Treatment of acute and chronic periodontitis. Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of granulomatous periodontitis, aggravation of chronic form of disease Existence of chronic granulomatous periodontitis
With diseases of a dental nature, almost every person faces, and far from once for his long life. Fortunately, in many situations, an experienced dentist is easily able to put the correct diagnosis and immediately start competent treatment, but sometimes for diagnostics it is necessary to make photos of teeth through radiography. Let's look at what a granulomatous periodontitis on an x-ray looks like, as well as a granulating type of disease.
What it is?
Periodontal is called fabric surrounding the roots of the teeth and holds it inside the alveoli. As for periodontitis, then such a name is inflammatory processarising inside the tissue. The focus of the inflammatory process can be located on the various portion of the tooth, therefore specialists identify several basic varieties of the disease: marginal or apical periodontitis. The apical type of disease is characterized by the fact that the defeat is observed near the top of the roots of items, which is almost always accompanied by a serious tissue infection.
Such manifestations arise due to infection in the pulp, and this causes a decay, the products of which begin to go out through the hole that occurred from top to the tooth root. Experts mention that apical periodontitis is very often a complication of an indispensable pulpitis, which was not cured in time. As for the marginal inflammatory process, it is observed directly from the edge of the gums for the following reasons:
- Trauming gums. A similar problem is the most frequency cause of marginal periodontitis, the injury of gums may occur for various reasons, for example, as a result of a vile of solid (nuts, some inedible objects) or with an unsuccessful attempt to keep the subject in the teeth.
- Allergic reaction. The consequences of this kind of allergies arise quite rarely, but it can still lead to periodontitis. Most often it arises due to allergic reaction on severe drugs.
The disease is also taken to divide on acute periodontitis and chronic periodontitis, which is a consequence of the absence of competent therapy in acute form. Negoties are still divided into the following types:
- purulent formontitis;
- serous periodontitis;
- granulating periodontitis;
- fibrous form;
- granulomatous periodontitis.
Let's analyze the granulating and granulomatous form in detail, considering their main features and differences.

Granuz tooth.
Granulomatous periodontitis
The human body seeks to defeat any infection that penetrates the body, even if it is dental. If a periodontitis of the tooth of this kind is beginning to develop, this indicates a periodontal infection, as a result of which the body undertook these actions, concluding infection into a certain "capsule", each of which is called granuloma. It allows you to stop the spread of infection and toxins on the other organism, and such a manifestation is called granulomatous.
Granuloma is a certain number of young fibers related to the connective tissue, that is, there are vessels in them. If infection in the body is detected in the body, immunity begin to work hard, activating all protective functions, which leads to the appearance of heavy, but the granuloma is still a serious danger. The fact is that cases are known when granulomas turned into cysts capable of provoking the decay process of bone tissues (as it is easy to guess, in this situation a similar problem can lead to a tooth losing or even several of them). Dangerous situations during periodontitis are connected with the fact that granulomas are simply revealed, it ends not only by such consequences as extreme heat, Melting I. headacheAfter all, an abscess may appear and even develop an infectious form of endocarditis.
The course of illness and its manifestation on x-ray
The birth and development of granuloma is a rather slow process, therefore this formontitis form is often asymptomatic until the capsule becomes big and the feeling of the gum swelling will not appear. Such a process is accompanied by painful sensations when emphasizing, sometimes the enamel darkens and the symptoms of the fistula are observed.
When conducting radiography at this stage, it will be possible to diagnose granulomatous periodontitis, despite the fact that the granulation tissue is very poorly visualized in the photo. The focus of inflammation will be characterized by an oval or even a round form, and the diameter in such situations already usually reaches at least 5 mm. The boundaries of such a granuloma are extremely distinct, and the destruction of the teeth are not yet observed. We mention the fact that almost never observed resorption of the root of the root, and the layer sclerosis can sometimes be seen.
It is important to understand that the prostatitis granulomatous forum may appear not only on the teeth subject to caries at the moment, it can start developing on previously marked teeth. In the presence of a carious cavity, it is far from always communicating with the cavity of the tooth. If a specialist will tapping, it will be able to identify a low degree of tooth sensitivity. Also in such cases will be:
- almost there is almost no response to probing;
- appear redness in the place where the inflammatory process is localized;
- elevated electrical excitability is observed;
- there is no destruction destruction.
Note! Granulomatous or granulating periodontitis on an x-ray can only be determined by a qualified specialist, in no case attempt to make a picture of the picture on their own, because even with proper decoding, it will be impossible to cure periodontitis without dental intervention.

An purulent periodontitis is shown on the x-ray.
Treatment
The process of treating granulomatous prostatitis is quite long, because you will have to visit the dentist's doctor at least 3 times. At the first reception, the doctor will cleanse the tooth, which is subject to the inflammatory process using special tools, also at this stage requires antifungal therapy. As a result, a special paste needed to create a temporary seal will be introduced into the root of the tooth. In the process of 2 reception, the specialist will begin an opening of the hole on top of the root of the tooth in order to perform exudation. At this stage, antibiotics should be applied, as well as antiseptics, but medications should not be too strong, otherwise the process of restoration of tissues after periodontitis can be slowed.
Other drug drugs will be required, for example, hyposensitizing medicinal products. The fact is that granuloma is able to cause high allergic sensitivity, and these drugs are able to cope with it. There are still medications that can stop the granuloma growth process and have the effect of tissue regeneration.
The essence of the third visit to the specialist will be in installing a seal and in the completion of treatment. When the cyst is not so rare, it should be removed, and sometimes it is necessary to do this surgical pathway (with large sizes of this neoplasm).
Granulating periodontitis
This type of disease should also be considered as a sharp or chronic granulating periodontitis. In this case, periodontal deformation occurs as a result of the growth of tissues. Such manifestations are easy to explain, because with their help the body seeks to destroy the focus of infection (in most situations of bacterial nature). These bacteria penetrate the periodontal by the hole located at the top of the tooth root, which is the complication of caries associated with the contact of infection in the pulp. Granulation in this case will grow very quickly, in parallel destroying the alveolar process. As a result, the channel can open through which the pus will begin to go out, and they can even be somewhat.
Features of the course of illness and its diagnosis
Dental doctors always characterize a granular periodontitis by the appearance of periodic patients, and they can manifest themselves arbitrarily. Pains can also manifest when putting something. The tooth may even become a little moving, but the rest of the clinical manifestations of this form of periodontitis:
- the appearance of unpleasant smell of mouth;
- the appearance of fistula and purulent discharge;
- significant redness of the mucous membrane.
As for the mucous membrane in the place where it develops into fistula, it becomes much thinner, and when the channel is closed, the scar is formed quite large. At this stage, it is impossible to slow, you chose any dentistry to be selected, where to contact.

X-ray is one of the main methods needed for diagnosis. chronic periodontitis.
The doctor's study never begins an X-ray, because a status description is made to begin. In the process of diagnostics, a specialist will detect many clinical manifestations observed with granulating periodontitis. For example, when patting, most likely, internal litter will be detected, which is always a consequence of a fistula, the connecting fabric of which is seriously compacted. It is important to understand that the fistulas can appear absolutely in different places, and even on the face and on the neck, which is often the surprise of patients.
What concerns how the picture will look like, on which the granulating prostatitis is observed, its main features will also be in granules and formations pathological characterseparated by all tissues from all tissues. Inside such formations, a granulation tissue is manifested, which is quite poorly visualized, as already mentioned earlier. In those places where there was a change in inflammatory character, a connecting fabric will appear, which will occupy a relatively much space, which simplifies its identification.
Important! X-ray is an indispensable study in many situations of this kind, but carrying out such a study without a contrast agent may not give desirable results, especially if we are talking about the early stages of development of the problem when education is still enough. In any case, you should contact the doctor when the first symptoms appear, otherwise you can lose a precious time, which will help you choose the diagnosis and start competent therapy, warning possible complications and hazardous consequences.
It is worth understanding that periodontitis can be attributed to any other form, because in this material there were only two of them.
In chronic inflammation of the oral cavity, granulomatous periodontitis is developing, granuloma is formed around the periodonta tissues.
There are four main stages of the development of granulomatous periodontitis - granuloma, apical granuloma, cystranslater, cyst. The causes of the disease may be caused by the following symptoms and diseases: caries, pulpitis, diabetes common imminent immune system, failure in metabolism, microflora violation oral cavity, intolerance to certain drugs, chronic diseases internal organs, as well as the pathology of the endocrine system, an incorrect bite or a medical error in the treatment of other diseases of the oral cavity. Granulomatous periodontitis is accompanied by a change in the color of the tooth, an edema, an unpleasant smell of mouth and the formation of a carious cavity (granuloma).
Granulomatous periodontitis Developed in chronic inflammation of the oral cavity. In this case, an cavity, referred to as granuloma, is formed around the periodonta tissues. It isolates the source of infection and slow down the distribution of productivity products of microorganisms.
Stages of development of granuloma
Granulomatous periodontitis There are several stages:
- granuloma;
- apical granuloma;
- cystograph;
- cyst.
In the formation of granulomas, the connecting tissue grows and causes a periodontal seal.
With apical granuloma, a connective tissue cavity is formed. This cavity is filled with granulation, fibrous elements, microbes (living and dead), leukocytes. The destruction zone does not exceed 5 millimeters.
Kistograntulm takes from 5 millimeters to a centimeter. In the focus of inflammation, an acidic medium is formed. It slows down the development of Osteoblasts and stimulates the growth of osteoclasts. Osteoblasts - cells engaged in formation bone tissue. Osteoclasts - cells that destroy bone tissue.
The cavity of the cyst is filled with liquid content, contributing to the destruction of the tooth. It is noticeable cholesterol crystals. This feature is used in differential diagnostics.
Causes of granulomatous periodontitis
Primarily Chronic granulomatous periodontitisdeveloped by the occurrence of caries and pulpitis.
The disease may be caused:
- infection;
- weakening the immune system;
- disruption of microflora inhabiting the oral cavity;
- failures in the metabolism;
- wrong bite;
- injury to the tooth (laying nuts, habit of gnawing pencils and handles);
- inadequate treatment of pulpitis;
- diabetes;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- intolerance to drugs or materials used in sealing;
- chronic diseases internal organs.
Often, people who are diagnosed granulomatous periodontitis, medical history Contains a chronic granulating periodontitis.
Symptoms of granulomatous periodontitis
Chronic granulomatous periodontitis Usually manifests itself in periods of exacerbations. The rest of the time the granuloma can be formed, without finding any signs. The activity of the inflammatory process and the resistance of the organism affect its growth rate. Therefore, the development of granuloma can be quite violent or stop at all.
The inflammatory process can cause:
- formation of carious cavity;
- changing the color of the tooth;
- lightweight;
- silver smell of mouth.
Lymph nodes in most cases do not change.
Diagnostics
When changing the color of the tooth and the presence of a noticeable defect to diagnose the granule is quite easy. But if the tooth is folded and does not detect any signs, then the granuloma remains invisible.
Therefore, for the diagnosis of patient's disease, they are sent to X-ray and electron contraction.
Treatment of inflammation
Treatment of granulomatous periodontitis Aims to destroy the focus of chronic infection. The choice of the therapy method affects the permeability of root canals, the structure and dimensions of the granuloma. The patient's age and the overall state of his health are important.
Conservative treatment prescribe with:
- small granuloma sizes;
- the absence of epithelium in the structure of the granuloma;
- good channel passability;
- high activity of the body, providing regeneration of bone tissue.
In this case, the root channels are expanding and processed by an antiseptic. Then the antibacterial drug is introduced into the dental cavity. It destroys the pathogenic microflora, neutralizes the acidic medium, ensures the restoration of the bone.
If necessary, operational treatment is most often removed by the top of the dental root. But if resection is required more than a third of the root, usually remove the entire tooth.

If you do not stop the inflammatory process in a timely manner, it can spread to nearby teeth.
Treatment of chronic granulomatous periodontitis Requires a long period of time. In the aggravation stage, it is carried out conservatively. The dental channel is treated and the necessary medicines are introduced into it. After the inflammation disappears, the seal is installed.
If there is phlegmon or periostitis, you may need operational treatment. In this case, remove the tooth. Then the gums are cut and create conditions for eliminating the purulent exudate and neutralization of intoxication of the body. Such actions do not allow infection to penetrate the nearby teeth.
Complications
In some cases, it is possible aggravation of chronic granulomatous periodontitis. It is accompanied
Periodont is a fabric that surrounds the roots of the teeth. In fact, it is she who firmly keeps all his teeth in Alveola. Inflammation of this tissue is called periodontitis. We find out in detail what is the disease, which types of periodontitis are distinguished and how they are treatable. Let us dwell in more detail on such types as a granulomatous periodontitis and granulating periodontitis.
Since the focus of inflammation can be localized in different parts, then the apical periodontitis and marginal is distinguished. When apical lesion is localized on the period of periodonta, which is located directly near the top of the tooth root. In this case, tissue infection occurs. Its reason - the pulp was infected, and the decay process began. In this case, the products of this decay go directly through the hole at the top of the root. If we clarify, then periodontitis of apical type is most often the result of an impenetrable pulpitis. Due to the lack of proper treatment, the pulp is inflamed and the decay of its tissues occurs.
In periodontitis, marginal inflammation begins directly from the edge of the gum itself. The reasons for such inflammation may be several:
- Grass gums. This reason meets most often. You can injury in various situations. For example, you bit the hard object, gnawed nuts, tried to keep solid tooth items or got a strong blow during sports activities or in mobile games.
- Allergy. Allergies less often leads to periodontitis. But it happens that an allergic reaction to some medicines arises, which can provoke inflammation of the edge of the gums.
The fabric can collapse and deform with varying degrees. In the inflammatory process of periodonta, the following types are distinguished:
- Purulent.
- Serous.
- Granulating.
- Granulomatosny
- Fibrous.
We will consider in detail each type, but let's stop in detail on the granulating, and granulomatous.
As the disease gains its development, the bone tissue is absorbed near the tip of the dental root. At the same time, the cavity begins to form. It is filled with granulations, accumulates pus. When the process of the suppuration is enhanced, pus or self breaks through the outside (the fistula appears), or the granuloma grows, forming the cyst.
Clinical manifestations of periodontitis can be different. Depending on their intensity, stages are distinguished:
- sharp;
- chronic.
So how can I recognize periodontitis? If you, flaying, feel the strongest pain, most likely it is periodontitis. We emphasize that the pain appears only when pressed onto the tooth, and accordingly, on its root and gums. Often pain converts into an attack, which has a swift character. This is an explicit signal of acute periodontitis. At the beginning of the disease, the pain appears only when the teeth are loaded, for example, when chewing. Well, over time, when the disease is enhanced, the pain begins to manifest themselves alone. The attacks become longer. If we talk about sensations, then many patients seem to be that the tooth just increased in its sizes. In this case, there may be other symptoms. Lymphatic nodes can be swollen enough. If the disease form is heavier, then the temperature increases. If chronic periodontitis is exacerbated, then the picture of its manifestation is identical to acute periodontitis. That is why it is important to seek to contact a specialist. Only to establish it, with what specifically the form of periodontitis you encountered and how to cure him quickly. For this, an X-ray is performed, which shows what state is the root of the tooth.
How does chronic periodontitis flow? In classical chronic form, the patient does not observe any vivid manifestations. This is a dangerous chronic form. The man seems to be acute pain, and at this time the mechanism of the inflammatory process is already launched. The chronic form is dangerous with its complications. It can go to periostitis or osteomyelitis jaws. Such may also happen dangerous complicationslike abscess and sepsis. In the chronic manifestation of periodontitis, patients almost feel no pain. Only during progress can be insignificant soreness or just discomfort. Therefore, it is important to carefully listen to your subjective sensations. In a certain area of \u200b\u200bgums or jaws appeared numbness? Shot slightly or red mucous? In the gum formed an incomprehensible fistula? Urgently contact the help of the dentist, since these symptoms can be periodontitis signals!
So, let's sum up a small result before considering the symptoms of acute and chronic periodontitis in detail. Inflammation of tissues in a sliding space, which is limited to the roots of the teeth and the alveoli, is called periodontitis. Most often, the reason for its appearance is an infection due to the fact that the gums were injured or the poisoning of medicines happened. The brightest manifestation is characteristic of the acute form of this disease. Especially painfully it flows in the case when the pus is actively accumulated. But when chronic form, the destruction is much slower. It is accompanied by not so pronounced sensations.
Periodontitis stage
Healthy gums are tightly held in the well teeth. Periodontitis develops into several stages.
- There is a bleeding and easy swinging gums. Most often to such a result leads the usual raid on the teeth. If it is not carefully removed, it turns into a dental stone and accumulates in the intervals between the teeth. The dental contains aggressive enzymes and toxins that irritate the tissue of the gums. Gingivitis begins to manifest.
- Foreign pockets appear. The cause of their occurrence is a hardened bloom on the teeth. On the roots of the teeth begin to take their necks. They become extremely susceptible to any influence external factors: chemical, physical, mechanical. That is why it is important to turn to the dentist twice a year. If he detects a stone on his teeth and deletes it in a timely manner, it will save you from many diseases.
- If the patient did not receive adequate treatment, then periodontitis progresses. Bone and connective tissues are very destroyed. This is a direct path to the loss of teeth.
How the sharp periodontitis is manifested
First of all, it should alert the feeling that the gums are constantly whining and sobs even with a small pressure on the tooth area. During the palpation, the dentist such pain makes itself felt. And the patient himself faces it in the process of meals. At the same time, the place where it hurts, is definitely determined. During the development of periodontitis, there is a feeling that the tooth grows. According to its origin, periodontitis most often has the character of carious. As the periodont is destroyed, the pulp ceases. It is easy to determine in the absence of a reaction at the place of lesion to the temperature stimulus.
There is also a noncaryomic periodontitis. In this case, the tooth crown is not damaged. In this case, the symptoms will be the following: the filling of blood vessels increases in the area of \u200b\u200bthe lesion. This is manifested in the form of swelling and redness. For this type of periodontitis, this symptomatic is not considered specific. But it is these symptoms that help determine the development of the disease.
The blasting of the gum can and during carious periodontitis. This happens at the moment when the serous exudate turns into purulent. Due to the fact that the disease develops, begins to swell the cheek and the lip from the side where the periodontitis develops. The patient is worried about the taming strong painwhich appears without any exposure from the outside. It acquires practically permanent. There is a swelling and soreness of lymph nodes under lower jaw. The temperature increases (up to 37.5). There is some mobility of the tooth. During clinical research The dentist will detect purulent allocations.
When percussion (tipping tooth), the patient also feels a strong pain. If periodontitis is located near the top of the tooth, the reaction will follow the performance vertical. But the prisoner periodontitis reacts more to the side skipping.
How is the periodontitis chronic
Chronic periodontitis makes itself felt much more weak signs. Very often it can be detected only by making X-ray. In this case, periodontal can be affected to varying degrees and form. Based on such differences, there are such types of periodontitis of chronic:
- fibrous;
- granulating;
- granulomatous.
With fibrous periodontal, the current passes almost asymptomatic. The main thing that should alert, is the fact that the tooth has changed in color. But full confidence will give only a X-ray. It will be noticeable on the radiograph that the periodontal slot was deformed, the root tip began to thicker, the bone tissue is partially scruised in the wall, which surrounds the zone directly, where inflammation began.
Chronic granulating periodontitis has such symptoms. During pressure on the tooth, periodically pain appears. Also, the tooth may be painfully reacting to supercooling, the gums blushes and swells. You can often see the fistula that appeared. At the X-ray picture, the doctor will detect a sufficiently strong destruction of bone tissue, this defect will not be a clear border.
Chronic granulomatous periodontitis makes itself felt by a sense of some sipping in the jaw region. This is due to the fact that granuloma is formed. Then she can grow into the cyst. Very often, this type of periodontitis happens due to the fact that the tooth filling was performed poorly. On the radiograph, the doctor will find that the bone tissue is damaged. But at the same time, the borders of damage will be clearly visible. They will find a spherical shape.
Forms periodontitis
Let us last in more detail on the forms of periodontitis. In dentistry, such forms are now distinguished:
- Exudition and intoxication as a result of acute periodontitis.
- Complex form and simple in the development of chronic periodontitis.
The form of intoxication is manifested by a sense of discomfort. It appears only in the place where the sick tooth is. Small allocations are observed. They can be blood and (or) serous. The tissue of the gums does not change in color or in volume. This very short period that takes place in two days. In the second period, the pus appears. Due to the fact that it accumulates, there is a strong pain. Periodonta fibers are separated. There is a violation in the distribution of the load on the tooth. You can visually observe the signs that the gums inflamed. At the same time, a lot of pus accumulates that wants to get out. Pump can go through the tooth root canal. If he did not find it, then the pus goes into the tissue of the bone, periost or in a soft fabric.
When a periodontal chronic simple form will manifest in different ways. It depends on the nature of those damage that periodont (granuloma, fibrosis) received. With a simple form, the pain can be disturbed. She makes itself felt both while eating and after it. A rather sharp painful response is manifested for performance. It may appear gingivitis or just gums can redden, swell. There are both forms that proceed practically without pain. In places even disappears sensitivity to different stimuli.
In case of complex form, the same symptoms are observed, which is described above, but periodontal slit is expanded. Because of this, the tooth becomes mobile. It is also observed vertical bone dissipation, pockets are formed inside it.
Periodontitis granulomatosny
Our body struggles with infection in it with all sorts of ways. In the event that a periodontal infection occurs, the body is trying to protect against infection and concludes it in a special capsule. Such a protective capsule is called granuloma. It appears so that infection and toxins do not apply further. This type of inflammation is called granulomatous periodontitis. It appears on those teeth who have fully formed the root system.
What is this granuloma. It consists of sufficiently young fibers of the connective tissue. There are in them blood vessels. Granuloma is capable of its appearance to push the body to combat infection. When the immune system determines its presence, then includes its own protective functions. Over time, the granulomas appear on the epithelium. But Granuloma carries danger. It can turn into a cyst, and it can push the bone tissue and provoke her decay. Because of this, a real threat appears that the tooth falls. It may even be a fracture in the bone area. If for some reason the granuloma is revealed, the poverty begins, the temperature appears, the headache. In an inflamed place, pain is enhanced. This is a very serious process that abscess can follow, and even infectious endocarditis.
Features of leakage
Granuloma originates and develops quite slowly, therefore, periodontitis granulomatous is almost impossible to know any symptoms. When the capsule grows to a sufficiently large size, a person appears a feeling that the tooth swells inside his gums. At this time, pain appears with each pricking. It can be rarely to darken enamel and a fistula appear. When the load rises, the tooth becomes more sensitive.
At this stage, the radiograph has a clear defect in the periodontal area. The focus itself of inflammation will have a round or oval shape. Its diameter can be up to half a centimeter. Borders will be distinct. Destruction in bone tissue near the granuloma is most often not observed. Sometimes near the granuloma layer can be scruvy. He isolates healthy bone tissue from granuloma. This is an explicit evidence that inflammation is already developing. long time. Resorption of the root of the root near the granuloma is practically not observed.
Periodontitis granulomatous can happen on carious teeth, and on already charged. If there is carious cavity, it often does not communicate with the tooth cavity. When attacking the doctor will detect a weak degree of sensitivity. And with the stimulus of temperature it will be absent. There will be no response to probing. In place of inflammation there may be easy redness, but more often it happens at the stages of later. The doctor also establishes increased electrical excitability. This is a characteristic feature of any kind of periodontitis. Lymphatic system React to this form will not be.
How to treat
Granulomatous periodontitis is treated for three visits to the dentist. For the first time, the doctor will purify the sample tooth with the help of tools and will hold antimicrobial measures. At the end of the tooth root, a paste for a temporary seal or disinfectant turgund is introduced. On the second session, you will need to operate the hole at the top of the root to perform the exudation. At the same time, antibiotics, antiseptics and enzymes are used. It is important that the doctor does not use too strong medicines. They slow down the recovery process of periodonta.
In the treatment of such periodontitis, hyposensesting drugs are used. This is explained by the fact that allergic sensitivity is growing due to granuloma. In addition, other medicines are prescribed. The doctor must be used in the treatment of medicines that suppress the growth of the granuloma and have a regenerator effect.
On the third session, if the exudation is completed, the doctor will fulfill the root obturation and put the seal. If the cyst was found, it needs to be aurateutically or surgically removed. It all depends on its size. If it is small, removal can be performed in an unpergrial.
Periodontitis granular
Its essence is that due to the growing granulation tissue, periodontal deforms. In this way, the body is trying to fight the focus of infection. This is the result of healing. Most often, the reason for its appearance becomes infected with bacteria. Through the hole in the top of the root, they penetrate in a periodontal, hitting it. This is the result of severe damage by caries, in which the infection penetrates into the pulp. Granulations are formed and proceeding with active growth. At the same time, they destroy the alveolar process, breaking out out. So the channel opens, through which the pus comes out. There may be several such fistulas. The microbes are easily penetrated through them. So the disease goes into a chronic form. If the fistula is closed, the granular periodontitis is sharpened, severe pain appears, soft tissues swell at the point of inflammation.
Features of leakage
In the area of \u200b\u200bthe gums appear stupid periodic pain. They appear arbitrarily. This is a clear symptom of periodontitis granulating. During chewing, the supervision, when contacting cold, tugging on the tooth and the cold most often appears soreness. The tooth becomes slightly mobile. Explicit symptoms of granulating periodontitis:
- Unpleasant odor;
- Purulent discharge;
- Fistula;
- Redness mucous.
In the place of the fistula becomes thinner mucous membrane. If the channel closed to ensure the outflow, the scar appears. If infection gets into a fatty fabric, infiltrate is formed.
In the study, the dentist is found that the reaction of the carious cavity is found to the probe, as well as the roots of the roots. With vertical testing there is a small soreness. The threshold of electrically excavability will be high (100 μA or more). If the doctor presses the probe to the gum region, will find that the mucule first pale, and then it redels greatly. This reaction is called a vasophack syndrome. The radiograph will show up that the upper zone of periodontitis and bone tissue, which adjacent to it is damaged. The defect will have fuzzy boundaries. The patient will have complaints of headaches, poor appetite, lethargy and irritability. These are all obvious symptoms of intoxication. Limph nodes often increase.
When patting the doctor can find internal litter. This is the result of the formation of a fistula, around which connective tissue has escaped. This litigation is called "migrant granuloma", since the purulent holes are periodically closed and appear in new places. Fistulas can even appear on the face at the bottom of the neck. Externally, it will resemble the subcutaneous actinomycosis.
How to treat
Granulating periodontitis is well treated. There are all chances to make the process reversible. But it is important to turn to the doctor on time, which will eliminate the emergence of infection. During treatment, activities are performed:
- tooth is prepared for the disinfection process;
- roots are cleaned with bacteria;
- for the restoration of the bone, special medicines are introduced;
- root canals are cleaned;
- the insulating therapeutic gasket is superimposed;
- put a seal.
So, we tried to provide the most complete information on two types of periodontosis - granulating and granular. Follow the health of the teeth, the gum, and be healthy!
Yet

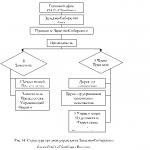
- This is a chronic inflammatory disease of the periodonta, in which granulomas are formed in the top of the root of the tooth - specific connecting units separating infectious focus from healthy tissues. The disease often proceeds absolutely asymptomatic, and complaints appear only when the inflammatory process is aggravated - in this case, they correspond to the picture of acute periodontitis. The diagnosis is established on the basis of the anamnesis data, clinical picture, radiography and electro-industry. Based on the size and shape of the granuloma, the maintenance of root canals and the overall resistance of the body, the treatment may be conservative or surgical.

General

Classification of granulomatous periodontitis
Depending on the form of connective tissue formations in dentistry, several morphological types of granulomatous periodontitis are isolated. So, at the very beginning of the pathological process, periodontal is compacted, the connecting tissue grows, and granuloma is formed. This education has a cavity that granulates, fibrous elements, living and deceased bacteria, their livelihoods and leukocytes. Most often, the granuloma is localized in the top of the root of the tooth, on the side of the root (apical-lateral granuloma) or in the bifurcation zone of multi-corneous teeth. Granuloma size rarely exceeds 5 mm.
Next of simple granuloma as a result of active reproduction of periodontal epithelial cells is developing cystic. This formation has an internal mucous membrane. In this zone, pH increases, which contributes to the activation of osteoclasts and the braking of osteoblasts, so the processes of bone resorption begin to prevail over osteosynthesis processes. Cysthodulm can reach 1 cm in diameter. The next type of neoplasms with granulomatous periodontitis is cyst. It is a long-catching formation having an outer connective tissue capsule and an inside-lined with mucous cloth. The liquid constantly produced by the mucous layer presses the surrounding bone structures, further contributing to their deformation and destruction.
Causes of granulomatous periodontitis
The main mechanism for the development of granulomato-periodontitis is associated with the presence of permanent foci of inflammation in the tissues of the tooth. In most cases, such foci are formed due to carious lesion and its launched shape - pulpitis. As a rule, granulizing periodontitis is preceded by granulizing periodontitis. Another reason for the development of the disease is traumatization of the teeth both due to the direct injury of the maxillofacial zone, and because of the habit of constantly solid objects or wearing an unsuitable orthodontic design. Granulomatous periodontitis can also occur as a response of the organism to drug effects, for example, if the dosage or allergic reaction is incorrectly observed. Additional factors of the development of chronic forms of periodontitis include endocrine diseases, insufficient digestibility of the organism of vitamins and minerals, an incorrect bite, a decrease in immunity and smoking.
Symptoms of granulomatous periodontitis
The formation and growth of granuloma usually occurs absolutely asymptomatic, and the intensity of these processes depends on the activity of inflammation and the state of immunity of a particular patient. Nevertheless, many patients talk about discomfort in the area of \u200b\u200bthe patient's tooth during meals, notice the change in its color or loss of the seal. Complaints may appear when aggravating the disease (then they correspond to the symptoms of acute periodontitis) or in the case when the process has moved into a cystic shape. If the cyst is shifted to the side, and not localized strictly in the area of \u200b\u200bthe root of the root, swelling is detected during palpation.
Diagnosis of granulomatous periodontitis
For diagnosis, it is necessary to collect anamnesis very carefully, conduct an inspection and appoint additional research. Patients with granulomatous periodontitis can tell that in the past there was pain in the tooth and an increased reaction to hot or cold food. But then the problem disappeared independently or after dental treatment. When inspection, a tooth with a changed color is found, often with a seal or crown, it may have a large carious cavity. When the root channel is probed, there are no uncomfortable sensations, a putrefactive smell occurs from the cavity of the tooth. Percussion is also painless, in rare cases, the patient talks about insignificant discomfort. In the projection of the top of the root of the tooth, hyperemia or lightweight swelling can be observed. But not always there are such bright diagnostic signsand inflammatory process for a long time leaks hidden.
Dental radiography is necessary to clarify the diagnosis. Granuloma on an X-ray is a shadow of a rounded form in the apical zone. It can come into contact with the root or form a "cap". As the disease progresses, the zones of the absence of a bone structure with smooth contours become increasingly noticeable. With radiography spend differential diagnosis Granulomatous periodontitis with other dental diseases. Chronic pulpitis and medium caries do not give any deviations on the radiograph. Fibrous periodontitis is characterized by an expanded periodontal slit. On the radiograph of a patient with granulating periodontitis expressed areas of bone tissue destruction with blurred torn edges. At the root cyst, the focus of the decay of bone tissue is more than 1 cm with clear even edges. The sensitivity of the tooth in a patient with a granulomatous periodontitis for the electro-stationometry occurs in the range from 100 to 120 μA, which corresponds to the pulp necrosis.
Treatment of granulomatous periodontitis
In each case, the treatment is selected individually. The choice of techniques affects the size and structure of the granuloma, root channels, the patient's age, the presence of accompanying diseases and the state of the immune system. For the treatment of small granulomes with a minimum number of epithelial tissue with good root channels in patients with high potential of bone regeneration, conservative-therapeutic methods are chosen. A comprehensive action preparation is introduced into the cavity of previously extended and antiseptic means of root channels. Due to the high acidity (pH 12.5), it causes the death of pathogenic microorganisms, and in the neutral medium the normal activity of osteoblasts is resumed. Calcium hydroxide restores and strengthens bone structure In the zone of action, and iodoform increases the bactericidal properties of the drug.
In patients with large granulomas often have to resort to surgical treatment, namely to resection of the top of the root of the tooth. However, resection is subject to more than a third of the top, it is preferable to remove the entire tooth at once. The rebellion operation of the root top consists of several stages. At first, the dentist conducts infiltration anesthesia, performs an incision in the projection of the apical zone, leans the gums of the flap and holds it to the tool or pair of seams for a full overview of the operating field. Then, with a cutter, a bone window is cut off, corresponding to the destruction area. The protruding part of the root is spilled and, if necessary, seal the distal root channel department. In the completion of the operation, the dentist-surgeon scraps bone cavity and fills it with material for the speedy regeneration of bone tissue. This operation leads to a good result, however, due to high traumatization, it is used exclusively in the presence of serious indications when conservative therapy is ineffective.
One of the unfavorable features of the flow of granulomatous periodontitis is the high probability of exacerbation. It is characterized by symptoms of acute periodontitis: a sharp pain, increasing when touched to the teeth, swelling in the field of lesion, increasing regional lymph nodes. In this case, it is necessary to immediately make a radiograph and, if it is advisable to save the tooth, the first thing to remove the symptoms of acute inflammation. To do this, it is necessary to surgically to provide an outflow of purulent exudate and assign a patient antibacterial therapy. Next, the treatment is carried out as with ordinary granulomatous periodontitis.
Prediction and prevention of granulomatous periodontitis
With competent conservative therapy, the granulomatous periodontitis goes into fibrous and does not require any treatment in the future. For some time the patient can disturb the feeling of pressure and discomfort in the gum, but this is a normal response of the body, and it is not a reason for anxiety. After surgical manipulations in the incision area, pain remains for some time. A sharp pain may indicate an incorrect operation and requires immediate medical control. AT postoperative period It is necessary to abandon alcoholic beverages, smoking, sharp and hot dishes, as well as chew food and brushing teeth in such a way as not to hurt the edges of the wound. After six months, a visit to the attending physician for conducting control radiography is required.
Lack of treatment leads to adverse consequences. Granuloma gradually develops in a cyst of large sizes, often covering the roots of neighboring teeth and the destructive bone tissue. In such conditions it is impossible to avoid the removal of teeth. In another embodiment, the granuloma is caught up, the doctor stops the acute inflammatory process and the treatment of granulomatous periodontitis is carried out according to a standard scheme with a conservative or surgical path. For timely detection, the granulul must be inspected from the dentist once every six months and fully treat inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
14610 0
Periodontium- Part of the fabric complex of periodontal, is represented by highly differentiated connective tissue, which is located in a closed space between the alveoli compact plate and the tooth root cement. Periodontitis is an inflammatory periodontal disease.
Classification
Periodontitis are classified by origin:- infectious;
- traumatic;
- medical.
- acute;
- chronic.
- intoxication;
- pronounced exudation.
- chronic fibrosis;
- chronic granulating;
- chronic granulomatous;
- chronic in the aggravation stage.
Etiology
The main cause of the development of periodontitis is infection when microorganisms, their toxins, biogenic amines coming from inflamed and necrotic pulp, are distributed in periodont. The cause can also be a tooth injury that arose as a result of the injury, dislocation, fracture (with untimely handling).The damage to the periodontal is possible in the treatment process (excessive removal of sealing material for the top of the root of the tooth, injury tool when expanding the root canal, chemical irritation - arsenic drugs, orthophosphoric acid, etc.).
Pathogenesis
Biologically active components and chemicals cause a sharp increase in vascular permeability, swelling and infiltration increase. Microcirculation is broken, thrombosis, hyperfibrinolysis and secondary hypoxia, is observed, which leads to the depolymerization of the main substance of the periodonta. Hypoxia is growing, Troof is disturbed, all five signs of inflammation are manifested. The fabric becomes permeable due to the formation of voids in the main substance, i.e. Its main function is not performed - protective.Clinical signs and symptoms
Acute periodontitis
Phase intoxication: Chalfactory complaints are characterized by a permanent localized pain of various intensity, amplifying when pricked. Percussion of the causation tooth is weakly painful. The phase of exudation: Characterized by complaints about continuous pain, the feeling of the "grown" tooth, pain during pricing and touching to the tooth. Percussion is painful in all directions, the tooth is movable. The cavity of the tooth is opened or not opened, but with its disclosure there is a necrotic breakdown of the pulp, the gums of the gumsample is hyperemic, edema, palpation of the painful. The serous phase of acute periodontitis can go to purulent.Chronic fibrous periodontitis
Usually does not cause complaints. Objectively marks the change in the color of the tooth; The pulp of the tooth is necrotic, EDO - 100 and more MCA.Chronic granulating periodontitis
It is characterized by asymptomatic flow, but with a thorough collection of history, it turns out that the tooth earlier was sick. The breakdown of the pulp is determined in the tooth cavity and root canals. It is characterized by a putrid smell, sometimes there is a pain in the top of the root channels and the bleeding, which is due to the growth of granulation tissue through a resubstant upper hole. On the gum can be observed a fistula, EDA exceeds 100 μA.Chronic granulomatous periodontitis
It is characterized by asymptomatic flow. Often there is a deep carious cavity, made by necrotic dentin, during the decay of the pulp - a rotten smell, EDA - more than 100 μA. Regional lymph nodes are increased, the palpation of their painful.The aggravation of chronic periodontitis
Characterized by localized continuous it's a dull pain When touching and flaws on the causal tooth. The pathological mobility of the II-III degree tooth mobility is possible; The mucous membrane of the gums around the causation tooth of the edema, hyperemic. A fistul move with purulent discharge can be detected. The late treatment of patient or delayed treatment contributes to the increase in the inflammatory process, the development of periostite, phlegmon and osteomyelitis. The diagnosis is made on the basis of anamnesis, patient complaints, inspection (the presence of a destroyed tooth, fistula), radiography data and EDA.Differential diagnosis
Acute forms Periodontitis differentiate:- with exacerbation of chronic periodontitis;
- a sharp upset periodontitis in the phase of intoxication - with sharp periodontitis in the exudation phase;
- with acute diffuse pulpitis;
- with exacerbation of chronic gangrenous pulpitis;
- with acute odontogenic osteomyelitis;
- with an incorporated near-the-corrosion of a jaw;
- with periostitis;
- with a local form of periodontitis in the stage of abscess.
- between themselves;
- with medium caries;
- with chronic gangrene pulpitis;
- with sharp periodontitis in the recruitment phase of the process.
- with acute top periodontitis in the exudation phase;
- with a local form of periodontitis in the abscess stage;
- with neuralgia trigeminal nerve.
The main tasks of the treatment of periodontitis:
- influence the microflora of root macro and microchannels;
- eliminate the effect of biogenic amines, to stop the inflammatory process in the periodontal;
- promote the regeneration of all periodontal structures;
- stop access to infection from the root canal in the periodont.
- phased, under the cover of antiseptics, evacuation of rotary masses from root canals;
- removal of necrotic fabrics and preconditions;
- expanding the apical hole of the root canals and give it a cone shape;
- sealing root canals.
For appliquancy anesthesia use:
Benzocaine / glycerin locally 5/20 g before injection or
Lidocaine, 2.5-5% ointment or 10% aerosol, locally before injection or
Tetrakain, 2-3% Rr, locally before injection.
Instead of glycerin in a benzocain solution, you can use olive or peach oil. For conductor and infiltration anesthesia, 4% aims of artician, 1-2% Lidocaine solution, 2-3% MEPIOVACAIN solution and 2% slip solution are used.
In case of pain and increasing body temperature, use nonarcotic analgesics and NSAIDs, which have an analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effect:
Ketorolak inside 10 mg 1-2 p / day, with pain or
Metamizole sodium / paracetamol / phenobarbital / caffeine / codeine inside 300 mg / 300 mg / 10 mg / 50 mg / 8 mg, with pain or metamizole sodium / Pitophenone / Fenpyurization Bromide inside 500 mg / 5 mg / 100 μg 4 p / sut in pain or
Metamizol sodium / triacetonemine-4-tensulafonate inside 500 mg / 20 mg, with pain or
Paracetamol inside 0.2-0.5 g (adult); 0.1-0.15 g (children 2-5 years); 0.15-0.25 g (children 6-12 years) 2-3 p / day, with pain.
With pronounced pain syndrome and the violation of the psycho-emotional sphere is prescribed tranquilizers (after the consultation of the psychoneurologist):
Diazepam inside 5-15 mg 1-2 p / day, 4 weeks or
Medazpame inside 10 mg 2-3 p / day, 4 weeks.
For disinfection of root canals, antiseptic drugs are used:
Hydrogen peroxide, 1-3% rr, locally, 1-2 times or
Iodine / potassium iodide, rr, locally, 1-2 times or
Potassium permanganate, 0.02% rr, locally, 1-2 times or
Miramistin, 0.01% rr, locally, 1-2 times or
Chloramine b, 0.25% rr, locally, 1-2 times or
Chlorhexidine, 0.06% rr, locally, 1-2 times or
Ethanol, 70% rr, locally, 1-2 times.
In order to accelerate purification of purulent cavity, proteolytic enzymes are used:
Tripsin 5 mg (in isotonic p d sodium chloride) locally, 1-2 times or
Hymmipcin 5 mg (in isotonic p-re sodium chloride) locally, 1-2 times.
For the reservation of the oral cavity, the destruction of the microflora root canals is prescribed antibacterial drugs:Amoxicillin inside 20 mg / kg in 2-3 reception (children under 2); 125 mg 3 p / day (children 2-5 years old); 250 mg 3 p / day (for 5-10 years old); 500-1000 mg 3 R / day (children over 10 years and adults), 5 days or
Amoxicillin / clavulanate inside at the beginning of a meal of 20 mg / kg in 3 reception (children under 12); 375-625 mg 3 p / day (children over 12 years old and adults), 5 days or
Ampicillin inside 250 mg 4 p / day, 5-7 days or
Co-trimoxazole inside after meals 160 mg / 800 mg 2 p / day (adults); 20 mg / 100 mg 2 p / day (children), 14 days or
Lincomycin inside 250 mg 3-4 p / day, 5-7 days or
Roxitromycin inside 150 mg 2 p / day (adults); 2.5-4 mg / kg 2 p / day (children), 5-7 days.
In order to hyposensitize the body and reduce the permeability of capillaries, antihistamin LS are prescribed:
Clemstine inside 0.001 g (adult); 0.0005 g (children 6-12 years) 1-2 p / day, 7-10 days or
Loratadine inside 0.01 g (adult); 0.005 g (children) 1 p / day, 7-10 days or
Mebirdoline inside 0.05-0.2 g (adults); 0.02-0.05 g (children) 1-2 p / day, 7-10 days or
Hyphenadine inside after eating 0.025-0.05 g 3-4 p / day (adults); 0.005 g 2-3 p / day (children under 3 years); 0.01 g 2 p / day (for 3-7 years); 0.01 g or 0.015 g 2-3 p / day (children of 7-12 years); 0.025 g 2-3 R / day (children over 12 years old), 7-10 days or
Chloropiramine inside 0.025 g (adult); 8.33 mg (children under 7 years old); 12.5 mg (children of 7 -14 years) 2-3 p / day, 7-10 days or
Cetirizine inside 0.01 g (adults and children over 6 years old); 0.005 g (children under 6 years) 1 p / day, 7-10 days.
Evaluation of the effectiveness of treatment
Treatment is considered effective in the case of complete filling of root channels with removal of biologically active paste based on calcium hydroxide. This gives reason to count on favorable long-term results - the gradual elimination of the focus of pouring (tissue resorption). The results of treatment should be monitored according to radiography not earlier than 6-9 months, because Bone recovery occurs slowly.Errors and unreasonable destinations
- Not enough complete anamnesis.
- Improper assessment of the degree of prevalence of the inflammatory process.
- Underestimation of pain syndrome.
- Incorrect diagnosis.
- Perforation of the bottom of the cavity of the tooth or the root canal wall.
- Incomplete or excessive disclosure of the cavity of the tooth.
- Seal tool in the root canal.
- Incomplete sealing of root canals.
- Excessive removal of sealing material for the apical hole and penetration into the apparent sinuses upper jaw or the mandibular channel.
- Internal choice of antiseptics.
- The use of potent drugs to handle root canals with a wide apical hole.
Forecast
With the successful treatment of periodontitis, the prognosis is favorable: the tooth is freely involved in chewing food, the patient does not experience pain, it shows that the root canal is completely polished, there are no complaints, there is no normalization of the periodontal gap width. In the absence of positive dynamics, it is necessary to remove the periapical focus by removing the tooth, reducing the top of the root of the tooth, etc. The preservation of a periapical chronic inflammatory hearth can provoke development and maintain chronic septic state and related complications.G.M. Barer, E.V. Zerana