of the Arabian Peninsula and North Africa. But Venezuela is not so lucky. Most of the oil produced in this country is considered severe and contains a lot of sulfur, which forces the leadership of this state to take additional measures to successfully implement their raw materials.

The main stocks of heavy and sour petroleum raw materials are concentrated in the Volga-Ural basin, the bitumen deposits are located here. Easy-recoverable oil sand MELEESS of the Volga-Ural basin can quite be part of the proven oil volumes of Russia. The total area of \u200b\u200bthe Arlan field is 460 km2, there are severe oil (density of 0.88-0.89 g / cm?, Sulfur content of 2.4-3.6%.) And bituminous sands. The overall depth of the open oil sedimentary cover is 3000 m.
Most of the bituminous fields and fields of severe oil in Russia requires the use of effective depth production technologies. In recent years, Russia began to use new methods of heavy oil production, in particular, a steam drainage method -Steam Assisted Gravity Drainage (SAGD) is applied. However, the use of SAGD in the extraction of severe oil is a single case and does not change the total complex technological picture that takes place in the Russian Federation. To date, the main technological investments in Russia were focused on classical oil production, as well as mining in Arctic conditions. During the USSR, the technologies for processing heavy and extra-heavy oil raw materials were advanced in a small amount, but at the moment there are not enough technologies in Russia even to reflect low-quality commodity oil.
Difficult and currently technically not restored bitumens of the Russian Federation are mainly in the Almazon and Zolotonny Leno-Anabar Messrarchier, located in the remote part of Eastern Siberia. The alleged volume of the oil supply of the field is 212 billion barrels (about 28.5 billion tons). Currently, the development of these deposits is a technically unrealized task due to the complete lack of infrastructure in this region. However, oil production from deposits in the Leno Anabar basin can be considered in the complex with gold and diamond mining. It should be emphasized here that the development of new technologies of deep oil sand production in the Leno-Anabar region may allow to derive technical-inaccessible reserves of extra-severe oil into the discharge of proven volumes of the Russian Federation, this can significantly change the overall world picture of oil reserves.
For the technical-affordable heavy oil of the Volga-Ural Basin, the use of "Removing" technology in order to increase its export potential is relevant. Obviously, the higher the density of raw materials, the more expensive technology. Recycling heavy oil allows you to get high-quality petroleum products with low specific density and sulfurity. It is economically advisable to improve the quality of heavy and acidic oil of the Volga-Ural basin, and not to mix it with a high-quality Siberian Light variety to obtain an export mixture URALS.
The technology of processing the extra-heavy oil into lightweight synthetic products is based on the combination of traditional technologies used on the refinery: coking, hydrotreating, sulfur removal, hydrocracking and hydrogen production. In recent years, the technology has been improved by production processes: bosbelling, deasphalotization, hydrocracking of residues, hydrotreating gas oil, heavy oil gasification.
Low-hearted high-quality oil without non-unauthorized residues are obtained by processing heavy residues of oil, hydrocracking and coking along with the hydrotreating of fractions. A small amount of sulfur is provided by the hydrotreating.
Heavy oil is a kind of crude oil of bituminous and viscous type, which has a density of 0.917-1.022 g / cm3 and characterized by the presence in its composition of very large molecules consisting of 90% of sulfur and various metals. Heavy oil in its natural state is impossible to pump out ordinary methods. In most cases, in order to ensure the flow of a fuel fluid of a similar type through a pipeline or enter it into a well, it is necessary to pre-dissolve or heating.
Heavy oil related to the second group, have a specific gravity of about 0 9 and higher; They have an already noticeable content of asphaltenes, the content of the resin rises to 10 - 15% and higher. Examples of this kind are heavy Baku, Maykop and Kaluga oil. There is still an intermediate type between light and heavy oils, not stacked in the border outlined above; This includes, for example, Bibeibat oil and light Maikopskaya.
Heavy oil, oil residues, as well as products such as bitumens, peks are structured systems already under normal room temperatures. Heavy oil containing high molecular weight asphalt-resinous components, polymeric solutions are dispersed systems.
Such a restructuring of the structure may occur for a very long time, for example, according to data, in polymeric solutions, the duration of the restructuring can be a day and even months. At the same time, the relaxation time of individual units of the macromolecules is little and is the fraction of a second.
Heavy oil can be used to dedust the soil, primrate and primer roads using the impregnation and mixing method on the site, for the device of protective rugs from oily sandy soils, for the base of bases and coatings on the roads of the V category and the extracategorical roads with the intensity of motion in no more than 200 - 300 cars per day. In some cases, integrated binders from raw heavy oil and viscous or solid (construction) bitumen can be obtained.
Heavy oils, as a rule, lie in the sands of more coarse-grained, better permeable and dedicated to the nizams of Balakhana and to the lower part of the productive strata.
Heavy oil and bitumens are one of the most important promising sources of hydrocarbon raw materials. On the territory of Tatarstan, there are large reserves of such hydrocarbons at a small depth. Currently, some deposits of natural bitumen are introduced into the development. Many mining methods and raising bitumevotes are tested on these deposits. The experience of their implementation will undoubtedly be useful in the near future.
Heavy oil from the III layer is extracted by a mine. Radium and various salts are extracted from the shale water. Gas from the water of shale goes to heating a large plant.
Heavy oil with a density close to 1 0 g / cm may sink.
Heavy oil is mined using secondary and tertiary methods. In Venezuela, horizontal ls are inclined wells, low-diameter wells, an increase in the degree of oil extraction using solvation and foam agents are important factors for reducing the cost of heavy oil production. New pumping equipment, integration with advanced modeling and 3D seismic are very effective.
Heavy oil and natural bitumens belong to unconventional types of hydrocarbon raw materials. At the same time, according to the physico-chemical characteristic, the conditions of mining and processing, heavy oil occupy an intermediate position between ordinary oils and natural bitumens.
Heavy oil and bitumeumes differ from ordinary oils in high metal content (vanadium, nickel, iron, molybdenum, copper, sodium), sulfur, nitrogen and asphaltenes.
Heavy oil of the Katangulial, Okhinki and 16th and 17th plars of East-Ehabinsk fields in their properties are close to the oil bitumens of the B-1 brand according to GOST 1972 - 52, used in road construction as a dedusted means and solvent bitumen of higher grades.
Heavy oil is fed to the dewatering and desalting unit. The process of dehydration and oo erasing is carried out at a temperature of 85 - 90 s in three steps. Heating to the desired temperature is carried out in the heat exchanger 13 due to the cooled ready bitumen. S Pump Pipe Pipe is fed by a 2% aqueous solution of the demulsor at the calculation of the ES-YU G of the YUS-GU DEMULGATOR (DISCOLVAN 4411, or PASS) on I T of Oil. The solution of the demulsifier is prepared in the tank 4 at a temperature of not sishe 40 C.
Heavy oil contains a small number of volatile fractions and, highlighting a small number of vapors, creates explosive mixtures with air. Crude oil (as well as gasoline, benzene) creates a high concentration of combustible vapors in the gas space and often above the upper limit of the explosability. The storage temperature of petroleum products has a big impact on the percentage of vapors in the gas space of tanks and the degree of their danger.
Heavy oils in the lamps were not burning, light light oil caused explosions and fires, and paraffiny gave a thick soot and flashes.
Heavy oil related to the second group, have a specific gravity of about 0 9 and higher; They have already noticeable asphaltenes, the content of resin rises to 10 - 15% and higher. Examples of this kind are heavy Baku, Maykop TT Kaluga oil. There is still an intermediate type between light and heavy oils, not stacked in the border outlined above; This includes, for example, Bibi-Eybatsky oil and light Maikopskaya.
Heavy oil is characterized by a high density (G20 - 0 970 - 4 - 0 980) and refers to a high osmole with an extreme (resin of sulfur-acid 25 - 72%; cokusability 5 5 - 9 0%), laparaphin oil. Oil practically does not contain gasoline fractions.
Heavy oil, which lies in the Lower Marmatian sediments of the XI-XIII horizons, has a density of Q4 0 986 and is highly resin (resins of sulfur acid to 70%), alone (sulfur 0 46%), laparachin. According to the group hydrocarbon composition, oil belongs to Nafthenic-aromatic.
Heavy oil can only be met in limited sections of the eastern board of the depression.
Bibeibat hard oil is a mixture of reservoir oils, starting from about XIV Sweets, including COP, with a resin content of up to 27% and low temperature of fuel oil.
Malgobeka heavy oil and oil area of \u200b\u200bBeckovichi according to the main properties are similar to the northern and southern anticlinals of the Voznesensky deposit.
Heavy oil of different horizons are similar to properties. These are highly brushed (cokshability up to 7 3%; sulfur resins up to 62%), laparachin, aliens oil.
More resinous and severe oil are heated in a water bath in a round-bottomed flask with reflux. To increase the efficiency of dehydration in the flask, calcium chloride is added. The released water is condensed at the top of the flask, and it is removed by filter paper after cooling the flask. This operation is repeated until the water stops stand out on the walls of the flask. It is necessary to monitor the bathroom to prevent the boiling of light oil fractions. Upon completion of drying, oil is filtered through fiberglass.
The most highly resistant, severe oil in the Ural-Embensky district of Kazakhstan lies in the Last South - the Kara-Arna deposit. At the beginning of the opening of this oil, researchers of the Institute of Oil and Natural Salts of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Kazakhstan, believing that there are valuable chemical products. Later, the institute was limited to a statement that in.
Heavy oil of individual areas of the Zybza-Gluba - Kiye Yar is mixed and under the name of Ilski heavy oil enters processing.
Although heavy oil belongs to unconventional types of hydrocarbon raw materials, in fact, in an economic and technological sense, it is a transitional link from ordinary lungs and middle oil to natural bitumens.
The concept of severe oil (Heavy Oil) has no definition. In different countries, oils characterized by various density and viscosity values \u200b\u200bare included in this group.
Such highly paratic and heavy oil are abnormally viscous.
The movement of heavy oils of some deposits is described by the law of filtration with the initial pressure gradient. In accordance with this law, the movement of fluid is terminated at small (less limit) pressure gradients. Therefore, when moving with an initial gradient, it is possible to form inside the reservoir of zones of stationary oil - stagnant zones and the whole, which affects the completeness of oil extraction.
For heavy oil, it can be significantly larger due to the larger residual hydrophobicity of sandstones in the deposits of severe resinous oil.
Separation of heavy oil and a small gas hat are installed in the sediments of the upper part of the productive stratum within the southeast perical voyage of the folds of the fold.
For heavy oil, wood chips do not apply. Oil filter, previously purified from the main amount of water, enters the seduction section, where its final purification occurs.
The sealing of heavy oil is timed to the carbonates of the fossil reef massif of the Rannerperm (PIAR) age. The permeable variability of the collector is determined by non-uniform details of cracks and cavernosis.
Heavy oil contains heavier hydrocarbons than in light, as well as more excise resins and surfactants that determine the lubricant.
For heavy oils, which are characterized by viscoelastic properties, the viscosity in the porous medium increases with increasing filtering rate.
For severe oil, the situation is different, since the DN is little and Native. A situation is possible when the coefficient is close to one and, accordingly, S is significantly less than the maximum value of the basement. Such a case corresponds to the partial removal of water from the slaughter.
From heavy oil, road bitumens can be obtained at atmospheric or shallow vacuum distillation. For light oil, it is not always possible, since it is difficult to achieve the desired depth of distillate selection on ordinary equipment.
For heavy oils, these curves go much cooler than for the lungs.
Tad of heavy oil and oil residues with high cokshability and metals, developed in the United States and put into operation in 1983, power of about 2 5 million tons / year.
For severe oil and highly viscous waterionate emulsions, the possibility of using mesh nozzles and other types of nozzles is determined in each particular case by experimenting.
Extraction of heavy oil on the Shaffranian field Oilfield business and oil transport: scientific.
The reserves of heavy oils of Volga - Ural NGP are 26% of all reserves in the Russian Federation. Heavy oil focused on depths of less than 1500 m in Tatar, Perm-Bashkir, Zhigulevsky, Verkhne-Kamsky, districts.
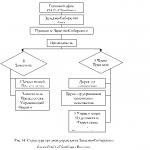
For heavy oil, the presence of correlation between the ratio of oil and water density and the index of the formality of the reservoir pressure equal to the ratio of the reservoir pressure of the RPL to the depth of the hydrostatic pressure / the guide at the depth of the deposit is. In fig. 3.7 shows such a dependence according to the Ural Volga deposits.
Heavy oil resources are currently subject to industrial development in areas where the development of deposits can be carried out using traditional technology. However, the real contribution of these resources to the global oil production is still very small, significantly less than their share in worldwater resources of liquid hydrocarbons.
The use of severe oil for the production of petroleum products is associated, as a rule, with the need for preliminary (primary) treatment (refining) of the extracted raw materials in order to reduce the density of the processed oil by hydrogenation (hydrocracking), coking or partial oxidation of its heavy fractions. Additional costs of primary processing of high-viscous oil are estimated at 9 5 - 22 $ 5.
The reserves of heavy oil in the United States are estimated at 19 billion tons of geological and 0 7 billion tons of explored. Heavy oil is currently currently an industrial production facility in Venezuela, Mexico, USA and a number of other countries.
The use of heavy oils in natural form solves the task of the coating and bases for low technical categories. This is confirmed by the experience of a number of foreign countries. Thus, in the US, more than 30% of the total amount of oil bitumen is made from specially selected heavy oils.
The exits of severe oil on the northern board of the North Caspian basin, in areas located between the Volga and the Urals, were well known, but they were not attached importance.
The use of heavy oils as a raw bitumen base will significantly simplify the problem of providing road and building organizations by bitumen and reduce the shortage of road bitumen, especially in agricultural road construction. The processing of heavy oils of low-riveted wells on a bitumen version at the installations located in close proximity to the fields is economically justified in agricultural areas, since the specificity of road construction allows the use of the received bitumen in the radius of the field with small transport costs.
hydrocarbon raw materials Heavy oil
The chemical characteristic of oil can differ significantly not only from the region of production, but even from the well to the well. Oil brand is the criterion of prices and the most important parameter for.
Brent.
Brent - Oil marker variety used to generate prices at the conclusion of transactions on international commodity markets. This variety is mined in the North Sea at the field of the same name since the 70s of the last century.
The brand Brent received its name while reducing the names of the layers of the occurrence in the Scottish and Norwegian shelves. The following physicochemical indicators can be attributed to the varietal features:
- Low density. Only 38 degrees according to the API standard;
- Small amount of sulfur contained from 0.2 to 1%.
It is these characteristics that determine the industrial attractiveness of this oil variety and make it reference. More than 40% of oil produced in different countries can be assigned a varietal characteristics of a broach. What actually happens when raw materials arrive at world markets.
The price of about 70% of the varieties of oil varieties is tied to the value of the Brent brand. Although in the 20th century, the leading positions belonged to WTI (West Texas Intermediate).
Mexico, Asia, Europe and the Middle East most of the oil produced are implemented under the Brent brand.
The formation of the price of the produced and exported oil depends on its compliance with the reference varieties.
Inside the oil-producing country, its standards of oil mixtures can be established, but they all focus on reference varieties, including Brent and WTI (Texas Brand).
Such a separation facilitates the procedure for pricing on oil and makes it possible to exporters to exporters on the exchange of their oil varieties with a discount relative to marker varieties. It is not difficult to guess that the price difference between Brent, Urals, WTI and other oil varieties is explained by the costs of their production and processing due to physicochemical properties.
- Brent Blend (deposit is located in the North Sea, the main sales market - Europe and Asia);
- West Texas Intermediate (WTI) (sales deposit and market - Western hemisphere);
- Dubai CRUDE (mined in the countries of the Persian Gulf for the Asia-Pacific region).
Modern oil-producing states exercise a certain type of "black gold": Russia - Urals and Siberian Light, Norway - Statfjord, United Kingdom - Brent, Iraq - Kirkuk, USA - Light Sweet.
Yurall
As for the Russian reference of oil, the Urals brand acts in his role. All refers to this brand. Yuralls is a mixture of light and heavy varieties of oil inferior to the main characteristics of world standards. The main characteristics of the variety are as follows:
- Density - more than 30 degrees API;
- Sulfur - over 1.2%.
The main varieties used to obtain the mixture are:
- Oil Volga region, different density and high sulfur content;
- Light oil, which lies in the depths of the West Siberian Plain.
Due to the similarity of the Urals characteristics with a Brent variety, the price of Russian oil is determined and depends on the price of the Northwest standard. The discount in relation to the Brent was due to higher costs when recycling Yurall. Mixing varietal components is carried out during transportation directly in the oil pipeline.
Oil mixture URALS is similar to its characteristics with Iranian Iran Heavy. In this connection, the valuation of this brand directly depends on the actual volume of production and export of black gold Iran.
Contracts for the supply of oil URALS are referred to international trading platforms, and their price depends on demand and suggestions, as in the case of other oil varieties. Currently, the price of Urals is expressed in dollars and is determined by the value of the Russian currency in relation to the dollar and the euro, and is proportional to the price of North Mountain oil, taking into account the discount.
The demand for the Russian standard is high enough, but is inferior to the Texas variety and varieties exported by Arab countries. Russia tried to market other oil brands, but attempts turned out to be unsuccessful in mind problems with quality and composition.
What affects the cost of different oil brands?
What other factors, in addition to differences in composition and quality, have a direct impact on the formation of the value of crude oil? The main of them are:
- macroeconomic situation in the field of the field and the whole world;
- existing demand and supply in the global oil market;
- the level of mining and exports.
For example, the value of the oil of the West Texas Intermediate (WTI) brand largely depends on the level of inventory. And the value of the Brent brand is from the regularity of supplies.
From the current situation on the global oil market, a fact can be stated: that if earlier the difference in value was directly dependent on the chemical composition of hydrocarbons, then foreign economic components are increasingly increasing.