Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the lumbar-sacral division and their treatment. Degenerate-dystrophic changes in the lumbosacral spine of the spine degenerative dystrophic changes in the lumbar spine of the hernia of disks
Pathological changes in the lumbar department arise over a variety of negative factors.
You can allocate the main reasons:
- A low-effective lifestyle. If there are no load on the lower back, then this leads to the weakening of the muscles. As a result, the ability to resist even low loads.
- Mechanical and generic injuries.
- Professional sport with exorbitant loads. Destructive changes are often starting due to raising excessive weights and sharp movements without heating muscles.
- Supercooling of the body.
- Inflammatory processes in the spine (arthritis, Bekhterev's disease).
- The aging of the body. The necessary components from cartilage and bone tissues occurs.
- Unhealthy diet. It often obesity is often observed, which negatively affects the spine.
There are many other factors that affect the emergence of dystrophic changes. In addition, several triggers can affect the vertebral pillar. It follows from this that it is almost impossible to identify the cause.
Possible consequences
If you ignore the development of degenerative changes, then serious complications may arise in the zone:
- Osteochondropathy.
- Loss of motor abilities and leg sensitivity.
- Paralysis of the lower limbs.
- Difficulties with defecation and urination.
- Violation of sexual dysfunction.

So that this does not happen, you need a timely and competently selected treatment that can stop the destruction of intervertebral disks.
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
Unfortunately, a person does not suspect the disease, not yet appear pain in the lower backwhich limits disability. The degenerative process does not show itself, the symptoms indicate its complications.
It is necessary to visit the neurologist if the following sensations appear:
- Pain syndrome after a long stay in an uncomfortable posture.
- Painful sensations after physical exertion.
- The appearance of weakness B. lower limbs.
- Difficulties with inclons and turns.
- Five of the spine B. morning time.
- Constipation and problem with urination.
- Cold skin in the loan area.
- Body symmetry broke.
- Sweets and redness of the skin in the lower spine.
Symptoms are enhanced depending on the stage of development of pathology:
| Stage 1 | Symptoms appear extremely rarely. Sometimes blunt pain Appears after loads, but usually, it is written off on a sense of fatigue. |
| 2 stage | Symptoms are already arising. It is difficult to beat, sometimes the back "takes over." Suggested nerve endings cause tingling in the pelvic zone. |
| 3 stages | Considered sharp. Damage blood vesselsMetabolism is disturbed in lumbar muscles, ischemia begins to develop. The pain syndrome is enhanced, the legs are neme and cramps. |
| 4 stages | Paralicate legs may occur since the spinal cord is already deformed. |
Symptoms manifest themselves most bright during exacerbation. When dystrophic processes take a chronic form, the signs of illness are characterized by muted discomfort.
 Determine the degenerative process in the initial stage of development is very difficult. It is usually detected only during a planned medical examination. But if a visit to the clinic is caused by the pain in the lower back, the disease is already progressing.
Determine the degenerative process in the initial stage of development is very difficult. It is usually detected only during a planned medical examination. But if a visit to the clinic is caused by the pain in the lower back, the disease is already progressing.
It is important to detect the problem before the appearance of the first complications. To do this, use various diagnostic methods covering wide spectrum stimuli. But initially inspected by a neurologist. The doctor then prescribes additional research, to clarify the diagnosis.
Usually carry out the following procedures: radiography, computed tomography, MRI.
X-ray is the most affordable method, but uninformative. It determines the disease in the late stage. CT and MRI are more priority. They allow you to more accurately determine the location of localization, as well as the degree of damage.
MRI most reliably indicates the presence of degenerative changes.
The results of the MRI on the presence of dystrophic processes:
- The disc is destroyed more than 50%.
- Dehydration disk. On MRI, he looks darker.
- Accurately determines the presence of protrusions and hernia.
- Resets erosion of the cartilaginous plate through which the cells inside the disk are powered.
Sometimes it is necessary to carry out an electronomyrography to understand where and how the nerve is amazed. Naturally, blood for analysis is handed over to detect endocrine disorders and possible infections.
Video: "degenerative dystrophic changes Spine: Lecture "
Treatment
Do you know that ...
Next fact
First, conservative therapy is carried out: various drugs for anesthesia, warming ointments, medical gymnastics, massage and physiotherapeutic procedures. If these methods do not help, then decide on operational intervention.
Preparations
First of all, it is necessary to remove pain syndrome, which will allow a person to move normally. For this appointed anesthetics (Ketanov, Kathetonal) and anti-inflammatory drugs (Movied, diclofenac). These medicines are applied externally, orally and by injection.
To relax lumbar muscles, use miorolaxanta (Middokalm, Sirdalud). They are used with intervals due to weakening muscles.
Hondroprotectors are used that will help speed up the regeneration of cartilage and joints.
Treatment with drugs gives a positive effect, but one should not forget about adverse reactions, as medications often violate the work of the gastrointestinal tract.
Surgical intervention
Usually conservative treatment of the patient's condition makes it easier. The operation is necessary if pathology continues to progress, and medical therapy powerless. The surgeon establishes special devices to maintain the lumbar spine. This removes the pressure and prevents the further deformation of the intervertebral disks in the lower back area.
LFK
Therapeutic gymnastics is necessary during treatment, and during the rehabilitation period. Exercise are shown in any manifestations of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the lumbar department. Naturally, the causes, sharpness of the process and the main symptoms of the disease should be taken into account.
In the acute phase of the disease, the FFC, naturally, is not performed. First you need to achieve a decrease in pain by other methods: absolute peace, NSAIDs, blockades, local cooling and other procedures.
With intensive manifestations, low-amplitude and static exercises performed very carefully and slowly shown. During the period of rehabilitation, dynamic complexes are preferable.
In the future, the complexes are complicated, and exercises with weighting agents are added.
Massage and physiotherapy
 Conducting this procedure in dystrophic changes in the lumbar department causes disputes in a medical environment.. Mechanical impact on discs harm and healthy spine. Massage can be allowed if soft tissues are massized by an experienced specialist and in the initial stage of the disease.
Conducting this procedure in dystrophic changes in the lumbar department causes disputes in a medical environment.. Mechanical impact on discs harm and healthy spine. Massage can be allowed if soft tissues are massized by an experienced specialist and in the initial stage of the disease.
Massage is prohibited in a sharp periodSince manipulations cause blood flow, and this provokes an increase in inflammation and waste.
During remission, when there is no inflammation and acute pain, and physiotherapy is applied. Electrophoresis, acupuncture and magnetotherapy accelerate recovery. Manual therapy will restore the normal position of the vertebrae.
Independent treatment at home is better to exclude. Not knowing the causes and accurate diagnosis of the disease that caused dystrophic changes in the lumbar department, you can only harm your health.
Prevention
To prevent degenerative dystrophic changes, much effort is required. But even simple preventive measures Let save mobility and health. It is impossible to stop the aging of the cartilage and bones, but each in the power to slow down the degeneration of any spine.
What is needed for this:
- It is necessary to strengthen the spine muscles. For the development of a muscular corset, power exercises are needed, and swimming will benefit.
- You always need to be active. The lack of movements leads to the atrophing of the muscles and loss of the elasticity of the ligaments. To spin is healthy, you just need to do a daily charge.
- It is advisable to avoid excessive physical exertion.
- It should be monitored, the back should always be straight.
- It is better to sleep at an orthopedic mattress that allows you to fully relax.
Compliance with these rules will not allow dystrophic changes and will extend activity to old age.
Forecast
Degenerative changes in the initial stage are treated relatively successfully. If the doctor correctly selects the procedure procedures, then the pain decreases significantly, and all processes in the intervertebral disc are artificially normalized. Full recovery will not succeed, but stop the progression of pathology is quite real.
Conclusion
If the back starts to hurt regularly, then this is a reason for anxiety. Unfortunately, our body agrees, and the first blow to the natural process takes the spine. At first symptoms, you need to visit the doctor, since even harmless signs can signal about serious diseases. Degenerative dystrophic violations irreversibleBut timely treatment can stop the process or at least slow down.
Different spine departments take over the load of varying degrees of complexity. And a sedentary or hyperactive lifestyle can aggravate the situation and lead to the destruction of bone and cartilage tissue. Very often, such changes arise in the sacrats and lumbar department, which leads to the appearance of sustainable owl syndrome and limit the mobility of the skeleton.
Under the degenerative-dystrophic changes, the resulting mechanical destruction of the bone and cartilage tissues of the spinal column is separated in lumbar-sacrats. Destructive changes are accompanied by deformation, loss of elasticity of cartilage. Degenerative processes are accompanied by systematic pains in the occurrence of complications in the form of pinching nerves and blood vessels.
The complexity of the diagnosis of the problem is slow progression, due to which it is not always possible to identify the initial degenerative changes of the lumbar-sacrive degenerate.
All destructive disorders have general features, symptoms and causes of occurrence. However, they are also possible to divide into the following types:

Such pathologies are also diagnosed in other spinal departments. However, due to the characteristics of the mobility of the skeleton, the lumbar-sacral is most striking.
Risk factors and causes of destruction
Women suffer from the diseases of this group significantly more often than men, since their muscular corset in the lumbar region is somewhat weaker. Because of this, the vertebral post does not get support and it is experiencing a large load.
In addition, the spine is a complex element of a skeleton consisting of a variety of vertebrae, vertebrates and connections. Cartickers play the role of the shock absorber and with a significant loss of moisture wear and thinned, and can also be sucked.
Among the main risk factors and prerequisites for the development of degenerative changes in the lumbar spine:
- Increased physical exertion with uneven distribution over the spinal column;
- Lifelong lifestyle and muscle frame weakness;
- Traumatic damage to the spine, muscles and ligaments;
- Overweight, obesity;
- Hormonal disorders in the body;
- Infectious pathology;
- Age-related changes in skeleton, ligaments and muscles;
- Bad habits;
- Irrational nutrition and lack of vitamins and mineral components;
- Bad environmental situation;

An earlieutful factor plays an important role in the degenerative and dystrophic changes of the lumbar department. The presence of genetic susceptibility significantly increases the risk of diseases of the spine and its components. In addition, the basis of the problem may be laid in childhood, especially with poor nutrition.
Symptomatics
In the early stages of the progression of the disease, they practically do not show themselves, in some cases quick fatigue is possible. Therefore, patients appeal to doctors only when visible symptoms occur.
The following pronounced signs of degenerative-dystrophic changes of the lumbar department are distinguished:
- Pain of different types (stitching, nunning, burning);
- Cold skin surface in the lower back region;
- Weakness in the lower limbs;
- Difficulties in slopes and corps turns, the occurrence of pain;
- Asymmetry of the case;
- Significant mobility of the body, mainly in the morning hours;
- The occurrence of pain syndrome with long-term finding of the body in one position;
- Difficulties when urination, stool violations.

The symptoms of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the lumbar and sacrilate spine manifests itself gradually depending on the development stage of the disease.
Select four main stages:

The faster the dystrophic changes of the lumbar-sacrive department will be found, the more the patient has a chance of recovery. Significant tissue destruction and pinching is practically not amenable to treatment.
Other signs are also helped to identify diseases in the early stages:
- Dryness and peeling of skin;
- Chlority;
- Increased susceptibility to cold.
Modern diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of the disease takes place in several stages. First of all, the doctor forms an anamnesis, studies the history of the patient's disease and makes a primary conclusion. There is no compulsory inspection on the subject of visible changes, mobility, muscle strength. Also applied palpancy affected area.
At the second stage, the following types of diagnostic studies are necessary:

Also consultation of specialists and other directions to eliminate other possible pathologies of the body may also be needed.
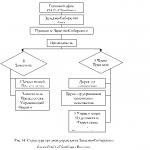
Methods of treating violations
In practice, three main types of treatment of the degenerative-dystrophic disease of the spine of the lumbar department are used: conservative, physiography, surgery. In some cases, it is possible to use combinations of methods in therapy.
Medicia treatment
The use of medicines in the form of tablets, injections, ointments and gels is necessary to reduce inflammatory processes and removal of pain syndrome. For this purpose:

Also additionally prescribed vitamin and mineral complex for restoring and maintaining cartilage and bone tissue.
Massage and therapeutic gymnastics
These measures are aimed at solving the following tasks:

Additionally, to improve the condition in degenerative-dystrophic changes, the lumbar is separated by swimming, acupuncture, point massage, physiotherapy (laser and electrophoresis).
Surgical intervention
At the last stages of the progression of degenerative-dystrophic changes, the lumbosacral department, conservative methods help only slightly alleviate the health of the patient. As a rule, in such situations, the main method of therapy is selected surgery. The course of intervention depends on the specific type of destruction.
Typically, treatment includes the following measures:

After the operation, the patient shows a full-fledged rest and sleep, a specialized diet, carrying a corset, receiving preventive drugs, therapeutic physical culture (in the last stages of recovery).
Folk remedies
For acute diseases Spine remove pain syndrome and reduce inflammatory processes help recipes folk Medicine:

Apply the recipes of traditional medicine as an alternative to professional treatment is extremely recommended. Before use, you must consult with your doctor.
Possible complications
In the absence of proper treatment, serious complications are possible in the form of a protrusion of disks, the expanding of osteophytes to a significant limitation of mobility, paralysis of the limbs, hernia.
Eliminating and facilitating the flow of pathologies is much more difficult and does not always bring positive results. Therefore, it is important to begin the therapy of destructive violations of the spinal column in the early stages of their appearance.
Prevention
Preventive measures against degenerative changes in the lumbar spine of the spine are carried out from young age, especially in the presence of genetic predisposition. This uses:

It is important to track posture and properly distribute the load on the spine. In the event of uncomfortable sensations in the back, it is necessary to contact an orthopedic or surgeon as soon as possible.
Conclusion
Degenerate-dystrophic changes in the lumbar spine - a complex of various diseases affecting cartilage and bone tissue, joints, muscles and ligaments. The occurrence of these pathologies is most often due to the incorrect distribution of loads on the skeleton or a sedentary lifestyle, in which the supporting muscles are atrophy.
That is why it is important to prevent extremes, apply the medical gymnastics in practice and in the event of the first signs of discomfort to see a doctor for professional help.
Degenerative diseases of the spine are a consequence of the loss of the elasticity of intervertebral discs, which had an influence of a sedentary lifestyle, excess weight, incorrect posture. The destruction of bone tissues, ligaments, joints leads to a violation of metabolic processes in organs, the absence of full-fledged cell nutrition. Thickening, the loss of the form of vertebrae of intervertebral discs leads to hernias, cracks, pinched nervous endings, limited in movements, loss of performance, and in running stages to disability.
The human body from nature is endowed with the ability to distribute physical exertion on the spinal departments. With proper posture, a strong corset from muscular fabric Withstands "Tests" without unpleasant consequences. People, not engaged in sports and physical exertion, ligaments, muscles in the state of weakness, which is why the destruction of intervertebral disks arises. Excessive loads that are not comparable to physical possibilities also harm the body.
Dystrophic changes of the spine occur due to not an active lifestyle. During the physical exertion, unprepared cartilage, ligaments, other fabrics are cleaned moisture, forming breaks and cracks. The absence of blood supply in intervertebral discs aggravates the process of restoring tissues.
Degenerative changes of the lumbar spine are caused by different reasons, regardless of age category, passive or active lifestyle. Main phenomena:
- The aging of cells and body tissues, which leads to a deterioration in the flow of nutrition, the necessary substances;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Smoking, excessive use of alcoholic beverages and other bad habits;
- Weakening of ligaments and muscles caused by a sedentary lifestyle;
- Fat deposits;
- The absence of essential substances in the diet;
- Collection in the hormonal field;
- Infectious diseases and inflammation;
- Microtraums and injuries of ligaments, muscles and spines, obtained due to excessive load;
- Sharp load when lifting heavy items;
- An exercise or sports exercise associated with the abundance of loads on the lumbar department.
Signs
Dystrophic changes in the disease of the spine proceed slowly, tightening for many years, so it is not always possible to define the first symptoms and turn to a specialist immediately. People resorting to folk methods, without surveys, accurately established diagnosis, exacerbate their own position. During the examination using MRI or X-ray, changes in the sacral spine, which exerted under the strong influence of the destructive power of pathology.
Dystrophic diseases of the spine are manifested by the following features:
- The pain in the area of \u200b\u200bthe lumbar department, which gains strength when a person sits, leans, is experiencing other loads. Pokes at night time at night;
- Degenerative changes in intervertebral discs are manifested by the pain of the berries, the lower extremities;
- The activity of the departments in the spine is reduced;
- The performance of the organs located in a small pelvis is disturbed;
- In the degenerative dystrophic disease of the spine swells and bluses the region of the sacrum of the lower back;
- A person is faster tires;
- The numbness and tingling of the buttocks and legs are felt;
- From dystrophic changes a gait is broken.
In the absence of treatment of degenerative dystrophic changes in the spine, the processes worsen blood circulation, causing paresis or paralysis.

The degenerative change in the spine denote the overall picture of pathologies accompanied by painful processes. Features and signs of dystrophic changes are summarized by several diseases developing together or separately.
- Due to the dystrophic changes, the thinning of the vertebrae, chronic osteochondrosis occurs;
- The destruction of the vertebrae during hondrosis by occurrence of microcracks appears in people in the youth, experiencing strong vertebrate loads, intervertebral discs;
- In case of degenerative dystrophic changes in the spine arises spondylosis. The growths from the edges of the vertebrae appear, with the time the possibility of the actions of the spine is limited due to ossification;
- The vertebrae is destroyed due to the defeat of the joints between them. Such degenerative dystrophic change is called. As with spondylise, bone growths appear, causing strong field sensations in any form of movements;
- The results of dystrophic changes in the bodies of the vertebrae are manifested in the hernia formed between the vertebrae, the cause of which is the spill of the fibrous ring of the disk. The squeezing and protrusion of nerves roots cause pain.

Treatment methods
Tasks facing therapy: Getting rid of pain in the field of pathology, slowing down the flow of the dystrophic process, the return of the muscles of strength, the restoration of bone tissues and cartilage, providing the spine to the former mobility.
The spine is pulled out, prescribed orthopedic bandages, limit mobility in the event of an acute period of the disease. Prescribe medicines for the removal of pain and accelerate the recovery process: hormonal injections, novocaine blockades, npvpt tablets. Physiosters, massage, therapeutic physical culture are prescribed during remission. When the treatment of dystrophic changes does not bring results, pain is not reduced, the surgery of surgeons are prescribed.
Benefits a special diet, fit into the overall complex of combating the disease. Useful products rich in calcium, vitamins. The duration of therapeutic process depends on how strong degenerative dystrophic lesions of the spine. Timely appeal for help allows you to get rid of pathology for twelve months, completely returning the spine health.
- We advise you to read:
Preparations
Remove pain allow non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics. Mioryelaxants are prescribed to get rid of spasms in muscle tissue. Vitamin complexes of a group B, drugs, accelerating blood circulation, sedative medicines support, nourish the body. Chondroprotectors responsible for the restoration of cartilage are used both for outdoor and internal use. Tablets, ointment, gels appoint a doctor, based on the general clinical picture. In the complex treatment, the vertebral dystrophy stops development.
Physiotherapy
With remission with missing pain syndrome, inflammatory process Assign:
- Massage accelerating blood flow in the body that improves metabolism;
- Manual therapy restoring the location of each vertebra;
- Acupuncture, magnetotherapy, electrophoresis, UHF.
Few people know what the concept is like a flavor, it allows not only to improve the mobility of the spine, but also to render positive impact All organism:
- Slow down the pathological development of the disease;
- Improve the metabolic processes and components, increase blood circulation;
- Return a healthy former look, posture structure;
- Strengthen the base of the corset of the muscles;
- Increase the mobility of the vertebrae, save the elasticity of all elements.

Degenerative dystrophic changes in the lumbosacral spine - this is a syndrome in which the pathology of the intervertebral disk provokes the appearance of pain in the lower back.
Although there is a small genetic predisposition to the emergence of this disease, the true reason for the appearance of degenerative changes in the spine, apparently, is multifactorial. Degenerative changes may be due to the natural process of aging organism or have a traumatic nature. However, they rarely become an extensive injury, for example, a car accident. Most often, it will be about a slow traumatic process, leading to damage to the intervertebral disc, which progresses with time.
The intervertebral disk itself is not provided by the blood supply system, so if it is damaged, it cannot recover in such a way, how other tissues of the body are restored. Therefore, even a minor damage to the disk may entail the so-called. "Degenerative Cascade", due to which the intervertebral disc is beginning to collapse. Despite the relative severity of this disease, it is very common, and, according to modern estimates, at least 30% of people aged 30-50 years have some degree of degeneration of disk space, although not all of them experience pain or have a corresponding diagnosis. In fact, in patients over 60 years old, some level of degeneration of intervertebral discs, detected by MRI, is rather a rule, rather than exception.
Causes
Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the lumbosacral spine are usually provoked by one or both of the two reasons below:
- Inflammation occurring when proteins in the disk space in the formation of an intervertebral hernia annoy nervous roots.
- The pathological instability of microdvatures, when the outer sheath of the disk (fibrous ring) is wears and cannot effectively withstand the load on the spine, which leads to excessive mobility in the affected spine segment.
The combination of both factors can lead to permanent pain in the lower back.
The combination of both factors is most common in the formation of an intervertebral hernia, which is a complication of the degenerative-dystrophic process in intervertebral discs. With the appearance of the hernia, the disk is also added to the mechanical compression of the vascular-nerve beam held in the spine channel, as a result of which the pain in the lower back is significantly enhanced and becomes permanent.
Symptoms
Most patients with degenerative dystrophic changes in the lumbosacral spine are experiencing a permanent, but tolerant pain, which from time to time is intensified for several days or more. Symptoms may vary depending on the specific case, but the main symptoms are as follows:
- Pain, localized in the lower back, which can irradiating into hips and legs;
- Long pain at the bottom of the back (lasting more than 6 weeks);
- Pain in the lower back is usually described as a stupid or novaya, as opposed to burning pain in those places where it is irradiants;
- The pain is usually enhanced in a sitting position when the discs are experiencing a more pronounced load compared to the one that turns out to be on the spine when the patient stands, walks or lies. Long standing can also increase pain, as well as tilting forward and raising objects;
- The pain is exacerbated when performing certain movements, especially when the slope, damages of the body and lifting weights;
- When the hernia is formed, the symptoms may include sensations of numbness and tingling in the legs, as well as difficulties in walking;
- With an average or large size of the intervertebral hernia, nervous spine coming out of spinal cord on the affected level, it may be squeezed (foormal stenosis), which, in turn, can lead to the appearance of pain in the legs (ISIASU);
- Neurological symptoms (for example, weakness in the lower limbs) or violation of the function of the pelvic organs (various urination and defecation disorders) may be a consequence of the development of horse-tail syndrome. With a horse-tail syndrome, immediate actions for the provision of qualified medical care are required.
- In addition to pain in the lower back, the patient may also experience pain in the legs, numbness or tingling. Even in the absence of squeezing the nervous root, other vertebral structures can cause irradiation of pain in the buttocks and legs. Nerves become more sensitive due to inflammation, provoked by proteins within disk space, which causes the appearance of sensations of numbness and tingling. Usually in such cases the pain does not fall below the knee;
In addition to degenerative changes in intervertebral discs, the cause of pain can be:
- Stenosis (narrowing) of the spinal canal and / or osteoarthritis, as well as other progressive diseases of the spine, the occurrence of which contributes to the degeneration of intervertebral discs;
- Intervertebral hernia, the consequence of the degeneration of the intervertebral disk.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of the presence of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the lumbosacral spine, as a rule, is carried out in three steps:
- The preparation of the patient's history, including when pain appeared, a description of pain and other symptoms, as well as actions, positions and treatment methods (if treatment was carried out), which weakened or, on the contrary, enhance pain;
- Medical examination, during which the doctor checks the patient for the presence of the latter signs of the degeneration of the intervertebral disk. This inspection may include an inspection of the amplitude of the patient's movements, its muscular strength, the search for painful areas, etc.
- MRI scanning, which is used to confirm suspicion of the presence of degenerative changes of the spine, as well as to identify other potential reasons that led to the appearance of painful symptoms in the patient.
The results of MRI, with the greatest probability indicating the presence of degenerative changes as causes of pain symptoms:
- Disk space is destroyed by more than 50%;
- Initial signs of degeneration disk space, such as disk dehydration (on MRI such disk will look darker, because it will contain less water than in a healthy disk);
- There are signs of erosion cartilage end plate of the vertebral body. The disc does not have its own blood supply system, but, nevertheless, living cells are located inside disk space. These cells are powered by diffusion through the terminal plate. Pathological changes in the terminal plate as a result of degeneration lead to cellular disorders. Similar changes are best visible on T2-suspended images made in the saggital plane. Usually, the terminal plate on MRI looks like a black line. If this black line is not visible, it speaks about the erosion of the end plate.
- Tarrow in fibrous ring
- Availability of protrusion or intervertebral hernia
Treatment
The prevailing majority of cases of degeneration of the intervertebral disk do not require operational intervention and are treated with conservative methods that include special medicinal gymnastics, physiotherapy, various types of massages. In addition, the degeneration of disks helps the stretch of the spine, since it increases the distances between the vertebrae, allows the intervertebral disc to obtain the water and nutrients they need, which contributes to its recovery.
Article Added to Yandex Webmaster 22.07.2014, 13:32
- 1) The hyperlink can lead to the domain www.Site or the page with which you copied our materials (at your discretion);
- 2) on every page of your site, where our materials are located, should stand an active hyperlink to our website www.site;
- 4) If you copied more than 5 materials (i.e., on your site more than 5 pages with our materials, you need to put hyperlinks to all author articles). In addition, you should also put a link to our website www ..
We bring to your attention a classic article on this issue.
Degenerate-dystrophic changes in the lumbosacral spine (prevalence, clinic, prevention)
ON. Pozdeeva, V.A. Socokikov
GU NC RVH of the ISTTS SO RAM (Irkutsk)
Diagnosis of displacements of lumbar vertebrae is one of the least studied issues in radiology. Interest in this pathological condition of the spine is not accidental. Unstable - vertebrae displacement - as one of the forms of dysfunction of the motor segment causes pain syndrome and subsequent neurological disorders. Taking into account the costs of diagnosis and treatment, as well as to compensate for disability working, disability, it can be argued that pain in the lower back is the third most expensive disease after heart disease and cancer.
Degenerative - Dystrophic Changes in Lumbosacral Part of the Spine
(Occurrence, Clinic, Prophylaxis)
N.A. POZDEYEVA, V.A. Sorokovikov.
SC RRS ESSC SB Rams, Irkutsk
Diagnostics of Dislocation of Lumbar Vertebrae Is One of the Less Studied Issues of Radiology. INTEREST TO THIS PATHOLOGICAL CONDITION IS NOT AT ALL CASUAL. Instability - Vertebrae Dislocation. - As One Form, Of the Dysfunction of Movement Segment Becom A Cause of Pain Syndrome and Further coming Neurological Disorders. Taking Into Consideration Expenses of Diagnostics and Treatment, And Also of Compensation of Disablement of Working Patients, Invalidity, We May Assert That Lumbar Pain Syndrome Is The Third, Of the Most "Expensive" Disease After Coronary Disorders and Cancer.
Degenerative diseases of the spine - one of the leading social problemsWith an important economic aspect, since this pathology is more likely to suffer from people of young and middle age, which constitute the most numerous category of the working-age population. According to Holger Pettersson (1995), the diagnosis of these diseases is difficult, because There is a weak correlation between the results of x-ray surveys and clinical symptoms.
Diagnosis of displacements of lumbar vertebrae is one of the least studied issues in radiology. Interest in this pathological condition of the spine is not accidental. Unstable - vertebrae displacement - as one of the forms of dysfunction of the motor segment causes pain syndrome and subsequent neurological disorders. Taking into account the costs of diagnosis and treatment, as well as to compensate for disability working, disability, it can be argued that back pain syndrome is the third most expensive disease after cancer and heart disease.
The medical and socio-economic significance of the problem of the diagnosis and treatment of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is due to a number of reasons. According to the World Drawing Organization (2003) osteochondrosis of the spine suffers from 30 to 87% of the most able-bodied population aged from 30 to 60 years. The share of osteochondrosis of the spine accounted for from 20 to 80% of cases of temporary disability. The incidence rates in Russia tend to increase, while in the overwhelming majority of patients the disease is accompanied by the defeat of the lumbar spine. According to the materials of the VIII World Congress dedicated to the pain, which took place in Vancouver in 1996, back pain is the second in frequency of treatment of the doctor and the third in frequency of hospitalization after respiratory diseases, while 60-80% of the population experienced it at least one day. In the structure of the incidence of the adult population of our country, the lumbar osteochondrosis is 48 - 52%, occupying the first place, including by the number of days of disability. Temporary disability in 40% of neurological diseases is due to lumbashing syndromes. In the overall structure of disabilities from diseases of the bone-articular system, degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the spine are 20.4%. An indicator of disability in degenerative diseases of the spine is 0.4 per 10,000 inhabitants. Among the disabled people with other diseases of the musculoskeletal system, this pathological state occupies the first place in the frequency of occurrence, and 2/3 of patients with disabilities are lost completely.
The mobility of the spine is possible due to the complex interactions of the elastic apparatus of the bodies of the vertebrae, the arms and intervertebral discs. The functional unit of the spine at any level is the motor segment - the concept introduced by Iunghanus in 1930. The motor segment includes two adjacent vertebra, a disk between them, a corresponding pair of intervertebral joints and a binder at this level. At the level of some single segment, the mobility of the spine is relatively small, but the summable movements of the segments provide it as a whole in broader limits.
Research LB Phialova (1967), Buetti-Bauml (1964) and others show that in the lumbar department, the L4 - L5 segment is the most mobile in terms of flexion and extension in the front plane; This explains its overload, leading to degenerative lesions and vertebral displacements.
Intervertebral joints belong to the group of sedentary, and are combined articulations. The main functional purpose of the spine joints is the direction of movement, as well as the limitation of the volume of movement within these directions.
Under normal statics, the articular processes are not carried by vertical loads: the effect of the amortization of the vertically grace (gravity of the head, the body) is carried out by intervertebral discs. In cases where the artic processes are forced to at least partially perform a support, not characteristic of it (for large static loads on the spine, in combination with obesity), local arthrosis develops in true joints (antaltlests), and with a significant, ever-increasing vertical load - neoarthritis of articular processes with the bases of the forehead.
The role of the disk in the statics of the spine lies in the depreciation of the pressure rendered on the spine weight luxury and physical exertion. This means that the force acting on the intervertebral disk must be balanced equal in magnitude, but opposed in the direction of the power of the disk.
Not only the entire spine resists the applied force, but also the muscular-ligament body of the body, which adjusts to the external load. The most important is the forces acting in the plane of the disks, in other words, the thrust efforts transmitted to the disk. They can achieve significant intensity and cause most damage to mechanical discs.
A certain form of damage to the spine can be classified as or stable or unstable damage. The concept of "stable and unstable damage" was introduced by Nicoll in 1949 for the lumbar spine, and in 1963 HoldSworth was distributed to the whole spine. According to this theory, the rupture of the rear structure is a prerequisite for the instability of the spine.
F. Denis (1982-1984) presented a three-pressure concept of spinal instability - the theory of "three columns", while the front support structure consists of: anterior longitudinal bundle, the front of the fibrous ring, the front half of the vertebral bodies; The average support structure from: rear longitudinal ligament, the back of the fibrous ring, the back of half the bodies of the vertebrae and the rear support structure includes: Supply ligament, interstice ligament, articular capsules, yellow bundles, vertebral arcs. According to this theory, for the occurrence of instability, a gap of both the rear and average support structures is required.
Degenerative-dystrophic changes in spinal segments are developing mainly as a result of sharp and chronic overloads under the influence of the summed microtrav.
Intervertebral discs have high strength and maintain a static load well, which is applied slowly, for example, wearing severity. The dynamic, instantaneously applied load, creating blows of large local power, as a rule, leads to varying degrees of compression of the bodies of the vertebrae, and also causes damage to the discs. When the disks are lesions, when the pulpseed kernel loses its function of the ball joint axis, movements are reduced in volume or blocked, despite the intactness of the rest of the musculoskeletal and ligament.
The disc is preventing not only rapprochement, but also the removal of the bodies of the vertebrae. This function provides collagen fibers of a fibrous ring plate, which is tightly fixed on the cartilage layer and in the peripheral portion of the limb. In cases where the relationship between them weakens, for example, with degenerative lesions in the spinal body segments, the body of the vertebrae, without being firmly connected to disks, can be shifted in various directions.
The diversity of the resulting pathological and pathophysiological situations causes clinical polymorphism of the disease. The pathological process turns out to be different anatomical entities involved in the structure and functions.
The clinical manifestations of this process is Dorsalgia - pain back syndrome (with possible irradiation in the limb), which is due to functional and dystrophic changes in the tissues of the musculoskeletal system (muscles, fascia, tendons, ligaments, joints, disc) with the possible involvement of adjacent peripheral structures nervous system (root, nerve).
In the pathogenesis of chronic dorsalgia, the decompensation of dystrophic changes in the tissues of the musculoskeletal system, as well as dysfunction of individual muscles and joints, is played, which leads to the formation of nociception sources with a subsequent segmental and sustained response.
In the mechanism of development of radiculopathy plays the role of grinding the root in a narrow "tunnel", the walls of which can be formed by various structures: the hernia of the disk, the yellow bundle, the tissues of the arc-forced joint, osteophytes. In this case, there is a violation of blood circulation root in the compression zone followed by edema.
The risk factors for the development of pain syndromes of muscular and skeletal nature include:
o Motor imbalance (irregular posture, scoliosis, reduction of extensibility, strength and endurance muscles, pathological motor stereotype);
o spinal dysplasia;
o Constitutional hypermobility;
o Distrophic changes of the musculoskeletal system.
They create prerequisites for the development of functional disorders in various links of the musculoskeletal system and the breakdown of compensation of natural age-related dystrophic processes under the influence of provoking factors.
The problem of instability of the vertebral motor segment arising from the action of various factors is far from permission. First of all, it concerns the systematization of the most important pathogenetic mechanisms, taking into account the role of morpho-functional changes in the structures of the spine, biomechanics, as well as the need to diagnose the instability of PDS in the early stages of the degenerative process.
LITERATURE
1. Galley R.L. Emergency orthopedics. Spine / R.L. Helley, D.U. Spite, R.R. Simon: Per. from English - M.: Medicine, 1995. - 432 p.
2. Epifanov V.A. Osteochondrosis of the spine / V.A. Epifanov, I.S. Roller, A.V. Epifanov. - M.: Medicine, 2000. - 344 p.
3. Mazo I.S. X-ray diagnostics of shifts of lumbar vertebrae / I.S. Mazo, I.L. Tager. - M.: Medicine, 1979. - P. 28.
4. Mushkin A.Yu. Vertebrology in terms, figures, drawings / A.Yu. Mushkin, E.V. Ulrich. - SPb.: ELBI-SPB, 2002. - 187 p.
5. Practical neurosurgery: Guide for doctors / under. ed. B.V. Gaidar. - SPb.: Hippocrat, 2002. - 648 p.
6. Socyokovikov V.A. Post travematic instability syndrome of the vertera-engine segment / V.A. Sokokovikov, V.V. Malyshev. - Irkutsk, 2003. - 117 p.
7. Chertkov A.K. Surgery Osteochondrosis patients with instability in lumbar motor segments: author. dis. ... dot. honey. science - Kurgan, 2002. - 45 s.
8. Kedizchj. EpidemioLogische Untersuchungen Bei Vertebrogenen Syndrumen / J. Kedizch, J.-u. Optitz, U. Klemm // MAN. Med. - 1985. - Vol. 23, N 2. - P. 43-46.
9. Kestler O.C. Pregnancy and Lumbar DegeNensence / O.C. Kestler // J. Neurol. PRTHOP. Med. - 1987. - Vol. 8, N 2. - P. 139-142.
Bulletin of the ISTC SO RAMS, 2006, № 4 (50)
When copying materials from our site and place them on other sites, we require each material to be accompanied by an active hyperlink to our website:
- 1) The hyperlink can lead to a domain or on that page with which you copied our materials (at your discretion);
- 2) on every page of your site where our materials are located, should stand an active hyperlink to our site;
- 3) hyperlinks should not be prohibited by indexing by search engines (using "NOINDEX", "Nofollow" or any other ways);
- 4) If you copied more than 5 materials (i.e., on your site more than 5 pages with our materials, you need to put hyperlinks to all author articles). In addition, you should also put a link to our site, on the main page of your site.
Degenerate-dystrophic changes affecting intervertebral discs may affect not only all this anatomical formation (fibrous ring and centers core), but also limited to the outer disk rings. In cases where the patient develops a localized lesion of the outer part of the fibrous ring and fabrics of the front longitudinal bunch of a spinal column while maintaining the normal structure of the rest of the disk located between the vertebrae bodies in the lumbar and sacral division, the doctor after a comprehensive examination may be diagnosed with spondyliza lumbly The sacrum of the spine.
Despite the smaller area of \u200b\u200btissue damage on one disk, the total surface of degenerative changes is inclined more than with the development of diffuse osteochondrosis, hernia and disk protrusion - the outcome of the disease, the occurrence of which is likely in the absence of treatment, the development of the instinction of the vertebrae bodies to one single whole. Such an outcome of the disease can lead to a significant restriction of the disability of the patient or the offensive of disability - that is why such importance acquires timely diagnosis and previously the beginning of the entire necessary complex of therapeutic measures.
Why develop spondylosis?
Spondyliza of the lumbosacral spine is a disease that develops at the initial stage as a compensatory response of the body - in response to an excessive load on the body of the vertebrae in the place of the largest overloads there is a compensatory sprouting of bone tissue, which contributes to a decrease in adverse effects. At the same time, the muscle fiber spasms surrounding the affected area of \u200b\u200bthe spinal column, which can only limit its mobility only to a slight degree.
When continuing the impact, the compensatory-adaptive reaction becomes pathological - gradually an increase in the area of \u200b\u200bcontact is gradually. Bone expansions are gradually turning into the so-called "skirt" - osteophyte growth capable of achieving huge sizes, and at this stage of development of the disease in the degenerative-dystrophic process can be involved and anterior longitudinal bunch of spine. The growth of bone tissue can injure the roots of the nerves, departing from the lumbosacral segment of the spinal cord (lumbar and sedanistic nerve), as well as affect the shell and the substance of the spinal cord.
Simultaneously in the tissue itself intervertebral disc The processes of dehydration are arising - the disk structure is gradually losing water, which inevitably causes further reduction in the height of the disc, and these processes only enhance the severity of the disease symptoms in the patient. It is according to this principle, with spondyliza of the lumbosacral spine, an intervertebral hernia is developing. At this stage of the disease, the disc is practically melted between the bodies of two adjacent vertebrae, and the area of \u200b\u200bthe disc (cartilaginous fabric) protrudes beyond the surface of the vertebral body. The deforming spondylosis develops with a launched, untreated timely osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spinal column.
The causes of spondyleze can be:
- traumatic damage (both straight and indirect) ligaments and muscles of the spine in the lumbar and sacral division;
- static load on the spine - long-term stay of the body in a physiologically disadvantage;
- dynamic loads - short-term physical tension of the muscles surrounding the spine, against the background of severe hypodynamics;
- constitutional and hereditary predisposition;
- age changes in the tissues of the spinal column;
- infectious diseases or tumors.
What are the manifestations of this disease?
The most frequent symptom that can be revealed in patients suffering from spondylosis of the lumbosacral spine, it becomes pain - it can occur at the time of movement or intensify during the day, with a sharp change in the position of the body. In some patients, pain is possible in pain when changing weather conditions (increased meteo sensitivity). On initial stages The pathological process of the back pain may be non-permanent, possibly periodic spontaneous strengthening and weakening of unpleasant sensations in the affected area of \u200b\u200bthe spine.
During the progression of changes, the volume of movements in the vertebrae of the lumbar spine can appear - the degree of restriction will be directly dependent on the severity of spondylosis. When palpation and self-esteem vertebral proges arises soreness, the zone of propagation of which corresponds to the location of the vertebrae and disks involved in the process.
In some cases, the first manifestation of the disease can be the development of the root syndrome and the appearance of signs of lesion of the fibers of lumbar and sacral nerves, as well as the symptoms of plexitis (inflammation) of lumbosacral plexus. The patient has a false "intelligent" chromotype (pain in the legs), which does not disappear in the state of physical peace - it differs from "chromotype" resulting from the development of obliterators of the enemetic vessels of the lower extremities.
The patient may complain about the pain that moves into the buttocks and the lower limbs, weakness in the legs that can decrease when moving up the stairs or tilt forward, because with these processes there is a physiological increase in the intervertebral disc area.
It is worth remembering that with osteochondrosis, unlike spondylesis of the lumbosacral spine, almost never occurs when pressing the affected vertebrae affected by the spontaneous processes.
Under the defeat of the lumbosacral spine spondylosis, it is most often localized in L3-L5, in contrast to osteochondrosis, affecting the L5-S1 vertebrae.
How is the diagnosis?
To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to carry out:
- comprehensive neurological examination of the patient;
- radiographic studies of the spine - snapshots must be performed in standard and lateral projections. This research method is used to estimate the state of the vertebrae, detect osteophytes, the pathological mobility of individual elements of the spine with extreme degrees of bending and extension, displacement detection;
- computer and magnetic resonance tomography - used to determine the height of intervertebral discs, the width of the spine channel and its condition.
Comprehensive treatment spondyleze
As with the identification of any other disease of the spinal column, the doctor in establishing the diagnosis of this disease must assign comprehensive treatment to its patient, the purpose of which will prevent the progression of degenerative-dystrophic changes in cartilage and bone tissue. It is important to remember that self-medication in this disease may worsen the condition of the tissue of the spinal column and limit the patient's ability.
The designated treatment should be complex and take into account all the features of the patient's body - it should be directed to:
- Improving the status of the cartilage of the intervertebral disk.
- Restoration of blood supply and innervation of spinal tissues and intervertebral disc.
- Saving pronounced pain syndrome.
- Reducing the friction and pressure of the vertebrae.
- Strengthening the muscular-ligament apparatus of the spine.
Medicinal preparations can be used primarily in the aggravation stage (to relieve pain syndrome), such treatment techniques such as:
- Igloreflexotherapy (relief immediately)
- Electrophoresis (but only the Ionoson apparatus)
- Hivamat (passes the pain for 2 sessions)
- Applique Ozokerita
Degenerate dystrophic spinal changes
Every adult man during his life at least once experienced back pain. In 80%, they are associated with degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the spine. It is believed that such devastating processes proceed in old age, since the degeneration of tissues is a sign of old age. But in modern society, these diseases raised. This is due to different reasons, but above all with a sedentary way of life.
Degenerate-dystrophic changes in the lumbar spine are often found in middle-aged people. This leads to loss of working capacity, and often to disability. It is very important to detect signs of the disease in time to stop the degeneration of tissues.
How degenerative-dystrophic changes are developing
The human body is designed to evenly distribute the load on the spine. With a normal posture and a strong muscular corset, it can withstand heavy loads without harm to health. But the trouble is that most modern people lead a low-wear lifestyle. This leads to the weakening of the muscles and ligaments. According to statistics, the spine of many people is 80% of the time during the day spends in an unnatural state.
Most of the cases of dystrophic changes are associated with the destruction of intervertebral discs. Due to long stay in one position or at large physical Loads They are thinning, losing moisture, they appear cracks and microen. There is no blood supply inside the discs, so they are restored very slowly. Because of this, even a small injury leads to degeneration.
The vertebrae under such conditions is experiencing heavy loads, therefore, they are also subject to change. Inside the damaged zone of the spine penetrate salts from blood flow. Calcification begins. More often, such degenerative processes occur in the lumbar department. After all, the largest load during standing and sitting is on the lower back. According to statistics, more than 30% of people over 30 have any dystrophic diseases of the lumbar spine.
Causes of such a state
Such pathological processes of the lumbar spine can be caused by different reasons. Therefore, they are developing regardless of age and human lifestyle. Most often, these changes provoke such phenomena:
- active sport with large loads on the lower back;
- sharp loads, for example, lifting severity;
- the injuries of the spine, muscles and ligaments, even microtraums due to constant overloads;
- inflammatory diseases, infections, hormonal failures;
- improper nutrition, resulting in a lack of nutrients;
- excess weight;
- bad habits;
- a sedentary lifestyle, due to which muscles and ligaments weaken;
- the aging of the body, leading to the nutritional disorders;
- genetic predisposition.
Symptoms of such diseases
In order to stop destructive processes in time, you need to consult a doctor at the first signs of tissue degeneration. But the problem is that such processes proceed very slowly, often years. Many people are trying to cope with periodically emerging spine pains by homemade. It happens that when carrying out a scheduled survey, for example, X-ray or MRI detects degenerative-dystrophic changes in the lumbar-sacral division. But often destruction is already very strong.
Therefore, it is very important to know the first signs for which it is possible to determine what processes have begun:
- backing pains in the lower back, increasing during seating, slopes and other loads, and subsided during a night rest;
- pains can spread to feet and buttocks;
- reducing the mobility of the spine;
- violation of the functions of small pelvis organs;
- swelling and redness in the affected area of \u200b\u200bthe lumbar-sacrive department;
- increased fatigue;
- feeling of tingling, numbness in the lower limbs and buttocks;
- violation of gait.
Without proper treatment Degenerative processes lead to impaired blood circulation and innervation in the spine. It causes paresis or paralysis.
Types of diseases
The term "degenerative-dystrophic changes" is indicated by the overall picture of pathological processes in the spine. But it summarizes several diseases that have not only common signs, but also their own features. They can develop individually or together with each other.
- Osteochondrosis is characterized by gradual disk thinning. The disease occurs in chronic form.
- Hondroz arises most often in young people who are exposed to the spine to large loads. At the same time, microcracks arise in the vertebrae, because of which they gradually destroy.
- Spondylosis is the formation of bone outs on the edges of the vertebrae. The gradual oake of the spine strongly limits the volume of movements.
- Spondilitrosis is the defeat of intervertebral joints, their gradual destruction. At the same time, disks are thinned, and bone growths are formed on the vertebra. This leads to severe pains at any movement.
- Intervertebral hernia arises due to the destruction of the fibrous ring of the disk. Pulpose core is protruding and squeezes nerve roots.
Diagnosis of diseases
The earlier the patient appeals to the doctor for examination and setting the correct diagnosis, the more successful the treatment. Usually, for the decision of the presence of degenerative-dystrophic processes, the doctor needs such information:
- the overall picture of the patient's health;
- x-ray data;
- MRI scan.
Features of the treatment of such pathologies
Based on the results of the survey and the diagnosis, the doctor chooses the most effective methods Therapy. Treatment should be directed to the removal of pain, slowing the dystrophic processes, muscle strengthening, the restoration of cartilage and bone tissues, as well as to improve the mobility of the spine. This uses different treatment methods.
In the acute period, the spine is applied, as well as the limitation of its mobility with the help of special orthopedic bands. Medical therapy is shown. In addition to the NSAID tablets, novocaine blockages or injection of hormonal means are used. During the remission, massage, leafc, physiotherapy, is shown. And in the absence of the result after conservative treatment and ongoing strong pain Apply surgical intervention.
Treatment of such processes in the area of \u200b\u200bthe belt must be comprehensive. Be sure to comply with a special diet rich in vitamins, calcium and jelly-like products. All recommendations should be followed. But still continues such treatment for several months. And if it started on time, the patient was patient and did everything right, you can completely restore the spine for the year.
Medical therapy
It is necessarily assigned to relieve pain. These may be analgesics or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Mioryelaxants, removing muscle spasms, are also used.
The obligatory stage of treating such diseases is the restoration of cartilage tissue. This is done with the help of chondroprotectors. All such drugs are accepted inside or used in the form of ointments and gels for outdoor use. Such comprehensive treatment more effectively stops the development of degenerative processes.
In addition, it is prescribed tools that improve blood circulation, sedatives, as well as vitamins of group V.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
During the remission, in the absence of sharp pain and inflammation, various methods of physiotherapy are applied:
- massage improves blood circulation and metabolic processes;
- manual therapy restores the correct position of the vertebrae;
- electrophoresis, magnetotherapy, UHF, acupuncture and other procedures are removed pain and inflammation, accelerate recovery.
LFK with degenerative dystrophic processes
A specially selected set of exercises helps the patient to preserve the mobility of the spine. LFC performs such functions:
- slows down degenerative processes;
- improves blood circulation and metabolism;
- returns the correct posture;
- strengthens muscle corset;
- keeps the elasticity of the spine segments and increases its mobility.
Prevention of the destruction of spinal tissues
Such diseases associated with degenerative-dystrophic changes in the lumbar spine are now very common. Therefore, every person should know what to do to prevent such processes and maintain activity to the oldest. This is possible when complying with such rules:
- protect the back from supercooling and humidity;
- avoid sharp loads on the lower back;
- regularly perform exercises that strengthen the muscles of the back;
- do not be for a long time In one position, during sedentary work periodically get up and make a warm-up;
- watch that the diet is rich in vitamins and minerals.
It is necessary to turn to the doctor in time when discomfort in the lower back. Only attentive attitude to the state of his spine will help keep it healthy and prevent destruction.