What is characterized by modern industrial production. Industrial production (Industrial Production) is
Modern Russia - industrial - an agricultural country with a significant predominance of industrial production.
The current situation of Russia in the global economy is characterized by contradictory trends. On the one hand, it has significant natural, labor resources, large industrial potential, occupies the leading positions in the production and export of many important goods (the truth, mostly fuel and commodity groups), has a powerful scientific and technical potential, a high educational level of the population. On the other hand, the economic decline in the 90s. led to a significant weakening of Russia's position in the world economy: the country's share in the aggregate GDP of the world decreased from 3.6% in 1990 to 1.7% in 2002 (according to the latest reports of Russia, up to 3%), and in world industrial products - from 4.6 to 1.8%. Being a medium-breeding country, for a number of parameters, it occupies an interim position in the global economy between developed and developing countries
Gas subgenital He is leading in the fuel and energy complex of the country. About thirds of the developed world reserves of natural gas are concentrated in Russia.
Russia supplies gas under the system of main pipelines European CIS countries, the Baltic countries, Eastern and Western Europe.
Oil industry Russia is presented with fuel mining in oil and gas pools and its use on refineries. They are focused on the consumption of products of its processing, so deliver raw materials on the network of oil pipelines to European regions.
Electric power industry. The electrobalance of Russia is dominated by thermal power plants (TPP) - they produce 2/3 of the entire electricity of the country. The largest TPPs in Russia are Surgut, Reftinskaya, Kostroma GRES.
Hydraulic power plants (HPP) - produce the fifth of electricity in the country. The most largest in Russia is the Angaro-Yenisei and Volga-Kamsky Cascade of the HPP.
Metallurgical complex . Susia is well provided with raw materials for development black metallurgy In the country there were three metallurgical bases, in which 90% of cast iron, steel and rolled steel are produced.:
The central metallurgical base, coal for which comes from Pechersk and Kuznetsky pools.
The oldest is the Ural base, the formation of which began on the basis of its own reserves of iron ore and firewood.
The youngest is a Siberian metallurgical base that uses the coal of the Kuznetsky pool, the iron ore of the Kemerovo region, Priangarya, the Brassens of the Sayan.
Non-ferrous metallurgy Specializes in the production of aluminum, copper, nickel and lead. The aluminum industry uses its own ores, processing them on the factories. The development area of \u200b\u200bthe copper industry in Russia is the Urals whose enterprises are used both local and imported raw materials from Kazakhstan.
Machine-building complexit takes an important place in the Russian economy and consists of 70 industries that can be divided into 4 groups:
1) Severe engineering (Ural);
2) Transport engineering: automotive industry (Tolyatti, Moscow, Nizhny Novgorod, Ulyanovsk, Naberezhnye Chelny); aerospace industry (Moscow, Nizhny Novgorod, Samara, Voronezh); Railway (central and north - western regions); Shipbuilding (St. Petersburg, Vladivostok, Komsomolsk - on - Amur, Arkhangelsk);
3) Agricultural engineering;
4) Standulating and instrument making.
Basic chemistry Russia is represented by the production of acids, mineral fertilizers and soda. The production of potash fertilizers is concentrated only in the Urals, the release of phosphate fertilizers is focused either to sources of raw materials or approximate to consumers of products-C \\ x regions.
Light industry: Cotton, shoe and fur industry.
The existing structure of the economy with the predominance of industries producing means of production does not comply with modern requirements. A structural restructuring is necessary in the direction of increasing the share of industries that produce consumption items, as well as non-productive sphere. Russia must move from the industrial to the post-industrial stage of development. Today, only Moscow and St. Petersburg committed this transition. Moscow region, Volga region, industrial zone of the Urals, areas of oil and gas production Western Siberia, Kuzbass, Priangary and some other territories are still on the industrial stage of development. And Kalmykia, Tuva, the districts of the North of Eastern Siberia and the Far East are on the pre-industrial stage. The remaining regions of the country are moving from pre-industrial to the industrial type of economy.
Ticket number 10.
1) Comprehensive economic and geographical characteristics of India.
Territory - 3.3 million km 2
Population - 1130 million people
Capital - Delhi.
The Republic of India is located in South Asia on the Indian Ocean Peninsula, washed by the Indian Ocean. India is bordered by Pakistan, Afghanistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh and Myanmar. Especially great length of the Indian-Chinese border. She passes through the main Himalayan ridge. India takes the seventh place in the world in size, second place in terms of population.
India is the most populated country in the world after China. According to the last census, India's population for July 2001 was 1030 million people. In other words, every seventh resident of our planet is Indian. The annual increase in the population of India is 14%. The country is carried out by a demographic policy aimed at reducing fertility. India is the most multinational country in the world. It has several hundreds of ethnic groups and tribal groups. Official languages \u200b\u200b- Hindi and English. According to the census, almost 100% of the population of India is religious. The main religious and ethnic system of India is Hinduism, it is confirmed by 83% of the country's population. About 12% - Muslims, the rest are Sikhi, Christians, Jain, Buddhists, Pars, and others. India's labor resources are very significant, but unqualified labor predominates. The share of competent among the adult population of the country is 48%. Great unemployment (more than 30mln registered. Man). India is one of the most polarized countries in the social relationship. More than 300ml. A person (1/3 of the population) lives for a "feature of poverty."
The population density in India is 260 people per km² (high indicator). Men in India is more than women. This is explained by increased mortality among women related to early marriages and numerous early childbearings. The average number of children in the family is currently five people. The most densely populated seaside territories (Karala, West Bengali) and Indo-Ganga lowland.
About 3/4 of the country of plains and plateaus. India is rich in minerals. The country has the world's largest stock ore reserves, which is ¼ world stocks. India also has significant reserves of manganese ores. From energy minerals, stone coal has the greatest importance. South India is rich in boxcites, chromites, magnesitis, brown coal, graphite, mica, diamonds, gold and uranium. An important source of energy can be a radioactive thorium extracted from beach sands. The country is located in the tropical and sub-screen monsoon of climatic belts. It is characteristic of a clear alternation of the wet and dry seasons of the year. The Rivers of India have a significant energy potential, as well as the main source for irrigation. Land resources are the main natural wealth of the country. There are more than half of the country's territory. A significant part of the soil has high fertility. The forests occupy about 1/5 of the India Square, but the wood lack still. For the rural population, the forest is an essential source of fuel and building material.
India is one of the leaders of the third world countries. On the one hand, this is an industrialized state, which mainly ensures its needs in almost all sectors. On the other hand, agriculture remains dominating the Indian economy. It employs about 70% of the workforce. Foreign trade is considerable for the country's economy. However, India is still not yet involved in the international division of labor. The share of finished and high-tech products is growing in exports.
India is an agrarian-industrial country. It is believed to the group of "key developing countries", which have enormous resource and human potential, intensively developing their industry and playing an increasingly prominent role in the global economy. The share of India in global income is about 2%, and in the population of the world - more than 17%. There are less than the disproportions and in the structure of GDP and EAN countries.
Specialization branches: Black Metallurgy, Fuel and Energy Complex, Color Metallurgy, Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Industry, Easy, Food. It provides the country with the necessary production.
India is a country of an ancient agricultural culture. The South Asian region is homeland rice, cotton, eggplant, cucumber, lemon, orange, mango, sugar cane, sesame. This is currently one of the most important agricultural regions of the world. The leading industry of agriculture India is crop production (4/5 of the cost of all products). The main part of the sowing area is occupied by food cultures: rice, wheat, corn, etc. In India, two agricultural seasons are summer and winter, which is associated with the agro-climatic features of the monsoon climate. Summer grown rice, cotton, jute; In winter - wheat, barley, etc. Livestock is the second in the meaning of India's agriculture, strongly inferior to crop production. Cattle (buffalo, cows, oxen) is used in peasant farms mainly as a major force. Despite the fact that the livestock of the cattle India occupies the 1st place in the world, animal husbandry is not a significant supplier of massive products. The population practically does not use animal meat to eat (Hindus traditionally vegetarians). Used milk, skin and animal leather.
Thus, from Table 3 it is seen that the industrial production of Russia is growing every year, gaining momentum.
In the process of statistical accounting and analysis, the industry structure of the industry is usually determined by finding the specific gravity of industries in the total production of products, the number of employed and value of the main production facilities industry. We define the proportion of each industry in the total production volume (Fig. 3).
Fig.3. The proportion of industries in total production
From the data of interest ratios, Fig.3 see that the greatest share in the total volume of production is occupied by mechanical engineering.
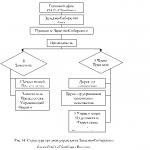
II. Prospects for the development of industrial production in Russia
The prospects for the development of industrial production of Russia are advisable to consider in two directions: the prospects for the development of the extractive industry and the prospects for the development of manufacturing industries.
2.1. Prospects for the development of the extractive industry
As is known, the stability of the mineral resource base (SME) largely depends on the balance between the ratio between the levels of mining and the increase in mineral reserves. Since 1991, the extraction of the absolute majority of mineral types is provided mainly to the reserves built earlier due to the specification of previously open deposits, as well as the transfer of reserves from previously estimated in the explored.
Until the mid-90s, the growth volume of oil and gas reserves on the continental part of the country exceeded their production. In the period from 1990 to 1997, there was a sharp drop in the volume of reproduction, caused by a decrease in exploration (GRA). The main reason is that the state system of SME reproduction in the USSR has been destroyed, and there was no complete set of conditions for its replenishment. The current state of the Russian SME of hydrocarbons on various sources is estimated in the range from critical to "threatening national security". Over the past 10 years, the replenishment of MSR reserves amounted to 73% on oil, 47%, 33% copper - 33%, zinc - 57%, lead - 41%.
Negative trends are most indicative when analyzing SME oil. Over the past years, no significant deposit has been explored. Proven oil reserves in the last decade are decreasing annually on average by 1, 3%, while in the world less mining they systematically grow by 1, 2-1, 6%.
There is a serious developmental lag and high-quality deterioration in the raw material base of the extractive industries of Moscow time. This means the need to make emergency measures to strengthen search and exploration, since the production of conditioned oil reserves with the current production level in the conditions of the three-time growth of world consumption of community resources forecast for the first half of the current century will be completed in 2010-2015. This is confirmed, in particular, the fact that large oil companies have the time of oil production provision of proven reserves slightly (from 15 to 35 years).
Compared to 1994, the financing of geological and exploration was tried three times at the expense of the federal budget. In addition, the share of budget funds (including regional), allocated for PRA on all sources of financing, is constantly decreasing: in 2000 it amounted to 36.5%, in 2004-2005. - less than 12, 0%. Large vertically integrated companies in Russia are not horched to attract investment resources for the implementation of PRR. Due to this, the departure of reserves for a long time are not compensated by their growths, which inevitably leads to the depletion of SMEs. Nevertheless, the targeted state policy in this area is not carried out.
However, the problem of the extractive industry consists not only in the exhaustion of stocks, but also in the deterioration of their qualitative characteristics, since the domestic practice of developing deposits is significantly lagging behind foreign technical and technological levels. A significant part in the structure of oil, gas, gas, coal is difficult and low-quality reserves.
Not the perfect, but the only encouraging gear mechanism (deductions for the reproduction of SMEs), which must be restored, was eliminated by the introduction of mineral mining tax in 2002. Currently, tax breaks for companies leading PRT are not provided.
A significant problem is a fiscal nature of the tax system. Application from January 1, 2002, a specific area-tied to global oil prices and not taking into account the rentrtaining tax rate for mining of minerals (NPPI). Built on such principles, the tax system is fiscal. It is focused on grossing extractors, does not have regulating functions aimed at the development of the mining industry. The development of a more efficient system of climbing NDPI, which takes into account the significant differences in the mining and geological conditions of deposits and allows for the establishment of subsoil users to develop deposits.
As for the lack of investment resources on the development of deposits and the maintenance of PRH, this problem is solved using the implementation of long-term non-commercial lending to the industry from Guikf.
In order to streamline the management system of the geological exploration process and the organization of its financing, it is necessary to recognize the expedient idea of \u200b\u200bcreating a national geological exploration company necessary to enhance geological exploration.
The decision of the remaining of the above problems is closely related to improving the quality of state control in the field of subsoil use.
In relation to the analysis of the problems of extensive development of the extractive industry, it is impossible not to affect the problem of collecting and disposing of associated petroleum gas (PNG) in Russia. This by-product of oil production in connection with the unpreparedness of the infrastructure for its collection, transportation and processing is simply incinerated by extractive companies in torches. As a result, the annual losses of the Russian economy from the combustion of the PNG make up at least 25 billion cubic meters. m (the annual production of natural gas of China). The combustion of the APG also causes significant environmental damage.
The scale of this problem was already forced to pay attention to her the attention of the President of the Russian Federation, which recently set the task of the task of minimizing the volume of incinerated PNG into the Government of the Russian Federation.
To solve this problem, the following management and decisions are required: Establishing the obligation of the subsoil user to equip oil fields with fruitful equipment controlling the flow of PNG, the development of technical regulations for the combustion of the PNG, Introduction to the license agreements Requirements to dispose of APG, the introduction of a direct ban on the legislation, the provision of a state loan To build a PNG processing and transportation infrastructure (with the help of the GBFF proposed on the creation).
2.2. Processing Products Development Prospects
The development of this segment of the economy determines the positioning of the country in the global market, contributes to the diversification and sustainability of economic development. Despite growth in the manufacturing industries in 1999-2006, the production volumes here are still significantly lower than the level of 1990. At the same time, the growth rate of processing industries, with the exception of ferrous metallurgy, is noticeably lagging behind the growth rate of the economy as a whole, and their share in industrial Production is reduced (see Table 3).
According to experts of the World Bank, the level of labor productivity at the enterprises of the processing industry of Russia lags not only from developed countries in Europe, but also from countries of Central and Eastern Europe, which carried out the transition to the market, and from many developing countries, such as Brazil or South Africa. Russian manufacturing enterprises in terms of labor productivity are close to Chinese and Indian firms, but noticeably losing them at the cost of labor, which reduces their competitiveness both in the world and in the Russian market.
The situation is exacerbated by the fact that in the medium term, the objective conditions for the functioning of Russian enterprises will probably be more stringent. The Russian economy is becoming increasingly open both for goods flows and foreign firms working in Russia. Extensive cheap sources of economic growth have already been exhausted.
Most likely, the prices for resources for production purposes will most likely grow, primarily on fuel, energy, land, etc. The preservation of competitive positions requires significant increase in the efficiency of using these resources, which, in turn, implies a fundamental technical re-equipment, change of product range, increase its quality characteristics. Otherwise, Russian enterprises are unlikely to be able to withstand competition with companies of large developing countries, such as China, whose industry is created on a more modern technical base. Cardinal modernization of production is impossible without significant investments. But at the level of the level of profitability, which is characteristic of most Russian industrial enterprises, they are not an attractive object for external investors, and their own means for solving large-scale modernization tasks are not enough.
The way out of the situation could be the creation of new, highly efficient enterprises in the manufacturing industry, not burdened by the legacy of an outdated technical base and a difficult financial situation. So far, new enterprises are mainly focused on the internal market of Russia and / or import substitution, arising in those segments that are relatively protected from external competition and are not able to radically change the raw material positioning of Russia in the global economy. In addition, the creation of new enterprises is inhibited by a number of factors, in particular, not enough favorable investment climate, high administrative barriers, tightening access to infrastructure (engineering and transport communications, energy supply) and cheap fuel sources (primarily gas), exacerbating the deficit of qualified personnel.
Analysis of the situation at the micro level shows that there are giant differences in the level and dynamics of efficiency in separate enterprises behind low averages.
Thus, the Russian manufacturing industry is distinguished by significant multi-tech, and the least competitive segment fell into a vicious circle of ineffectiveness. In fact, the task of increasing competitiveness and is to break this vicious circle: increase the number and increase the sustainability of competitive advantages of leaders and reduce the share of non-competitive enterprises.
The results of the survey allow us to talk about the availability of in industry, and in various industries, groups of leaders and outsiders groups. According to different estimates (using various criteria), 20-25% of enterprises can be attributed to the competitive group. Of these, about half of them not only have a higher level of labor productivity, but at the same time expand the release, increase the performance by rates exceeding the average industry. It is these enterprises today have the greatest growth potential, being an engine of economic development.
At the same time, 35-40% of sampling enterprises constitute a group of outsiders, which demonstrate the low level and dynamics of production efficiency and obviously lose their competitiveness. In the future, these enterprises must be either seriously restructured, or are ousted from the market more efficient companies.
The analysis showed that the likelihood of the group of competitive enterprises increases with the growth, the size of the company, when placing an enterprise in a major city with the status of a federal or regional capital. Thus, among enterprises with a number of more than 1000 people, the share of companies with high competitiveness more than twice the corresponding indicator in a group of 100-250 people. Thus, the concentration of production at large enterprises in industrial agglomerations, as before, largely predetermines the position of the company.
At the same time, even in the group of competitive leaders, not all well. So, half of the enterprises with high competitiveness did not deal with technological innovations over the past three years, and 9% - neither technological nor organizational. The physical wear of equipment in the leader group also reached a threatening degree: only 1/4 of them, the park of machines and equipment can be considered acceptable, and half the equipment is completely worn out. Therefore, it can be concluded that the group of competitive leaders is unstable. When preserving today's trends, it was probably after 3-5 years the share of competitive enterprises in the manufacturing industry will be reduced by half to 10-12%.
Conclusion
Industry - a set of enterprises (factories, factories, mines, mines, power plants) engaged in the production of workers of labor both for other sectors of the national economy and the industry, as well as the extraction of raw materials, materials, fuel, energy, the production of forest and further processing Products obtained in industry or manufactured in agriculture, consumer goods manufacturing. Industry is the most important sector of the national economy, providing a decisive impact on the level of development of the Company's productive forces.
Industry consists of two large groups of industries - mining and manufacturing industry. The mining industry includes enterprises for mining mining raw materials, ores of black and non-ferrous metals and nonmetallic raw materials for metallurgy, non-metallic ores, oil, gas, coal, peat, shale, salt, non-metallic materials, light natural aggregates and limestone, and Hydroelectric power stations, water pipelines, forest-operating enterprises, fishing and seafood mining.
The manufacturing industry includes mechanical engineering enterprises, enterprises for the production of black and non-ferrous metals, rolled products, chemical and petrochemical products, machinery and equipment, woodworking products and pulp and paper industries, cement, etc. Building materials, lightweight products and food industries, and enterprises On the repair of industrial products (steam-term-reference, locomotive repair) and thermal power plants.
The achievement of the strategic objectives of Russia's development in the medium term is possible only under the condition of recreation of growth economy. At the same time, not only quantitative, but also qualitative characteristics of economic dynamics are extremely important.
The positive future of Russia can be based only on the advanced development of processing industries. It is their dynamics that determines, on the one hand, the level of investment activity and technological renewal of production, and on the other - the dynamics and structure of population consumption. Consumer standards of the population, in turn, determine the formation and reproduction of labor motivation, and, consequently, the possible contribution of social factors into improving production efficiency.
The development of the domestic manufacturing and construction can provide a fundamental improvement in the quality of life of Russians, to create opportunities for a positive change in living conditions due to the large-scale offer of affordable housing, effective automotibal and advanced infrastructure development.
The primary sector of the Russian economy, the extractive industry and especially export-oriented industries represent the most important material resource for economic growth and maintaining the level and dynamics of export income. The latter is especially important during the restoration of the technological potential of the manufacturing sector of industry, construction and transport. The primary sector of the economy of the tasks of material support for economic growth in Russia and maintaining the positive values \u200b\u200bof pure exports in the medium term also requires development within the mining industry of complex processing of raw materials, increasing the share of final products in exports.
List of references
Modern state and perspectives development credit insurance in the Russian Federation
Degree work \u003e\u003e bankingTopic: " Modern state and perspectives development Credit insurance ... Car loan »2.4 Analysis credit market ... public production and ... trap industrial chambers ... V.V.// Some results and perspectives development insurance market Russia // Finance. - ...
Analysis modern state and directions development Engineering of the Krasnoyarsk Territory
Essay \u003e\u003e Economy... Analysis modern state and directions development ... perspectives development ... industry. Aviation industry. In aviation industry enterprises of almost all industries are coexisted industrial production ... economy Russia: Studies ...
Modern state and perspectives development Publishing and Printing Activity
Examination \u003e\u003e Management... Modern STATE AND Perspectives Development ... production ... industry. 2.tendencies development Publishing and printing activities. IN development modern Publishing system Russia ... Book Market Russia: analysis, Problems, perspectives / Under ...
Agapova T. A., Sergina S. F. Macroeconomics. Business and service, 2007. - 496 p.
Bogdanov I.A. Economic security of Russia: theory and practice. - M.: Spairan, 2005.
Voronin Yu.M., Seleznev A.Z., Cherednichenko L.G. Russia: Economic growth. - M.: Publishing House "Financial Control", 2004.
State regulation of the economy: Tutorial / Ed. Morozova T.G. - M.: Uniti, 2005.
Zagashvili V.S. Economic security of Russia. - M.: Gardaria, 2004.
Ivashkovsky S.N. Macroeconomics. M.: Case, 2002. - 472 p.
Lisin V. Macroeconomic Theory and Economic Growth Policy: Monograph. - M.: Economics, 2004.
National Economics of Russia: Potentials, Complexes, Economic Security: Textbook / Ed. Lisova V.I. - M.: Economics, 2007.
Tarasevich L.S., Grebennikov P.I., Leusky A.I. Macroeconomics: textbook. - 5th ed., Act. and add. - M.: Yurait-Edition, 6th ed., 2006.
Economic Security: Production - Finance - Banks / under. ed. VC. Senchagova. - M.: Finstatinform, 2004.
AND perspectives development production Toilet soap Abstract \u003e\u003e Culture and Art
... Modern state and perspectives development production toilet soap. Modern Process production ... questions. 3. Analysis Assortment of toilet ... Production Soap B. Russia: (problems of raw materials) L.N.Lishaeva, V.I.Pochnikov // Oil and fat industry ...
Entry into the XXI century is characterized as the time of the grand achievements of humanity in all areas of its livelihoods and primarily in the field of industrial production. At the same time, it is necessary to characterize it with respect to the immutable fact that the level of achievements in various countries and industries is not significantly the same, and this differentiation has both objective and specific reasons. But the main trends in the development of machine-building production can be considered on the example of industrialized countries.
In the context of the globalization of the economy, each country forms and conducts state industrial and economic policies aimed at developing certain industries. During this kind of processes, trends characterizing the integrated sectoral orientation of the economy of various countries are clearly manifested:
- - The states in the economic structure of which the processing industries are prevailing the manufacturing industries, based on high technologies, that is, countries supplying finite goods and services of highly organized industries. These countries are defined as the most developed;
- - States where extractive industry prevail, that is, countries that are substantially living in the expense of resources, data from nature, and which, due to the weak development of manufacturing industries, often even these resources supply the world market as a final product, but as the initial raw materials for the subsequent Recycling. Such countries are presented as underdeveloped.
The task of state economic policy is to develop an industrial concept and the economic mechanism, based on the priority domestic industries, which will provide the country with the proper level of development of manufacturing industries in the framework of the international division of labor.
Today, the market dictates its requirements that must be taken into account at all stages of creating commercial products - from idea, design, production before disposal.
Industrial production of industrialized countries is characterized by the use of large-scale advances in high-tech flexible industries. Today, there is already a real opportunity to carry out technological management of the formation of the specified properties of products. At the same time, the role of information technologies at all stages of the product life cycle increases sharply.
Currently, many new technologies are created on the basis of the latest scientific achievements in the field of solid physics, high pressure physics, optics, biochemistry, microelectronics, etc. This leads to revolutionary changes in commodity saturation in industries such as energy, transport equipment, communications, Computer equipment, genetic engineering, etc.
Scientific and technical progress and competition that dictate the need to reduce production costs at the same time as in the process of producing a particular product (that is, within the framework of the production goal) and in the system of the actuator (that is, directly in the production structure) lead to the fact that many of the largest earlier Top specialized enterprises become multidisciplinary. Under these conditions, the sectoral orientation is no longer in the form of a specialized enterprise, but in the competitive struggle of multidisciplinary enterprises, the analysis of the functioning of which is currently becoming increasingly important both in the aspect of the production of a product and in the nature of the actions of production structures - manufacturers of this or other product submitted on industry markets.
Globalization, the creation of international strategic alliances led to the fact that competition between enterprises accepted an international character. Therefore, the development and development of new technologies matters not only for individual enterprises, but also for the industry as a whole. This means that stimulating the development of new technologies is dictated by both intra-profit interests and the interests of the entire industry.
Orientation for new technologies and the rapid progress of production equipment led to the emergence of progressive and flexible concentration of production, which found its expression in the concept of computerized integrated production . Reducing the duration of the production cycle, reducing funds, stocks in conjunction with the manufacture of products according to the principle of "exactly during" gave the production of certain reserves.
At the same time, production processes and machines began to connect to complex high-performance systems in which technological and organizational chains depend on each other.
Investments in flexible manufacturing systems strengthen the need for maximum use of time and technical capabilities. Errors and violations of the process will quickly lead to the downtime of this expensive system than with traditional or manual manufacture. According to research, many errors and violations of the manufacturing process are caused by non-manufacturing equipment and not in the chain of the direct processing process, but mainly in the field of planning and supplying
In order to have competitive production, it is necessary to learn to ensure the work of complex computer industries with maximum performance and quality. Highly developed progressive production with highly qualified personnel has additional benefits if it comes to the development of complex complex processes.
Thus, computerized integrated production can be considered as a global leading concept of industrial production of the second half of the XX century.
The greatest progress in the development of computerized integrated production has reached major aircraft and automotive enterprises, the electronic industry. However, the practice has shown that even these enterprises failed to fully implement the concept of computerized integrated production, but it became generally recognized that only this direction is able to activate the extensive rationalization potential in all areas of production.
Figure 1. Functions of computerized integrated production
The high cost of labor and a short working day, as well as permanent control of the performance of production tasks, accelerate the process of applying automated production. However, full automation and computerization of production is only the theory.
The most important stage of production development was the implementation of the Japanese concept "Lean Production" - "skinny production".
For LEAN Production, a number of basic principles can be formulated:
Each employee is assigned the maximum number of tasks and responsibility for their implementation.
Disadvantages and problems in production are eliminated immediately.
An extensive information system that each employee can take advantage of high flexibility and a quick response to violations or changes in the production process.
Working groups have a high level of independence.
The production climate is subordinated to a single enterprise strategy and determines mutual responsibility for the quality of work.
Analysis of these principles shows that the integration of production and elimination of non-productive losses are in the first place. Here, the system technology has already displaced the classical division of labor. Automatic regulation systems and high reliability contribute to a significant increase in productivity. These provisions are prerequisites for high efficiency of automated production.
The totality of the principles of "Lean Production" allows the continuous improvement of the production process in the form of a continuous (monotonous) or accelerated (jump-shaking) reduction of expenses by reducing wasteful (non-production) costs.
All that directly does not contribute to the manufacture of products is considered wasteful (non-productive) costs and eliminates, with the exception of the most necessary activities of indirect employees. As evaluation criteria, the duration of the productive cycle, the timing and costs of manufacturing, the volume of funds and product quality are used.
The concept of production development at the turn of the Millennium is based on a combination of advantages of the concept of "skinny production" and the concept of computerized integrated production of the first generation, since both persecute the same goals follow the same principles. The integration of the principles of these concepts can lead to other concepts capable of ensuring an increase in production efficiency on the paths of its increment and decentralization, accounting for the leading role of the human factor, which cannot be replaced by any level of development of the computer.
This concept is, of course, is associated with the reliability of technological processes, technological processes within the possible, managing the integrated process of process capable of teaching evolutionary production systems, using new computing architectures. Use systems must follow the decentralized structure of the organization of production. The introduction of neural networks and evolutionary algorithms allow the best way to manage processes.
Modern industrial production is characterized by the fact that most technological processes are implemented in the area bordering the utmost possibilities.
High performance and quality, intensive use of equipment - these are the characteristics that fundamentally exclude each other. The wider we spread the borders of productivity and quality in the process, the wronghength it becomes. On the other hand, the processes in the field of high speeds can be operated and at the same time achieve high processing and cost savings. A classic contradiction can be solved by controlling the technological process, the technological system.
Dynamically changing industrial production, requires such a dynamic change in organizational structures.
The world practice of post-industrial development confirms that both the overcoming of difficult social problems lies, first of all, in the field of intensive development of national production, its manufacturing industries, and it is on a basis to create a proper number of jobs that provide a high living time to the absolute majority of the country's population. In industrialized countries, this is not only an economic, but also a social task that unites the actions of both the state and business, and only due to their joint efforts the rigid social confrontation on the basis of social orientation of the economy is overcome.
At modern plants, the share of salaries and social insurance payments is about 50-70% of total production costs without the cost of materials. As a result of such development in the manufacture of products, it became possible to use the work of a noticeably smaller number of people. At the same time, the creative proportion of work is increasingly shifted towards planning and management, i.e. Further leaves from the immediate process of manufacture.
There is a movement of production personnel from the field of direct manufacturing in the planning and management area or in the field of maintenance of means of production.
The most important basic task of solving social problems is the development of manufacturing industries, and, it means that the creation of the proper number of jobs in this spectrum. Assessing the role, the structure of the machine-building complex, the state, the costs of its restoration and provision of the necessary pace of development can be argued that these tasks cannot be solved within its individual enterprises and even other larger production structures. This means that the problem of workplaces in mechanical engineering is an essential national task.
The degradation of engineering industries in the last fifteen-twenty years has led to the fact that a large number of specialists are lost both due to their transition to other areas of activity and "brain leaks". That is why the problem of creating jobs in mechanical engineering when setting the tasks of ensuring its development is closely related to such issues in personnel policy, as the formation of highly qualified specialists - doctors and candidates of science; preparation of engineering and technical composition; Ensuring the preparation of masters and workers of various levels of qualifications.
In industry as a whole and in the machine-building industry, in particular, a number of negative factors are operating, which again and reproduce the named and other problems, creating a large-scale system crisis in mechanical engineering.
The main systemic negative factors must be attributed:
the degradation of fixed assessment funds that have reached the critical mark;
low product quality, high production costs (metal-intensity, energy consumption, transportation), low profitability of production and, as a result, lack of working and investment funds for development;
ineffective personnel policy that does not contribute to attracting qualified specialists in the sphere of industrial production, scientific and technical and technological activities;
imperfection of the legislative framework for state industrial policies, technical regulation, pricing for engineering products, etc., generating:
b leading rise in prices for products and services of natural monopolies;
l lack of standards provided to international requirements;
limited capacity of the domestic market due to insufficiently high growth rates of the country's economy;
low competitiveness of Belarusian engineering products in the domestic and foreign market and low investment attractiveness of mechanical engineering (as a result of the factors outlined above).
At the same time, it should be recognized that the main reason for the established situation is the lack of an informed, based on the achievements of science and technology, a unified state strategy of transformation and the leading development of the domestic industry.
The manufacturing industry is a set of industrial and agricultural raw materials processing industries obtained by the mining industry in nature (mining, agriculture). This industry includes enterprises of black and non-ferrous metallurgy, woodworking enterprises, oil processing, gas and chemical products, metalworking and mechanical engineering, food, textile and pulp and paper production, sewing and shoe industry, production of building materials.
Geography of the manufacturing industry
The leaders of the manufacturing industry in the world are economically developed countries in which they are focused on the high-tech production of more expensive and innovative products. Championship, despite the weakening in recent years, the share of global production in the last years, keeps the manufacturing industry of the United States, then the Japan and the European Union country led by Germany. Ultrafast growth rates demonstrate asian industrial countries, in particular, China and South Korea industry. Processing production in Russia after a substantial decline in the 90s of the 20th century now demonstrate stable growth in many industries.
Types of processing industries
This type of production implies physical and / or chemical treatment of substances and materials in order to convert them to new products. The exception is the processing of waste. Products manufacturing can be ready for consumption or semi-finished products for further processing. Thus, a non-ferrous metal cleaning product is used to produce primary products (for example, aluminum or copper wire), which, in turn, will be applied to the production of machinery or machine components.

The structure of processing industries in Russia and the main types of products:
- Food products, including tobacco and beverage production (meat, vegetable and animal oils, bread and bakery, confectionery, sand sugar).
- Production of petroleum products (gasoline, automotive gasoline, diesel fuel, fuel oil).
- Metallurgy, including finished products (steel, finished rolling of ferrous metals).
- Chemical production (mineral fertilizers, synthetic resins and plastics, paints and varnishes).
- Production of rubber and plastic products (tires for various vehicles, pipes and pipe fittings from thermoplastics).
- Processing and manufacture of finished products from wood (lumber, plywood, chipboard, fiberboard).
- Mechanical engineering (production of machine tools for various purposes, industrial equipment).
- Cellulose and paper production (paper, cardboard).
- Textile and sewing production (fabrics, shoes).
The significance of the manufacturing industry
The manufacturing industry accounts for the overwhelming part of the product produced in the world. About 40% of the cost of all industrial products in the world falls on mechanical engineering. Significantly inferior chemical and food processing production. The share of these industries in total industrial products is approximately 15%. Woodworking and pulp and paper industries produce about 9-10% of all world products, and 5-7% fall on metallurgy and electric power industry.

In Russia, the shares from the volume of production between the manufacturing industries are distributed in approximately the following:
- Mechanical engineering - 22%.
- The oil refining industry is 21%.
- Black and non-ferrous metallurgy - 16%.
- Food industry - 16%.
- Chemical - 10%.
- Building materials production - 5%.
Metallurgy in the processing industry of Russia
The machining production of the metallurgical complex covers almost all stages of the technological process (except for raw materials) of obtaining finite products in the form of metals and alloys. This is an interactive combination of processes:
- Preparing raw materials (agglomeration, enrichment, concentrates).
- Metallurgical redistribution - obtaining steel, cast iron, various rolled products.
- Production of alloys.
The specificity of metallurgical production is the scale and complexity of the technological cycle. Production of many types of products provides 15-18 redistribution.

Ferrous metallurgy as part of the processing production
In terms of annually produced ferrous metals, Russia is significantly ahead of many countries of the world. Each of the eight largest enterprises of the country produces more than 3 million tons of products every year. Black metallurgy serves as a foundation for the development of the largest manufacturing industry - mechanical engineering. The technological process of producing ferrous metals as a type of processing production covers all stages, from the preparation of raw materials and auxiliary materials to the release of rolled and further redistribution. The metallurgical manufacturing industry, which is characterized by industrial combination, in Russia covers a large number of enterprises, eight of which are particularly large:
- Magnitogorsk, Chelyabinsk, Nizhny Tagilsky, Orsko-Khalilovsky Metallurgical Combines (Urals).
- Cherepovetsky Combine.
- Novolipetsky (Central Black Earth District).
- Kuznetsky and West Siberian Combines.
More than 90% of iron ore and 40% of secondary raw materials are processed by these enterprises.
Mechanical engineering
Machine-building machining productions are the largest consumers of products produced by ferrous metallurgy. The territorial proximity of these industries gives metallurgical enterprises the opportunity to specialize in accordance with the needs of mechanical engineering and use their waste as a redemption.

Machine-building enterprises producing difficult to transported products are located in the consumption areas. The products manufactured by the industry includes: agricultural machinery, mining equipment, turbines, machinery and mechanisms for other industries. Features of accommodation of heavy engineering enterprises play a large role in the implementation of the supply of finished products.
Oil refinery
Part of the country's oil industry. Since oil, in contrast to other types of fuel, requires mandatory primary processing for its further use, the oil refining industry has a sufficiently large scale. The resulting main products after oil treatment: kerosene, gasoline, diesel fuel and fuel oil. Recycling occurs at the refinery (oil refineries), the totality of which is the oil refining industry. Russia has 32 large and 80 small refinery with a total industrial capacity of about 300 million tons. In terms of processing, Russia ranks third in the world. Transportation of 95% of the entire crude oil from places of mining to the refinery in Russia provides trunk oil pipelines.

Outcome
The manufacturing industry reflects the degree of industrial development of the country. This is the leading sector of the global industry, which accounts for much of the cost of all products. Processing production is closely interconnected with other industries. In many countries of the world, advanced growth rates are always observed in this industry, and the share in the aggregate product volume often reaches 90%.
The developed industry and high level of the country's economy are key factors affecting the wealth and well-being of its population. Such a state has large economic opportunities and potential. The weighty component of the economy of many countries is the production.
What is modern production?
It is a type of manufacturing material and based on the use of science and technology achievements. Intensive changes in traditional production occurred in the mid-1990s, when the industry began to use technical innovations and develop world scientists of the 20th century. All spheres of modern production depend on science and information.
Structure of modern production
Modern production is divided into two types of activity:
- Material production, which includes the sectors of the national economy producing real benefits: agriculture, industry, construction, etc.
- which, in turn, is divided into two types:
- material services are aimed at meeting the physical needs of the consumer, the continuation of the manufacturing process, ensuring the necessary conditions for business activities. These include food production, transportation, communications, trade, storage of goods, tourism, maintenance of processes in enterprises, housing and household service;
- intangible services - actions directed directly to humans and its surrounding conditions. The result of such services does not acquire a substantive form. These include insurance, social services, health care, scientific activities, spiritual and intellectual services, reception in public areas and hotels, entertainment events, education and consulting.
Such a structure of modern production is due to the rapid development in recent years of various types of services and information technologies.
Features of modern production
Modern production is characterized by such features:
- an increase in the importance of services in industrial processes;
- the ability to satisfy not only the real needs of the consumer, but also its potential requirements;
- the development of information technologies that underlie production processes;
- the economy of many countries is significantly dependent on intangible areas: culture and art.

Factors of modern production
- Personnel - the company uses the work of specially trained people to create goods or changes in the objects of nature to meet the needs of society.
- Whether goods - various kinds of material things, with the help of which the goods and services are created by humanity. These include machinery (machines, tools, equipment, different apparatus and tools), natural resources (for example, water on hydroelectric power plants). Thanks to the means of labor, natural wealth is transformed into useful items and benefits.
- Labor objects are things or their aggregate that humanity uses to meet their needs. They are divided into natural substances that were not subject to change (coal layer), and raw materials that have passed some processing (separated by ore).
- Information - Recently, it plays a decisive role in production processes. Even if the enterprise owns the first three factors, without information it is doomed to closure.
Production technology

The technology of production of the enterprise is a set of special techniques and knowledge that apply to the product of the product of the appropriate quality. The use of technology must be accompanied by documentation describing all the requirements, conditions and quality standards on which the enterprise is focused during the production process.
The manufacturing company applies a set of input factors that form the technology of the enterprise. For example, the owner of the confectionery shop uses the labor of hired bakers, raw materials in the form of flour, sugar, different additives and capital - equipment, furnaces, various techniques for the production of bread, pies and confectionery.
Modern technology is more progressive, and the company can make some adjustments to it in order to increase the amount of finished products when set of standard production factors. Thus, the owner calculates that more profitable: time-consuming manual production process or the use of capital-intensive equipment.
Modern production technologies play a key role in the efficiency of activity. For this reason, the world actively distributes and exchanges advanced know-how. Thus, economists have identified information as a new special factor of modern production.
Information as a key to success
Information is a set of certain knowledge and information. All spheres of modern production are largely dependent on it. Information plays a crucial role, providing software management technique, the organization of the production process and its control, the possibility of rapid changes, instantaneous distribution of progressive ideas and technologies, advanced training and level of knowledge of workers.
The value of knowledge in all spheres is growing every day. Economists have identified this trend in a separate process called the information revolution. It was she who caused the transition of developed countries from the industrial type of society to the information.

Types of modern production
The XXI century is characterized by a large variety of production activities. The largest enterprises compete for mastering new niches of the market, creating unknown products and services.
List all the products currently existing in our days is very difficult. But all of them, depending on the subjects, are combined into such groups:
- Food production.
- Construction.
- Consumer goods manufacturing.
- Recycling recycling.
- Production of building materials.
- Manufacturing material base for enterprises.
- Chemical production.
In each country, the development of these may differ and depends mainly on the availability of the necessary raw materials and production facilities.

Organization of modern production
The organization is an association of all processes and elements of production, ensuring their interaction, creating conditions for the implementation of the economic goals of the enterprise and the social needs of employees.
Thanks to the rapid technological development and development of new activities, the organization of production has significantly changed.
So, in the era of industrial society, industrial production was considered the main sector of the national economy. It was based on mass production, which went down in history as Fordism - on behalf of Henry Ford, who first used this method of organization in his automotive factory. The key components of the mass production of that time were:
- rationalization - the alignment of each employment to the simplest operations and the definition of such a sequence that would lead to the most rapid production;
- standardization of parts and processes - reducing the diversity of operations in order to reduce the cost of time;
- conveyorization of continuous production is an increase in the volume of manufactured products and a reduction in its cost.
Thus, mass production ensured a large increase in labor productivity and considerable resource savings.

However, in the future, society faced the first problems of such an organization. The mass production of goods overstended the market to the same type of products, and consumer demand was increasingly displaced towards exclusive goods. Such an individualization of demand forced most industrial enterprises to change and start applying multipurpose equipment with software control, which is used to this day.
The widespread introduction of such flexible production systems is the main feature of the organization of modern production. Thanks to this, products can still be large, but the goods are distinguished by a variety of assortment.
Problems of modern production

In modern conditions for the development of the economy, manufacturing enterprises face important problems:
- Any type of production requires constant technical upgrades. In order for the activity to be effective and brought profits, it is necessary to ensure the growth of production, increase competitiveness, expand the markets for the sales of goods. To implement these tasks, technological upgrades should be applied.
- Deficit of financing and logistical base. In such conditions, the enterprise does not have the opportunity to develop, introduce new technologies and innovations, master the highest level of production.
- Insufficiently developed research and development in the enterprise. This problem negatively affects the state of the industry as a whole. Improved knowledge, lack of developments and modern studies lead to a gradual decline in activities and a decrease in production growth rates.
- Worsening social conditions at the enterprise, which leads to a sharp outflow of qualified personnel. The lack of specialists negatively affects the development of industry.
It is possible to solve these problems using investment in modern production technologies. To do this, you can use the internal capital of the enterprise or to attract funding from.
Modern production and ecology
Production is largely associated with nature. Modern industry in large volumes uses natural resources. As a result, nature is depleted, the health of people, the conditions of their existence deteriorate. This problem is so urgent that the governments of all countries have set themselves the task in obligatory to keep records of the environmental factor.
Such a decision made significant changes to the production of modern enterprises. They are forced to switch to waste-free and use protective and cleaning devices, conduct scientific developments and research on environmental protection.